 Hello, readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will discuss What is a Rectifier Diode. The rectifier diode is a device that is used for the conversion of AC to DC. There are different types of applications of rectifier diodes like power supplies, chargers, welding machines, etc. The diode comes with two pinouts, an anode and a cathode. An anode is positive and the cathode is negative. So let’s get started with a diode rectifier.
Hello, readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will discuss What is a Rectifier Diode. The rectifier diode is a device that is used for the conversion of AC to DC. There are different types of applications of rectifier diodes like power supplies, chargers, welding machines, etc. The diode comes with two pinouts, an anode and a cathode. An anode is positive and the cathode is negative. So let’s get started with a diode rectifier.
Introduction to Rectifier Diode
- The rectifier diode is a semiconductor component used to convert AC to DC. During AC to dc, the conversion negative half cycle of ac is blocked, and the positive converted into DC
- The rectifier diode has a Pn junction which helps the current flow in one direction. These diodes are the main parts of power sources, rectifier circuits, and switching applications
Working Principle of Rectifier Diode
- The working principle of the rectifier diode is based on features of PN Junction to allow current flow in one direction and block current in a reverse direction
- If AC voltage is given to the diode current flows in one direction for a positive half cycle and is blocked for a negative half cycle. That results in DC voltage at the output of a diode
Types of Rectifier Diodes
- There are three types of rectifiers
- Half Wave Rectifier
- Full Wave Rectifier
- Bridge Rectifier
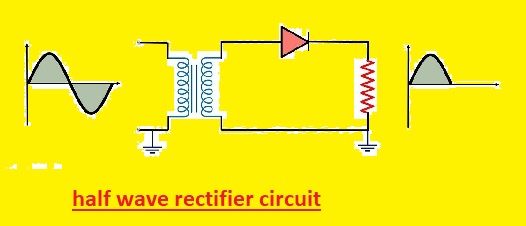
1. Half-wave Rectifier Diode
- It is a simple type of half wave rectifier circuit. That consists of one diode which operates during the positive half of ac cycle and blocks it during the negative half cycle
- The output voltage of half wave rectifier is pulsating dc volts which has a frequency of half input ac volts
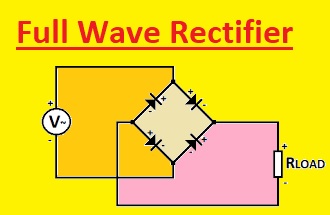
2. Full-wave Rectifier Diode
- The full wave rectifier diode consists of four diodes and converts the complete AC wave to DC. Two of its diodes operate during the positive half and the other two for the negative half.
- The output full wave rectifier is smooth dc volts which have a frequency equal to the input of AC volts
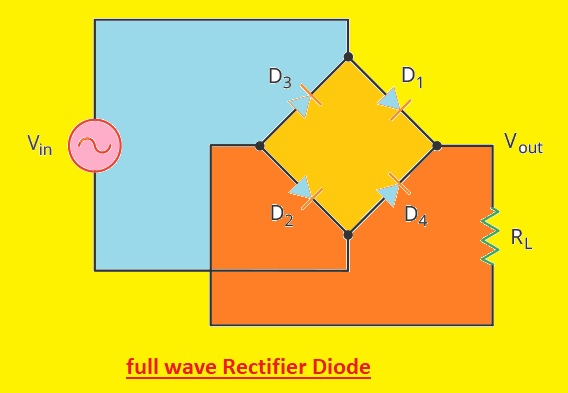
Bridge Rectifier Diode
- The bridge diode is a very commonly used rectifier circuitry. It comprises four diodes which are configured in a bridge-like structure. The bridge rectifier transforms complete AC volts to dc volts and the output is smooth dc volts which has a frequency equal to the input AC volts
How rectifier diode convert AC to DC?
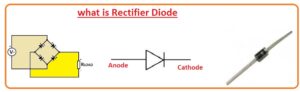
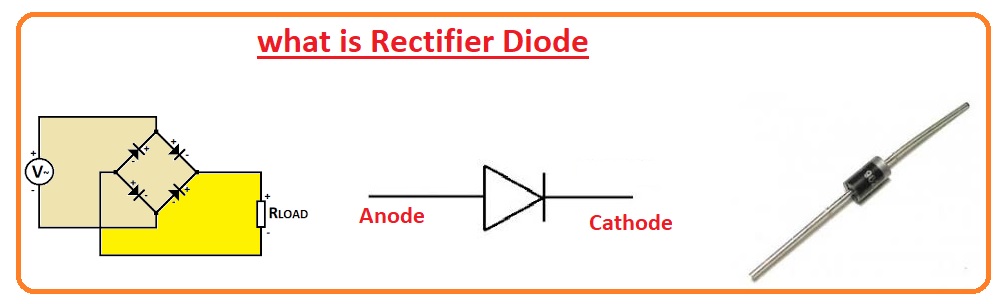
Symbol of Rectifier Diode
- The symbol of the rectifier diode consists of the arrow that directs the direction of the current flow. The arrow is normally lies at the anode side
What are the Applications of Rectifier Diodes?
- Some common applications of rectifier diode are listed here
Power Supplies
- The common application of diode in power supply. Ac voltage transformed DC voltage with the use of rectifier circuitry that uses one or more rectifier diodes
Battery Chargers
- These diodes are also used in battery charges to ac to DC conversion that is used for battery charging
Voltage Regulators
- Voltage regulators also use rectifier diodes to regulate of the output level of the power source
Welding Machines
- These diodes are also part of welding machines for rectification that provide the power to welding devices
Audio Equipment
- This diode is part of audio devices to make DC voltage for amplifier circuits
Voltage Multipliers
- These diodes are also part of voltage amplifier circuits that can help to increase the voltage magnitude
Advantages of Rectifier Diode
- Some advantages of rectifier didoes are listed here
- It is a highly efficient diode
- It is the less expensive diode
- It uses less power
- Its construction is simple and easy
Disadvantages of Rectifier Diode
- Some disadvantages are explained here
- It has a high value of ripple voltage
- it has limited current and voltage ratings
- It has limited operating temperature values
Which Rectifier is Used Most?
- A Silicon rectifier diode is a commonly used rectifier diode. This diode has higher ratings and a lower power leakage current than other types of rectifier diodes.
- Silicon rectifier diode has high-temperature tolerance and larger working life so it is the best option for different applications
What Does the Diode Rectifier Symbol Do?
- The diode rectifies symbol is used for representing the diode in circuits. The symbol has a triangle pointing to the line that denotes the direction of the current flow.
- The line at the end of the triangle denotes the anode of the diode and the line at the other end denotes the cathode. The symbol is important since it helps engineers to define the location of the diode in the circuit.
Ratings of a Rectifier Diode
- There are different values of rating of rectifier diodes that define their features and other parameters. So rating parameters are explained here
- Peak inverse voltage (PIV): It is the maximum voltage that can be provided in the reverse direction before the diode breaks down. It is also known as maximum reverse voltage.
- Surge current (IFSM): It is the highest current that the diode can handle for a short time interval without getting damaged. It is also called peak forward surge current
- Forward voltage drop (Vf): It is voltage loss about the diode when it conducts current in the forward direction. Its value is about 0.5V to 1.5V in the case of the silicon rectifier diode
- Average forward current: It is the average current that which diode can easily carry in a forward direction without overheating
- Junction temperature (Tj): It is the highest temperature that the junction of the diode can handle
- Reverse recovery time (trr): It is the time taken by the diode to throw forward a biased state to reverse a biased state. This parameter is considered for high-frequency switching applications
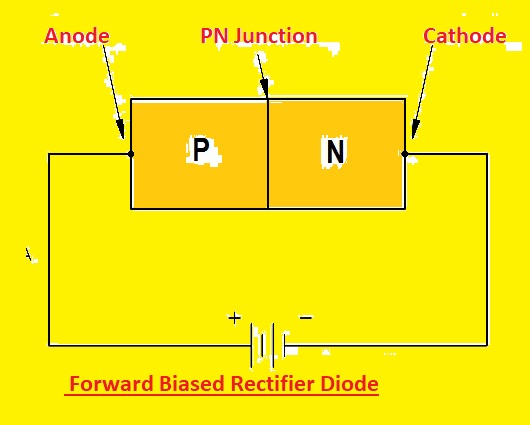
Forward Biased Rectifier Diode
- In a forward-biased circuit, the diode is connected in the forward direction, and DC volts are applied to it. This voltage is known as biased voltage or forward voltage.
- The forward bias voltage causes the diode to flow current in the forward direction and voltage drop across it. The value of forward voltage loss depends on the diode type and the current flowing across it
Reverse Biased Diode
- In the reverse biased circuit, the diode is connected in the reverse direction which means the positive of the diode is with the negative of the battery and the negative of the diode with the positive of the battery.
- The voltage applied in this state is called reverse bise voltage. That causes the diode to block current in the reverse direction and store charge in the junction. The value of revere bias voltage depends on the diode connected
Why rectifier is called a diode?
What are the Popular Rectifier Diodes?
- Some rectifier diodes are explained here
| Diode | Maximum Voltage | Maximum Current | Maximum Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1N4001 | 50V | 1A | 1MHz |
| 1N4002 | 100V | 1A | 1MHz |
| 1N4003 | 200V | 1A | 1MHz |
| 1N4004 | 400V | 1A | 1MHz |
| 1N4005 | 600V | 1A | 1MHz |
| 1N4006 | 800V | 1A | 1MHz |
| 1N4007 | 1000V | 1A | 1MHz |
| 1N5400 | 50V | 3A | 100kHz |
| 1N5401 | 100V | 3A | 100kHz |
| 1N5402 | 200V | 3A | 100kHz |
| 1N5404 | 400V | 3A | 100kHz |
| 1N5406 | 600V | 3A | 100kHz |
| 1N5408 | 1000V | 3A | 100kHz |
| 1N5820 | 20V | 3A | 1MHz |
| 1N5821 | 30V | 3A | 1MHz |
| 1N5822 | 40V | 3A | 1MHz |
| 1N5824 | 60V | 3A | 1MHz |
| 1N5825 | 80V | 3A | 1MHz |
| 1N5829 | 120V | 3A | 1MHz |
How to Test a Rectifier Diode?
- The testing process of the diode is important and needs some steps that are explained here
- First off the power supply from the circuitry and remove the diode from the board
- Adjust the digital multimeter to diode testing mode. If your multimeter does not have diode testing mode then set it to measure resistance
- Connect the positive terminal of the multimeter with the positive of the diode and the negative with the cathode of the diode
- Now record the values on the multimeter. If the diode is operating well reading should be 0.5 and 0.8 volts for silicone and for germanium 0.2 and 0.4 volts
- Reverse the leads on the meter and again note the reading. Now values should be infinite which shows that there is no reverse current flowing
- If readings do not lie in above mentioned readings then the diode can be faulty.
what is the difference between a diode and a rectifier?
- The diode is an electronic component that helps the curent to flow in a single direction. It has two terminals and a semiconductor device. The rectifier is a device used for the conversion of ac to DC voltage. The diode is used as a switch and the rectifier is used for conversion.
What is the difference between half and full-wave rectifiers?
How to Use a Rectifier Diode
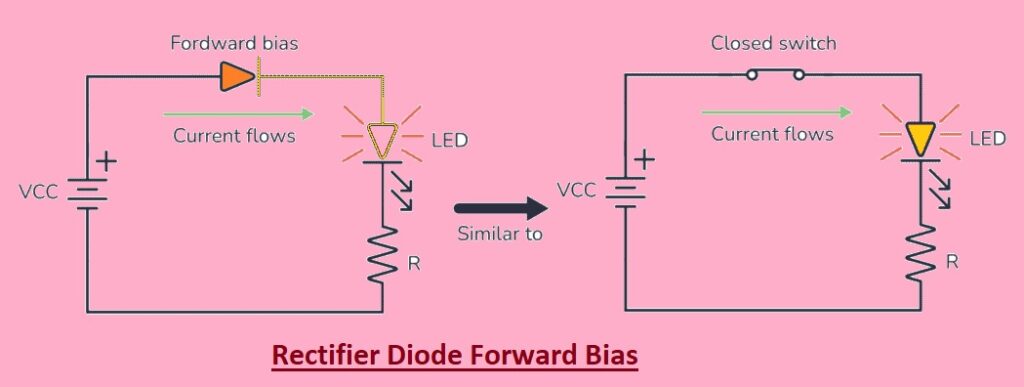
The rectifier diode moves current in one direction from anode to cathode called Forward bias. The rectifier diode in the forward biasing state is made through the connection anode with the positive terminal and the cathode with the negative side.
In the above circuit, the diode is forward biased which means the curent flow in this circuit and the LED connected will glow up. In this configuration, the diode works as a closed switch
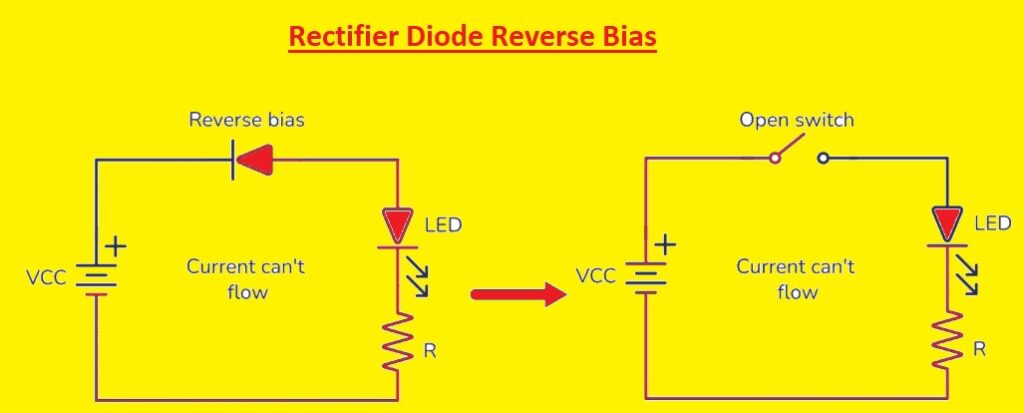
Here diode is connected in a reverse-biased state where the anode is connected to the negative terminal of the battery and the cathode to the positive terminal of the battery. Here no curent flow and the diode works as open switch.
Conclusion:
Rectifier diodes are very important components in electronic devices and circuits. They are used for the conversion of AC to DC. Its circuit learning and understanding of its working is important for electronic projects
Related Posts
Difference between normal Rectifier Diode and Schottky diode
Introduction to FR102 Diode Pinout, Datasheet, Applications, Uses Features
Forward biased p-n junction diode
Introduction to 1N4004 Diode & Pinout
Types of Diode and Applications
FAQs
Write the Purpose of a Rectifier Diode.
It is used for AC to DC conversion by blocking negative half cycles of the AC waveform.
What is the symbol of a rectifier diode?
The symbol of the rectifier diode is a triangle having a line at the base. The line at the base denotes a cathode that is the negative pin of the diode
What are the types of rectifier diodes?
There are two main types of rectifier diodes half-wave and full-wave rectifiers.
What are the advantages of rectifier diodes?
The main advantages of rectifier diodes are their low cost, small size, and easy structure.
What are the types of rectifiers?
Uncontrolled Rectifier and Controlled Rectifier
What is a half-wave rectifier?
it is a rectifier that converts half wave into dc curent called half wave rectifier.
Half-wave rectifiers are used as mosquito repellent.
Yes it used for this purpose
Where are rectifier diodes used?
The electric devices use a DC power supply to operate. The use of rectifiers in power supplies helps to convert AC into dc power. Bridge rectifier used for larger devices that convert high AC voltage into low DC voltage.
Can Zener be used as a rectifier?
Which device is used as a rectifier diode?
What is the function of a rectifying diode?
The rectifier is a certain type of diode that transforms AC in Direct current. In this process, AC can reverse direction after some time and DC flows in one direction.
How rectifier diode convert AC to DC?
The diode helps the curent move in one direction making it best for converting from AC to DC. For this bridge circuit is used that converts both halfs of AC into DC Current.
What is an example of a rectifier diode?
A common example of rectifier is the use of mobile phone chargers. The phone charge can only be charged effectively if a constant, uninterrupted voltage supply is given. It can be done with the use of a rectifier in the phone charger circuit.