 Hello fellows, I hope you are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at Introduction to Photodiode. The photodiode is an electronic instrument that used to transform light into current. Production of current is due to the absorption of a photon of light. These diodes comprise an optical filter for transmission of light at a different wavelength, lens, and surface area according to requirements. With the increment in the surface area, their response time decreases. While when they are operating in solar cells their surface area is large.
Hello fellows, I hope you are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at Introduction to Photodiode. The photodiode is an electronic instrument that used to transform light into current. Production of current is due to the absorption of a photon of light. These diodes comprise an optical filter for transmission of light at a different wavelength, lens, and surface area according to requirements. With the increment in the surface area, their response time decreases. While when they are operating in solar cells their surface area is large.
These diodes are alike to the normal diode with the difference is that these diodes have exposed surface for detection of UV light or X-Rays and have such packaging that has a window to send light to a sensitive portion of the diode. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at its working, applications, construction, and some other related parameters. So let’s get started with Introduction to Photodiode.
Introduction to Photodiode
- The photodiode is also called a photodetector, photosensor, or light detector uses light to produce current.
- These diode function in reverse biasing condition in reverse biasing anode of the diode is connected with the negative terminal and cathode of diode with a positive terminal of the battery.
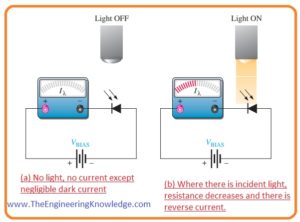
- In below figure circuitry denoted (a) explains the reverse biasing condition of a photodiode. In circuitry, Iλ is the current generating through this diode.
- There is a window on the diode through which light enters the diode and collides with the PN junction due to that current generated.
- The symbols for the diode are also shown in the figure.
- As we know in reverse-biased diode there is very less amount of current flows this is the same for a photodiode.
- This reverse current flows due to the movement of minority charge carriers across the depletion region.
- For the diode used in the rectifier circuits the reverse current increases with the increment in temperature.
- Due to increment in temperature the numbers of electrons and holes pairs increases due to that current increases.
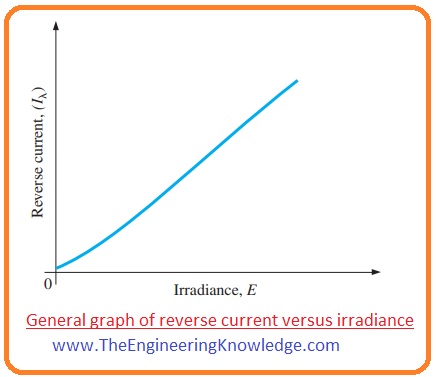
- But the behavior of a photodiode is different than normal diode is that when the PN junction of photodiode gets rays of light then value of reverse current increases with the increment in the intensity of light.
- When the light incident on the photodiode is zero, then the reverse current is almost zero which known as dark current.
- The increment in the intensity of light is known as irradiance and measured in (mW/cm2) due to irradiance reverse current also increases as shown in the below figure.
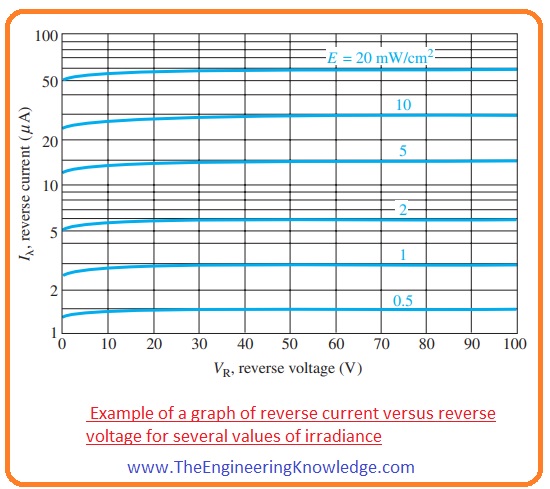
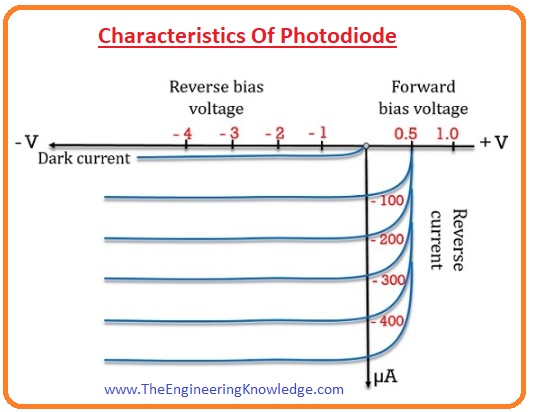
- In the below figure graph you can observe that reverse current is 1.4 uA for reverse-biased voltage of ten volts and irradiance value of 0.5 mW/cm2.
- Resistance value will be given.
RR = VR/ Iλ=
=10 V/1.4 μA= 7.14MΩ
- At 20 mW/cm2 the current is almost 55 mA at VR = 10 volts. Resistance value for this condition will be given as.
RR = VR/ Iλ=
=10 V/55μA= 182 kΩ
- From the above measurements, we can conclude that photodiode can also be used as a variable resistor with the regulated through the intensity of light.
- The below figure explains that there is no reverse current when there no light on the diode.
- When light falls on the diode reverse current flows directly proportional to the intensity of light.
Photodiode Construction
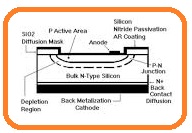
- In the below figure you can see the internal structure of photodiode.
- You can see that PN junction of a photodiode is assembled in a glass. Glass provides a path for external light to fall on the PN junction.
- Only that part of PN glass is transparent that fall light on the junction other is coated with the paint.
Working of Photodiode
- The working of the photodiode is very simple as light falls on the diode electrons in the N region move to the P region of diode and combine with the holes existing in the P region and creates pairs of electrons and holes.
- This process is also called the inner photoelectric effect.
- When light falls on the depletion region or near the depletion region it minimizes the effect of electric field existing in the depletion region and holes combine with the electrons and photocurrent generated.
- The net current produced by the photodiode is equaled to the sum of dark current, the current produced in the nonappearance of light and photocurrent.
- Due to this dark current should be lessened to increases the sensitivity of photodiode.
Photodiode Mode of Operation
- There are normally three modes of operation of the photodiode that is listed. Let’s discuss them with the detail.
- Photovoltaic mode
- Photoconductive mode
- Avalanche diode mode
Features of Photodiode
- These are some features of photodiodes.
Responsivity
- The spectral responsivity is calculated by the ratio of current produced through the photodiode to the light incident on the diode and its unit is A/W.
- The dependence of wavelength can be defined in terms of quantum efficiency.
Dark Current
- The current generated by the photodiode without light is called dark current and this occurs in photoconductive mode.
- The dark current comprises of photocurrent produced by the background radiation and saturation current produced by the semiconductor junction.
- If photodiode is used for correct optical power calculations, then dark current should be used for calibration.
- For optical communication applications dark current works as a source of the noise.
Response Time
- The taken by the diode to respond to the incident light is known as response time.
- Due to the absorption of light photons, electrons holes pair will be created due to that current generated.
- The limited period of this current is identified as the transit-time spread and can be assessed by using Remo’s theorem.
Characteristics Of Photodiode
- In the below figure you can see the VI characteristic curve of a photodiode.
- In this graph denoted the reverse current passing in the diode at a vertical axis and reverse-biased voltage at the X-axis.
- The first curve on the graph defines the dark current produced due to minority charge carriers without light.
- All other curves on the graph have equal distance among them it due to constant increment in current with the increment in luminous flux.
Types of Photodiode
- The operating principle of all types of a photodiode is similar but the difference is their uses.
- For instance, PIN photodiode is used to increase response time.
- There are numerous types of photodiode are listed here.
- Avalanche Diode
- PIN Photodiode
- PN Junction Photodiode
- Let’s discuss them with the detail.
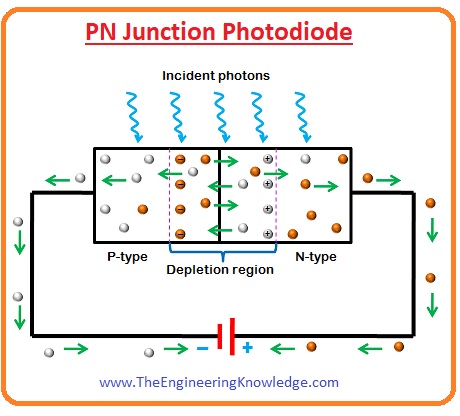
PN Junction Photodiode
- The first time photodiode created was PN junction photodiode. Before the creation of other diodes such as PIN photodiode, PN junction diode was mostly used.
- PN junction photodiode is also known as a photodiode. But currently, these diodes are used in limited applications.
- When the light is provided to the PN junction photodiode from these voltage valence electrons existing in the depletion region gets energy.
- If the energy of light falling on the photodiode is larger than the band gap of semiconductor material used for diode, the valance electrons get energy and left the atom with which it connected.
- Due to these free electrons current start to flow. When electron left the atom hole created on that place.
- So pairs of electrons and holes created this process are known as the inner photoelectric effect.
- There are 2 forces act on the minority carriers existing in the depletion region first one is due to the electrical field of depletion region and the second one is due to an exterior electrical field.
- For instance, positive ions existing at the end of P region and N region apply the force of repulsion and attraction on the electrons of the depletion region.
- Due to that free electrons enters into the N portion. After entering in the N, region electrons attract towards the positive terminal of the battery. Holes move in the opposite direction.
- If there is no light incident on the reverse biasing photodiode, then there will be less value of current will flow due to exterior voltage.
- This very minor current without light is known as dark current and denoted as Iλ.
Related Posts
- Current Regulator Diode
- Zener Diode
- Step Recovery Diode
- PIN Diode
- Schottky Diode
- Photodiode
- Varactor Diode
- Diode
- Zener diode Applications
- Laser Diode
- LED
So friends that is complete post about photodiode I have written each and every parameter related to a photodiode. If you have any query ask in comments. See you in next post have a good day.








My husband and i have been really satisfied that Peter could round up his survey via the precious recommendations he obtained while using the web pages. It’s not at all simplistic to just happen to be releasing instructions that many many people might have been trying to sell. And we also recognize we now have the website owner to be grateful to for this. These illustrations you’ve made, the easy website navigation, the relationships your site help to promote – it’s all fabulous, and it’s really letting our son and our family consider that the subject matter is cool, which is incredibly vital. Many thanks for everything!
If you wish for to increase your knowledge only keep visiting this web page and
be updated with the hottest information posted here.
Peculiar article, just what I wanted to find.
magnificent post, very informative. I’m wondering why the other experts of this sector do not understand this. You should proceed your writing. I’m sure, you’ve a huge readers’ base already!