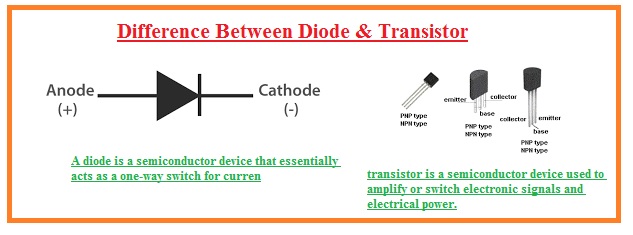
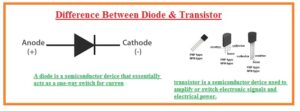
 Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Diode & Transistor. The basic difference between diode and a transistor is that diode is used to transform AC current into the DC but transistor transfers input signal from less resistive circuitry to a circuit having a large value of resistance. The name of diode is crystal diode since it is created with the crystals of silicon and germanium. A diode has two terminals anode and a cathode it starts operation when the anode is attached with the positive terminal of the battery and the cathode with the negative terminal of the battery.
Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Diode & Transistor. The basic difference between diode and a transistor is that diode is used to transform AC current into the DC but transistor transfers input signal from less resistive circuitry to a circuit having a large value of resistance. The name of diode is crystal diode since it is created with the crystals of silicon and germanium. A diode has two terminals anode and a cathode it starts operation when the anode is attached with the positive terminal of the battery and the cathode with the negative terminal of the battery.
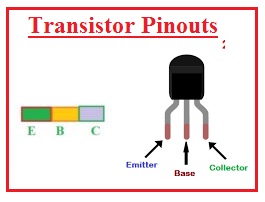
There are 3 terminals of the transistor emitter-base and collector. The emitter is largely doped so it can send a large amount of charge carrier to the base region. The base has a small area and less doped so charges can move to the collector. A collector is the third region of the transistor and has a large area than the other two since it can dissipate heat generated at the base-collector junction. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at both diode and transistor and compare them to find their differences. So let’s get started with Difference Between Diode & Transistor.
Difference Between Diode & Transistor
What is Diode
- A diode is a semiconductor instrument that used to transform ac into dc.
- A diode is used in the rectifier circuit and the process is known as rectification.
- The diode has 2 terminals anode and a cathode.
- It is an uncontrolled switch.
- The types of a diode are Junction diode, LED, Photodiodes, Schottky diodes, Tunnel, Varactor and Zener diode, step recovery,
- It has two regions N and P. N has minority charge carriers and P has holes’ charge carriers.
- There is one depletion region in the diode.
- It is desinge with the usage of 2 differnt P and N mateial
- P region is psotive and N is negative
- As silicon can withstand high temperatures used to make diodes also germanium used for diode creation for less voltage applications
What is Transistor
- The transistor is also a semiconductor device that used to send signals having weak strength for less resistive circuitry to a circuit having a large value of resistance.
- Its common applications are Regulators, Amplifiers, and Rectification
- It has three terminals which are emitter-collector and base.
- It Fet there is single charge carrier exist in BJT two charge carries exist
- In FET there is a single charge carrier and in BJT two charge carriers are used for conduction.
- The size of the transistor is less than the tube and uses less energy.
- It is a controlled switch.
- Its common types are BJT and FET JFET, MOSFET.
- It works as a switch and amplifier
- There are four modes of operation it has forward bias reverse saturation and cutoff
- It has three regions which are emitter-base and collector.
- There are 2 depletion region exits in the transistor.
Diode vs Transistor
| Features | Diode | Transistor |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | Controls current flow in one direction | Amplifies or switches electronic signals and power |
| Structure | PN junction diode | Combination of PN junction diodes |
| Number of Terminals | Two | Three |
| Current Flow | Only in forward bias | Controlled by the base current |
| Amplification | Not an amplifying device | Amplifies weak signals or acts as a signal amplifier |
| Voltage Regulation | Not good for voltage regulation | it used for voltage regulation in certain scenarios |
| Applications | Rectification, protection, signaling | Audio amplification, switching, digital circuits, logic |
| Types | Zener diode, PN junction diode, LED, etc. | Field-Effect Transistor (FET), Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT), |
| Switching Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Noise Performance | Less noisy | It can introduce noise in the amplification |
| Controlled Current Gain | N/A | Yes |
Difference between Diode and Transistor
- The diode has two terminals and is used to flow current in one direction and the transistor is3 a terminal device that is used as a switch and amplifier
- P and N material is used for the creation of the diode while in a transistor P or N region is placed between two N or P regions since it has three parts
- There is one PN junction in the diode and the transistor has two PN Junction
- The pins of the diode are anode and cathode and transistors have emitter-base and collector
- Common types of the diode are Zener, LED, power diode, and transistor types are BJT and FET
- The diode has one depletion region and the transistor has two regions
- A diode is a passive circuit component and the transistor is the active component
- Diode work as a switch and operate in forward and reverse-biased state and the transistor operate is the amplifier and switch it has three regions of operation active, saturation and cut-off regions
- Transistor provides the control switching and diode uncontrolled
- The diode used as a rectifier clipping circuits and voltage multiples and the transistor is used in oscillators and regulators, etc
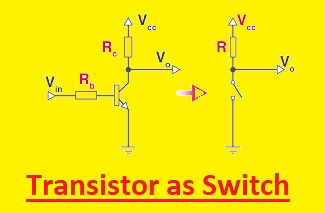
Transistor as Switch
- A switch used in digital electronics to control the function of a circuit is made using a transistor.
The figure below shows the circuit configuration for the transistor as a switch, which means that as the base voltage increases, the emitter and collector currents increase as the base acts as a control to control the applied voltage.
Collector loss voltage as the collector-emitter resistance value decreases.
If there is only 0 resistance between the collector and the emitter, then the value of IC can be regulated using the resistance offered by the load.
This mode of operation is the saturation of the current passing from the collector to the emitter.
In saturation, the state switch is on
Related Articles: Rectifier Diode
Characteristics of Diodes
Forward Bias
A diode can conduct current when it is forward-biased, which means the anode is at a high voltage than the cathode. For current to flow, the forward bias voltage should be larger than the forward voltage loss of the diode, which is generally 0.7 volts for silicon diodes.
Reverse Bias
Reverse bias stops current flow through the diode since the anode is at a lower voltage than the cathode. There could be a small reverse leakage current, though.
Breakdown Voltage
The voltage at which a diode reaches the breakdown region, permitting a high current to flow in the opposite direction, is the breakdown voltage of the diode. For Zener diodes and other types of diodes intended for breakdown operation, this feature is essential.
Forward Voltage Drop
The voltage needed to overcome a diode’s barrier potential and let a significant current pass is known as the forward voltage drop across the diode. The type of diode and the materials used to build it determine this.
That is a detailed post about the difference between diodes and transistors if you have any queries ask in the comments. Thanks for reading.