![]() Hello, readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will discuss Difference Between Semiconductors and Superconductors. These two materials are conductive materials but have different levels of conductivity. The basic difference between these two materials is that the conductivity offered by the semiconductors lies between conductors’ and insulators’ conductivity and support conductors have conductivity larger than conductors.
Hello, readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will discuss Difference Between Semiconductors and Superconductors. These two materials are conductive materials but have different levels of conductivity. The basic difference between these two materials is that the conductivity offered by the semiconductors lies between conductors’ and insulators’ conductivity and support conductors have conductivity larger than conductors.
Conductors is material that has the ability to flow current through it. Semiconcits and superconductors are electrical conductors that have different conductivity. Here we will discuss different parameters that will help us to find differences. So let’s get started.
What is Semiconductors
- Semiconductors are a category of conductors that provides conductivity values between insulators and conductors. That means their conductivity is less than the conductor’s.
- They are crystalline solids used in different applications like diodes transistor ICs. Normally conductive semiconductors have sensitive nature to magnetic fields and impurities.
- Common examples of semiconductors are germanium, tin, selenium, and tellurium.
- Pure semiconductors do not have accurate conductivity but the addition of impurities to pure semiconductors material provides high conductivity.
- The type of semiconductor on the basis of impurity added are two. P and N semiconductors that are according to the addition of P elements from the periodic table group three and N are from group five.
- The addition of different types of impurities to two semiconductors comes with different types of majority and minority charge carriers.
- A certain energy gap exists between the conduction band valance band. The current flowing taking place majority carries must pass from the valence band to the conduction band. This energy level is called a bandgap
- Normally semiconductor has one crystal. Atoms are configured in three-dimensional patterns. Through considering silicon crystal every silicon atom has four silicon atoms bonded.
- Atoms consist of covalent chemical bonds. The energy gap for semiconductors lies between 0.25 and 2.5ev
N-Type Semiconductor
- For the addition of conduction electrons, elements from group five of the periodic table are doped with pure material semiconductors such as antimony, phosphorus, arsenic, etc.
![]()
- All of these groups of five elements have five electrons in their valence shell.In the above pictures, you can see that the 4 electrons of the group of five elements form a covalent bond with the four nearby silicon atoms and the one-electron of antimony, which is pentavalent, is not released.
- The fifth electrons move freely in the structure and flow due to this electron. Due to the release of an electron, a pentavalent atom is called a donor atom.
- The number of free electrons can be changed by changing the doping material. These free electrons also do not create a hole in the material because these electrons have been stripped of the pentavalent impurity that is the extra electron.
P-Type Semiconductor
- If semiconductors are doped with the elements of group three of the periodic table then P types of semiconductors are formed.
The elements of group three are boron, gallium, indium, etc. 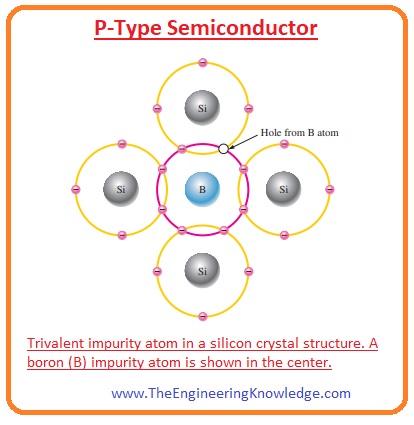
If we doped silicon with the trivalent impurity then three electrons of impurity make a covalent bond with the three electrons of silicons and the hole is generated due to one remaining electron.
- In the given figure, the impurity atom is boron that P-type material with the silicon atom.
In P-type substance, the number of holes can be varied by varying the trivalent impurity amount.
What is a Superconductor?
- Superconductors are material that comes with conductive values larger than conductors. It has an element or compound structure that loses electrical resistance when gets cooled less than a certain temperature.
- So super conductors permit the flow of electrical energy without loss of energy. This energy flow is known as a supercurrent
- Though it is difficult to generate superconductors. The temperature at which this material loses resistance is known as critical temperature.
- The material that has less value than Tc or critical temperature can not be converted into superconductors.
- Superconductors are of two types type 1 and type 11. Type I superconductors material are conductors in nature at room temperature and converted into superconductors when get cooled less than Tc.
- Type II materials are not good conductors at from temperatures. Transform into superconductors when get cooled.
- The band gap of superconductors lies above 2.5eV
Difference Between Semiconductors and Superconductors
| Semiconductors | Superconductors |
|---|---|
| Conductivity is between that of conductors and insulators | Zero electrical resistance |
| Become more conducive as temperature increases | Conductivity only occurs at very low temperatures |
| Commonly made of silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide | Commonly made of metals and metal alloys |
| Widely used in electronic devices such as computers and cell phones | Used in a variety of applications including medical imaging and transportation |
| Used to control the flow of electrons in electronic devices | Used to generate strong magnetic fields and in energy storage applications |
| Have a bandgap that separates the valence and conduction bands | Do not have a bandgap |
| Electrons are excited from the valence to the conduction band to conduct electricity | Electrons form Cooper pairs and move without resistance |
| Can be doped to create an excess or deficiency of electrons | Cannot be doped |
![]()
- Semiconductors are material that has a conductivity between conducts and insulator; superconductors have conductivity larger than conductors.
- The band gap of the semiconductor lies between 0.25 to 2.5ev and for superconductors larger than 2.5ev
- Semcicnsutors examples are silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide.
- Examples of superconductors are Aluminum, niobium
That is all about the Difference Between Semiconductors and Superconductors all details has explained. If you have any question ask them here