Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at the Full form of AC its working, generations, and uses. The full form of AC is the alternating current first time in 1832 alternating current was generated by the dynamo working on the principle of Faraday Law and was manufactured by the Hippolyte Pixii (it is an instrument-making company from Paris). FIrst-time ac current was distributed to longer distance for commercial use in 1891 and long-distance transmission line was placed in Colorado than after some months in Germany.
Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at the Full form of AC its working, generations, and uses. The full form of AC is the alternating current first time in 1832 alternating current was generated by the dynamo working on the principle of Faraday Law and was manufactured by the Hippolyte Pixii (it is an instrument-making company from Paris). FIrst-time ac current was distributed to longer distance for commercial use in 1891 and long-distance transmission line was placed in Colorado than after some months in Germany.
With the invention of alternating current, some restrictions offered by the use of direct current were covered. Thomas Edison (had numerous patents about DC) also explains the importance of AC over the DC because it covers limitations of DC. In 1893 first power plant generating 3 phase alternating current was manufactured in California near Redlands. The name of this first three-phase commercial use power plant was Mill Creek Hydroelectric plant. Now almost in every industry, home, office, and commercial markets alternating current is used. In today’s post, we will have a look at its generation, application, and some other related parameters. So let’s get started with the Full Form of AC.
Full Form of AC
- The word AC stands for alternating current its behaviour is opposite to DC current. AC current varies its polarity continuously after some time interval.
- AC current is the type of electrical energy it uses to transform electrical power from one place to another or in our, homes, buildings, schools, restaurants alternating current is used to run appliances.
- The mostly used wave of AC current is sinusoidal in which one half has a positive polarity and second has negative polarity.
- With the sine waveform, AC is also used in different waveforms like square, triangular, etc.
- The simplest example alternating current is the radio and sound signal transferred through the wires.
- In this audio and radio transmission, the AC carrier signal is used by the modulation process to transfer signal.
- The frequency of AC current is fifty in some countries and sixty in some countries.
- A transformer is used to change the level of ac current during transmission.
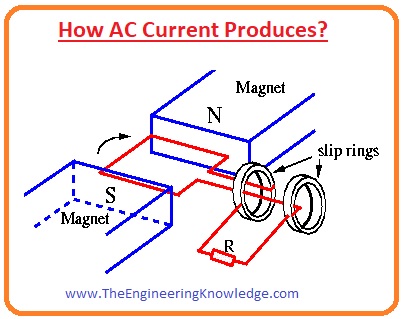
How AC Current Produces?
- The generator is an electrical device used to generate alternating current. In the construction of generator, there is a loop of wire and magnet that exits at the stator of a generator.
- If we rotate loop of wire by some mechanical method or used some prime mover due to rotation of loop flux varied in the loop that generates emf in the loop according to faraday law.
- During rotation flux induces in the loop in one side as it completes one rotation or rotates at 180 degrees then the flux induces in complete loop of wire.
- After 180 degrees the rotation of current flowing through the loop due to flux linking also changes in this way we get the resultant current that is alternating current.
- At the end terminals of loop, slip rings are connected through wich ac output is obtained.
- In the given figure, you can see the practical working of a generator during ac production.
Difference between AC and DC
- Now we discuss the difference between alternating current and direct current.
|
AC |
DC |
| The full form of AC is alternating current. | The full form of DC is direct current. |
| The polarity of alternating current changes after a certain time interval. | The polarity of direct current does not vary. |
| It produces during rotation of loop of wire in field or loop is static and field is varying. | It produces due to constant field across the loop of wire. |
| Its frequency is fifty or sixty according to the country. | Its frequency is zero. |
| Its power factor remains between one and zero. | Its power factor remains always one. |
| There are two types of polarities ac has negative and positive. | DC is polarity less. |
| It generated by the alternators. | DC can be obtained from a battery, solar cell, generator, etc. |
| It can be connected to inductive, capacitive or resistive load. | It operates normally resistive load. |
| Its graphical representation in the form of sinewave, rectangular, or square, etc. | Its graphical representation is only a straight line. |
| It can be transmitted from one place to another with some losses. | It transmitted with almost zero losses. |
| It can be transformed into a direct current. | It can be transformed into ac current. |
| For the production and transmission of alternating current, some substations are enough. | Large numbers of a substation are needed for the generation of direct current. |
| It is less dangerous than DC. | It is more hazardous than the alternating current. |
| It used in home, industries and for some commercials areas. | It used for different processes like electroplating, electrolysis, etc. |
| Impedance is its passive parameters. | Resistance is its passive parameter. |
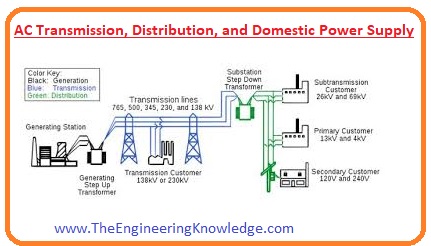
AC Transmission, Distribution, and Domestic Power Supply
- The AC voltage can be step up or step down with the transformer. Before the invention of AC current DC were used to transmit power from one place to another.
- The transmission DC was very expensive as compared to the modern ac transmission system.
- Using a transformer for changing the level of voltage from high to low or low to high has reduced the power losses during the transmission.
- The power loss during the transmission from any conductor can calculate this given formula.
P =I2. R
- In this formula, P is power I is current and R is the resistance through which current is flowing.
- From this equation, lets suppose that power is transmitted through the conductor and the value of current is doubled then the power losses will be 4-times.
- As we know the power transmitted is given as.
P = IVcosφ
- From this equation, we can observe that if we increase the voltage instead of current similar power can be transmitted to long distances with less losses.
- So we can conclude that for longer distance transmission high voltage is the best option to reduce power losses.
- With the advantage of high voltage, there is some advantage high voltage needed a special type of insulation and handling of high voltage also becomes difficult.
- During generation voltage are generated according to the generation rating than the output of a generator is step up to a high level and transmitted to load.
- After reaching at the load side voltage again step down by using a transformer to operate load according to countries load side voltage step down.
- Usually, three-phase power is generated at the power plant. 3 windings are wounded at the stator of a generator at an angle of one twenty degrees.
- Three-phase outputs of generator produced and step up at a safe level and transmitted to the load.
- There are 4 conductors are used in three-phase transmission three phase conductors and one is neutral.
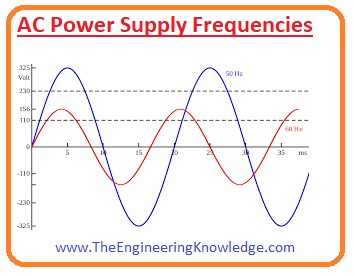
AC Power Supply Frequencies
- The frequency used for alternating current is different for different countries some countries have fifty and some have a sixty-hertz frequency.
- A less frequency comforts the designing of less speed electric motors, mainly for lifting, overwhelming and rolling applications.
- With the benefits, less frequency also causes of dimming of incandescent lights and an intolerable flash of fluorescent lamps.
- Some European countries like Germany, Norway, Sweden also used 16.7-hertz power in a rail system.
Mathematical form of AC voltages
- With the ac current, there are also ac voltages exits. In mathematical form AC voltage can be defined as.
V(t)=Vpeak . sin (wt)
- In this equation.
- Vpeak is the peak voltage.
- ‘W’ is the angular frequency. it related to the physical frequency by the given equation as w=2πf
- ‘t’ is time.
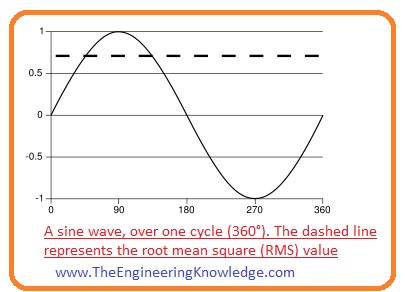
- The difference between the positive peak of ac voltage and negative peak is called peak to peak value of ac voltage.
- As the extreme value of sin(x) is plus one and minimum value is minus one and ac voltage waveform move between +Vpeakand −Vpeak.
- Peak to peak voltage can be denoted as Vpp so, (+Vpeak)-(-Vpeak)= (2 x Vpeak)
- Normally AC voltages are defined in RMS value.
Vrms =Vpeak/2
- Vrms is best to measure the power used by the load.
- In a circuit, DC voltage is providing power to the load this power will be equal to the power delivered by the AC Vpeak voltages to similar load. Vrms=VDC.
Applications of AC
- These are some applications alternating current.
- AC is used in homes to provides power to different electrical appliances.
- It used in industries.
- It used in different restaurants, hotels, and markets.
So friends that is the complete post on the full form of AC I have mentioned each and every parameter related to AC. If you still have any questions about this post ask in comments. Thanks for reading see you in the next interesting post. Have a good day.