 Hello, readers welcome to the new post. Here we will learn Difference between a normal Rectifier Diode and Schottky diode. The diode is an electronic component that is used to flow current in one direction and not allow current in the opposite direction which means it transforms ac to DC current.
Hello, readers welcome to the new post. Here we will learn Difference between a normal Rectifier Diode and Schottky diode. The diode is an electronic component that is used to flow current in one direction and not allow current in the opposite direction which means it transforms ac to DC current.
There are different types of diode used in electronics like LED, photodiode, Schottky diode, etc. In this post, we will discuss he differences between the Schottky diode and the rectifier diode. So let’s get started Difference between a normal Rectifier Diode and Schottky diode
Introduction to Diode
- A Rectifier diode is an electronic component that converts alternating current to direct current through a rectification process and allows current to flow in one direction only.
- The operation of a diode is similar to that of a non-return valve, which allows liquid to flow in one direction only, similarly current flows through the diode in only one direction.
- The diode is made of a combination of two different semiconductor materials P and N.
- The P side of the semiconductor is positive and is called the anode, and the N side of the diode is negative and is called the anode.
- Because of the high-temperature bears, silicon is used in diode construction, but germanium is also used to make diodes when less voltage drop is needed.
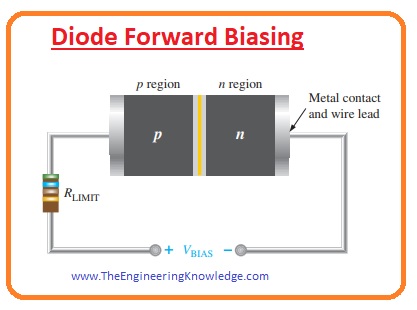
Diode Forward Biasing
- Biasing is the process by which the input power is secured across the diode terminals.
In the biased state, current flows through the PN junction due to the movement of electrons and holes.
In the given figure, you can see that the diode is connected to a DC voltage source in the forward direction., - The bias voltage supplied by the external DC source is represented as Vbias.
You can see that in the circuit a resistor is connected in series with the battery and the diode, this is to limit the current value and is known as a current-limiting resistor.
For the bias condition, 2 conditions should be met. - The first is to connect the anode of the diode to the positive pole of the battery and the cathode to the negative pole of the battery.
- In the second condition, the value of the voltage source connected to the diode should be greater than the potential barrier.
Diode Reverse Biasing
- Under reverse bias conditions, no or very little current flows.
- In a reverse bias situation, the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the cathode and the negative terminal is connected to the anode of the diode. It is shown in the given picture.
Application of Diode, What is Diode, Types of Diode, Difference Between Diode and Transistor, Difference Between Diode and Photodiode, Difference Between Diode and LED, Reverse Breakdown, Reverse Current, Reverse Biasing Diode, Effect of Forward Biasing on Depletion Region, Diode Forward Biasing, Typical Diode Packages, Introduction to Diode, Surface-Mount Diode, - The voltage source connected to this reverse bias is labeled Vbias.
In the image above, you can see that the depletion region area is wider than the feedforward depletion region.
Introduction to Schottky Diode
- Schottky diodes are also called hot carrier diodes or Schottky barrier diodes used in such applications where large frequency and high switching speed are required.
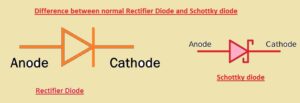
It was called a hot carrier diode because of the high energy level of the electrons in the N part than in the metal part of the diode. - The diode symbol is shown in the figure below. To construct this normally N-doped diode semiconductor material, the material is combined with metals such as silver, gold, or platinum.
There is no PN junction in this diode like other diodes but it has a semiconductor-to-metal junction.
The forward voltage loss for this diode is normally 0.3 volts due to the absence of depletion of this diode.
The current flow of this diode is due to majority charge carriers and there are no minority charge carriers and also no reverse leakage current flow in this diode.
- The metal part of this diode is completely covered by conduction band electrons and the n region of this diode is less doped.
When the diode is forward-biased, the high-energy electrons existing in the N part move to the metal part and lose their energy in that region.
Due to the absence of minority charge carriers in this diode, the bias voltage changes rapidly.
This diode is used in higher frequency and switching applications such as digital circuits.
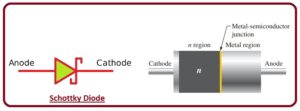
Schottky Diode Construction
- In a Schottky diode, a metal-semiconductor junction is formed between the metal material and the semiconductor, which is called the Schottky barrier.
The construction of this diode uses gold, platinum, tungsten, and some silicides with a semiconductor material that is N-doped.
The metal part of this diode acts as the anode and the N part is the cathode, which means that the current can move from the metal part to the semiconductor according to the conventional current direction.
The Schottky barrier of this diode ensures high-speed switching and less forward bias loss.
The forward voltage required for a diode depends on the metal and semiconductor material used. Both N-type and P-type semiconductor materials can be used to make the Schottky barrier, but the forward bias for the P-type material is smaller.
As the forward bias voltage decreases, the reverse leakage current increases so that the voltage value for the P-type material is maintained in the range of 0.5 to 0.7 volts.
| Parameter | Normal Rectifier Diode | Schottky Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Drop | High | Low |
| Reverse Recovery Time | High | Low |
| Forward Voltage Drop | High | Low |
| Efficiency | Low | High |
| Applications | Power Supplies, Battery Chargers, and AC-DC Converters | Power Supplies, Voltage Clamping, and RF Applications |
Basic Characteristics of a Diode
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Forward Voltage | the voltage necessary for forward-moving current to pass through a diode. Normally 0.7 and 0.3 V for silicon and germanium diodes |
| Reverse Voltage | The highest voltage that a diode can withstand before failing when applied in the opposite direction. |
| Reverse Current | the negligible amount of reverse current that occurs when a reverse voltage is supplied to a diode. |
| Forward Current | when a forward voltage is supplied, how much current travels through the diode in that direction? |
| Power Dissipation | The much power that a diode can safely dissipate before overheating and suffering damage. |
| Junction Capacitance | The capacitance between the diode’s p-n junction has an impact on how rapidly it switches. |
| Temperature Coefficient | the modification of the diode’s forward voltage drop as a function of temperature. |
| Reverse Recovery Time | when the voltage polarity is switched, the amount of time it takes for the diode to change from the forward conducting condition to the reverse blocking state. |
| Breakdown Voltage | the voltage at which a diode fails and a significant amount of current can flow through it in the opposite direction. |
| Operating Temperature Range | The range of temperatures that the diode may safely operate within without being harmed. |
| Maximum Forward Surge Current | The highest current a diode can sustain for a brief amount of time without being harmed. |
| Cut-in Voltage | the voltage at which a diode begins to conduct electricity in one direction alone. |
| Leakage Current | the minimal current that continues to flow through the diode in the forward direction even in the absence of voltage. |
| Series Resistance | The voltage drop across the diode is influenced by the resistance connected in series with it. |
| Reverse Breakdown Current | While a diode is working in breakdown mode, an opposite-direction current passes through it. |
| Reverse Recovery Charge | The quantity of charge that has to be discharged from the diode for it to go from the forward conducting state to the reverse blocking state. |
| Rectification Efficiency | A diode’s ability to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) with efficiency. |
| Reverse Voltage Leakage | The most amount of reverse-direction current that can pass through a diode without damaging it.. |
| Size | The diode’s physical dimensions and form, may influence whether or not it is appropriate for a certain application. |
| Cost | a diode’s price, which varies according on its kind and features. |
Normal Rectifier Diode vs Schottky diode
| Property | Normal Rectifier Diode | Schottky Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Made of p-type and n-type semiconductors | Made of metal and semiconductor junctions |
| Forward Voltage Drop | Around 0.7 V | Typically around 0.2 V |
| Reverse Leakage Current | Lower | Higher |
| Switching Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Recovery Time | Slower | Faster |
| Maximum Reverse Voltage | Up to several thousand volts | Up to several hundred volts |
| Maximum Forward Current | Several amps | Several amps |
| Junction Capacitance | Higher | Lower |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Higher | Lower |
| Thermal Stability | Lower | Higher |
| Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Operating Temperature Range | -65°C to 175°C | -40°C to 125°C |
| Reverse Recovery Time | Longer | Shorter |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Power Supplies, Rectifiers, Voltage multipliers | Power Supplies, Switching regulators, Voltage clamps |
| Size | Larger | Smaller than normal rectifier diode |
| Noise | Generates more noise | Generates less noise |
| Reverse Breakdown Voltage | Can be higher | Lower |
| Reverse Recovery Current | Higher | Lower |
| Output Voltage | Depends on the input voltage | Depends on the input voltage |
Related Posts
- Current Regulator Diode
- Zener Diode
- Step Recovery Diode
- PIN Diode
- Schottky Diode
- Photodiode
- Varactor Diode
- Diode
- Zener diode Applications
- Laser Diode
- LED
That is all about the Difference between a normal Rectifier Diode and Schottky diode all details has explained. If you have any query ask here