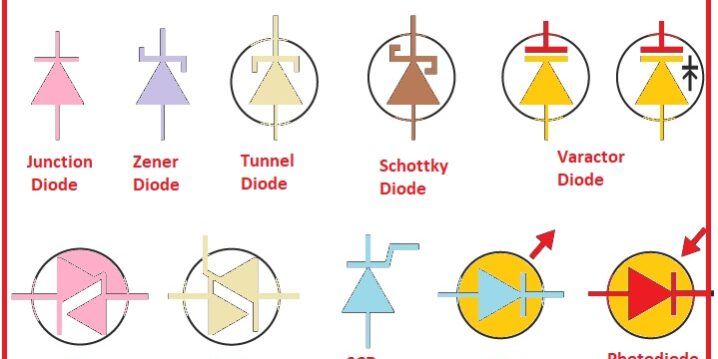
 Hello, friends, I hope you all have fun in your life. In today’s lesson, we will look at Types of Diode and Applications. It is an electronic device that has two terminals first is positive and the second is negative. The diode allows current to flow only on one side as it shows a high degree of resistance on one side and a small resistance on the other side. Diode was first created with mineral crystals and is known as Cat’s Whisker diode.
Hello, friends, I hope you all have fun in your life. In today’s lesson, we will look at Types of Diode and Applications. It is an electronic device that has two terminals first is positive and the second is negative. The diode allows current to flow only on one side as it shows a high degree of resistance on one side and a small resistance on the other side. Diode was first created with mineral crystals and is known as Cat’s Whisker diode.
There are many types of diodes available on the market and used in various electrical projects and devices. The main function of a diode is to convert the current ac into dc as another device requires a dc to work. The diode is therefore used to operate these devices with AC in the input terminals. In today’s post, we will take a closer look at its design, functionality, diode types, and practical application for different projects. So let’s get started with Types of Diodes
Types of Diodes and Applications
- Here are some of the types of diodes that we can discuss in detail.

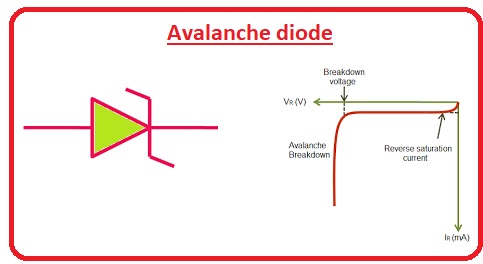
Avalanche diodes
- The activation of these diodes occurs when the reverse power falls through the decaying force.
- The performance of these diodes is almost identical to Zener but with some variation in the demolition effect which is the result of an avalanche.
- It occurs when a voltage back voltage breaks a potential barrier and the current current flows in large amounts such as an avalanche.
- The formation of these diodes that do not allow them to be corrupted in the case of reverse reversal.
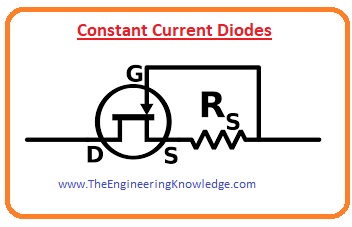
Constant Current Available
- This diode is also known as the Junction field-effect transistor (JFET) whose end of the gate is attached to the source.
So it acts as a voltage limiter. - This diode is also known as CLD (the current constant diode) due to the connection of transistors.
Crystal Diode
- This diode is also known as the point diode when it was first designed for use in a microwave receiver.
- The performance of this diode depends on the pressure between the point and the semiconductor material used in its construction.
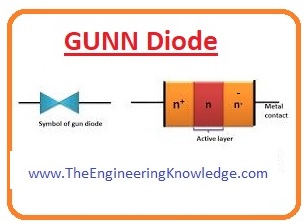
Gunn Diode
- This diode is also known as the electron transfer device (TED) has a negative conjunction with 2 terminals.
Used in electronic projects where high frequency is required. - It is used for the production of microwaves on electric oscillators.
- Due to the production of microwaves, rental in RADAR, microwaves and automatic door openings.
LED
- The lead represents the emitting light emitting light when the input output is given to its terminals.
- The process of emitting light is achieved when the electrons move from the N side to the P side and meet through the holes.
- When electrons meet a hole they release their energy and this energy is released in the form of light.
- The color of the emitted light depends on the semiconductor materials used in the construction of the LED.
Laser Diode
- A laser (light amplified stimulated emission) is a diode also called an injection laser diode.
- It also emits a diode-like light but in this extraction process, it is different. It uses a selective process and promotes light output.
- The performance of the diode laser has been stated before and you have learned in detail. Laser Diode
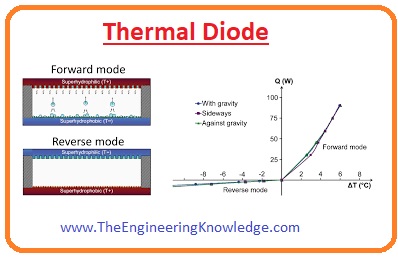
Thermal Diode
- This diode is similar to a normal diode and flows energy in only one way as the current flow to a standard diode.
- Used in heat engines, refrigerator, and other applications related to heat transfer.
Photodiode
- The diode type converts light to current. Light photons that collided with a photodiode were converted to current.
- With an increase in surface area, its response time decreases. A practical example of a photodiode is a solar cell that uses multiple photodiodes to convert light into current.
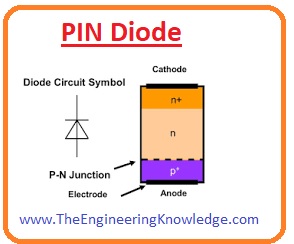
PIN Diode
- The working photodiode is similar to a photodiode that converts light into a current.
- There are 3 main components of the PIN diode the first is P, the second is (intrinsic) and the third is the N circuit.
- The inner circuit is built between P and N with very strong semiconductor materials.
- The PIN diode is used for various switching circuits, imaging devices, and large electronic devices.
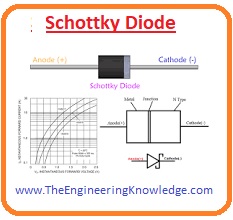
Schottky Diode
- This diode is made of metal and semiconductor materials. The voltage drop projected forward for this diode is small compared to the conventional PN junction diode.
- The current transmission voltage per milliampere is 0.15 volts at 0.45 volts, due to this feature we used in circuit breakers.
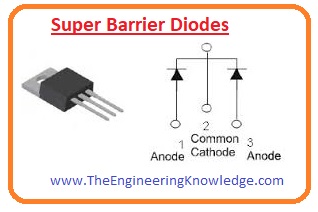
Super Barrier Diode
- This diode used in rectifier circuits is due to the small amount of transmission power losses and better handling capacity.
It also has a smaller amount of flexible current leakage than a standard diode.
Gold Top Diode
- In this diode, gold is a dopant material and in some cases a platinum diode is used as a dopant material.
- The use of gold increases the flow of electrons from the N region to the P region.
- The performance of the gold dye is faster than that of any other diode but less than the Schottky diode.
- The current leakage rate is lower compared to Schottky diodes.
Steps to Get Steps
- This diode is also called a voltage-capacitor-dependent capacitor. Its doping rate is very close to the PN organization.
Also, the number of carriers is very close to the organization. - This diode operates much faster than the low-frequency value and is therefore used as a charging-controlled circuit.
- It works with advanced bias and does not work in a reputable circular circuit.
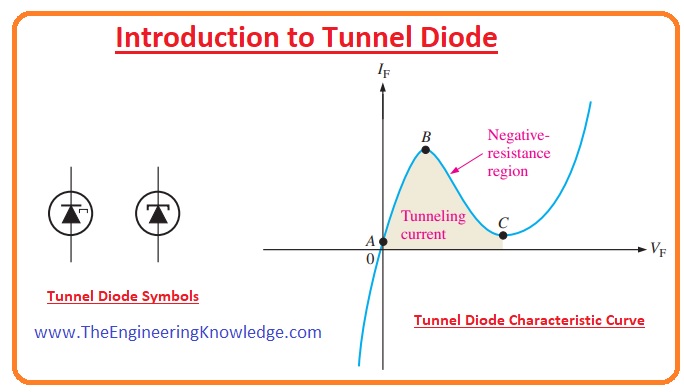
Diode Tunnel
- This diode has features in which the voltage drop decreases.
- It is used on computers due to rapid switching and is also used in high-frequency amplifier circuits.
- Another name if this diode is an Esaski diode because of its creator name.
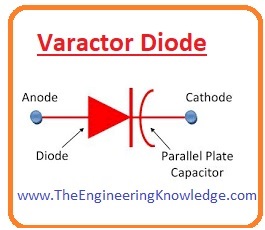
Varactor Diode
- The term varactor is derived from a flexible capacitor. This diode is only in reverse.
- The word varactor is derived from the variable capacitor. This diode is only in reverse biasing.
- It is similar to the variable capacitor during its reverse biasing.
- There are some other names of this diode like varicap tuning and variable capacitance diode.
Related Topics
Types of Diode
| Type of Diode | Description |
|---|---|
| Rectifier diode | used in power supply to convert AC to DC. |
| The Zener diode | used as a voltage reference and for voltage control. |
| Schottky diode | used in high-speed applications including power rectification and RF circuits. |
| Light-emitting diode (LED) | when a current flows through it, it emits light. used to lighting and display purposes. |
| Photodiode | light into the current is converted. utilized in optical communication systems and light sensors. |
| Varactor diode | It has the function of a voltage-controlled capacitor. utilized in frequency modulation and tuning circuits. |
| Tunnel diode | Useful in high-frequency oscillators and amplifiers, it exhibits negative resistance. |
| PIN diode | has an inherent (undoped) area between the extensively doped p- and n-type materials. used in RF switches and as a variable resistor. |
Diode types Technical Features
| Type of Diode | Forward Voltage Drop | Reverse Breakdown Voltage | Maximum Current Rating | Junction Capacitance | Reverse Recovery Time | Maximum Operating Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rectifier diode | 0.5 V to 1.5 V | 50 V to 1000 V | 1 A to 50 A | 10 pF to 1000 pF | 10 ns to 100 ns | -65 °C to 200 °C |
| Zener diode | 1.2 V to 200 V | 2 V to 200 V | 1 mA to 50 mA | 1 pF to 50 pF | – | -55 °C to 175 °C |
| Schottky diode | 0.15 V to 0.45 V | 20 V to 100 V | 1 A to 100 A | 1 pF to 50 pF | 10 ns to 100 ns | -65 °C to 150 °C |
| Light-emitting diode (LED) | 1.5 V to 4 V | – | 10 mA to 50 mA | – | – | -40 °C to 100 °C |
| Photodiode | – | 10 V to 100 V | – | 10 pF to 1000 pF | – | -40 °C to 100 °C |
| Varactor diode | – | 10 V to 50 V | – | 0.1 pF to 10 pF | – | -55 °C to 125 °C |
| Tunnel diode | 0.1 V to 0.3 V | 0.1 V to 1 V | 10 mA to 100 mA | 1 pF to 10 pF | 0.1 ns to 1 ns | -55 °C to 125 °C |
| PIN diode | 1 V to 3 V | 10 V to 100 V | 1 mA to 100 mA | 10 pF to 1000 pF | – | -55 °C to 150 °C |
That is all about the diode types all details explain have given about the different types of diodes. If you have any query ask here