 Hello, friends, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we will explain What is Laser Diode. The white light composite of seven colors violet, indigo, brown, green, yellow, orange and red. All these seven colors have different frequencies and wavelengths. Contrary to the light the normal light-emitting diode gives an output of a single color. There are numerous diode are used in electronic engineering projects and circuits such as Zener diode, PIN diode, photodiode, etc. Each diode provides its own benefits and advantage to the circuit for which it using.
Hello, friends, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we will explain What is Laser Diode. The white light composite of seven colors violet, indigo, brown, green, yellow, orange and red. All these seven colors have different frequencies and wavelengths. Contrary to the light the normal light-emitting diode gives an output of a single color. There are numerous diode are used in electronic engineering projects and circuits such as Zener diode, PIN diode, photodiode, etc. Each diode provides its own benefits and advantage to the circuit for which it using.
In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at the laser diode it uses a single frequency of light for operation. It not only used in electronic instruments but also used in medical and optical fiber industries for the detection of diseases and faults in optical fiber. So let’s get started with What is Laser Diode.
What is Laser Diode
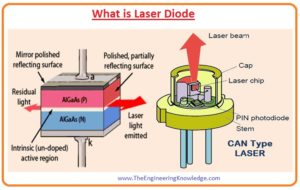
- The laser diode also called injection laser diode stands for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation.
- This electronic device transforms the electrical energy provided by the input source into the beam of light.
- The light beam produced by the laser is monochromatic, unidirectional and visible.
- The semiconductor material used for the construction of this diode defines the wavelength of a wave produced by the laser diode.
- Nowadays used laser generates beam in the range of infra-red to ultraviolet spectrum.
- A laser beam is currently used in numerous applications such as in fiber optics for fault detection, such pointers are manufactured that used laser, barcode reader used laser beam for a reading of data, compact disks, etc.
- It can also used be used for lighting purposes if phosphors is used in its construction like used in light-emitting diodes.
Working of Laser Diode
- To a detailed understanding of laser, we must have an understanding of two terminologies first one is stimulated emission and the second one is population inversion.
- Let’s discuss them one by one with the detailed.
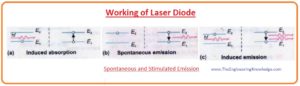
Spontaneous and Stimulated Emission
- Let’s suppose that there are some free atoms in the ground state with the energy E1 and some electrons are in an excited state with the energy E2 as shown in a given figure.
- If photons of light collide on this arrangement of atoms having energy hf= E2-E1.
- This photon of light can affect the atom by two possibilities first is that it can collide with the atom in the ground state and this atom will reach an excited state.
- This process is known as stimulated or induced emission and in the figure, it denoted as a.
- When atom move to excited state then there will be two further possibilities. The first one is that it losses photon of energy hf= E2-E1 spontaneously and move to ground state it denoted in figure as b.
- The second possibility is it may get collide with another photon of energy hf= E2-E1 and move back to a ground state.
- The generated photon from an atom will move in the direction of the incident photon it denoted in figure as c.
- We can see that for every incident photon we will have two photons moving in a similar direction.
- So we can find 2 things from this experiment amplified and coherent (wave having a single wavelength) wave moving in one direction.
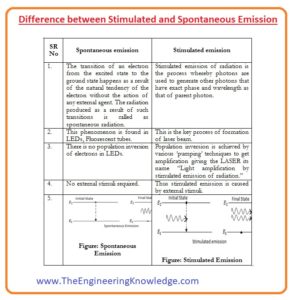
Difference between Stimulated and Spontaneous Emission
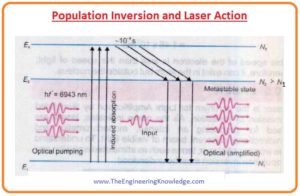
Population Inversion and Laser Action
- For practical understanding, let’s take an atom of material that can stay in three different conditions as shown in a given figure.
- In the figure, you can see that the first state is E1 that is ground state second is excited state E3 in which atom can stay for 10-8s third is a metastable state E2 in which atom can stay for 10-3s.
- The metastable state is also an excited state where atom resides unusually for some time interval then spontaneously moves to a lower energy state.
- The transition of an atom from or in this state is a little bit difficult as compared to other excited states.
- Due to this reason, electrons do not directly excited about this state but move to high energy state then move spontaneously to this state.
- Let’s suppose that an incident photon of energy hf=E3-E1 move atom from a ground state to directly to the excited state E3.
- Atom then moves to a metastable stable and stays there for a long time interval. Atom reaches very quickly in the metastable state but leaves it after a long time.
- Due to this such condition comes when the quantity of atoms in the metastable state is larger than the excited state this situation is known as population inversion.
- After obtaining the metastable state it is very easy to get the lasing action of the laser.
- The atoms in metastable condition E2 have collided with the external photons of energy hf=E2-E1 and the result is induced emission that causes to emit intense, coherent, beam moving in the direction of incident photons.
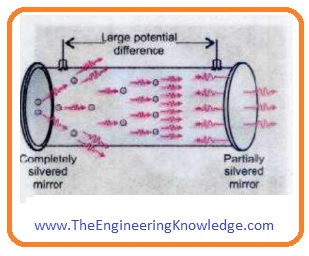
- The generated photons are controlled or confined in a closed structure to further stimulated emission.
- It can be done by using a mirror on both sides of the structure by making one end completely covered or reflecting and another half reflecting to provide a path for the beam to move out from the structure.
- This shown in a given figure.
- All photons move randomly in the mirror confinement and collide with other atoms and produced a more intense and coherent beam of light.
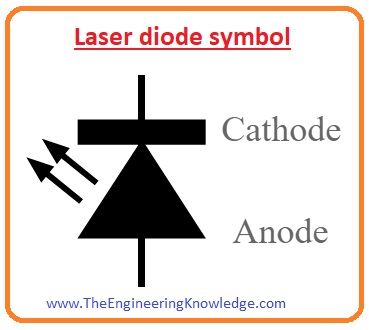
Laser Diode Symbol
- The symbol of laser diodes used in different circuitry is similar to the light-emitting diode.
- The arrowhead on the symbol of a diode defines the light emitting from the diode.
Laser Diode Characteristics
- These are some characteristics of a laser diode.
Monochromatic:
- The light beam produced by the laser is monochromatic mean has a single color.
Unidirectional:
- The beam produced with this instrument move in a single path or uni-direction due to this feature it used in optical fiber for fault detection.
Coherent:
- The light beam produced has a single wavelength.
Laser Diode Hair Removal
- Laser diode uses the SPTL (selective photothermolysis) to hit the chromophores exits in the skin usually find in blood.
- The laser beam removes the chromophores by heating them and not affect nearly exits tissues.
- When it used to remove unwanted hair the melanin existing in hair follicles is only damaged by the light beam and it stops the further growth of hair on that part of the body.
- The use of cooling technology with the laser diode for decreasing pain makes this treatment more effective and increases its efficiency.
Types of Laser Diode
These are some types of laser diodes that are described with the detailed.
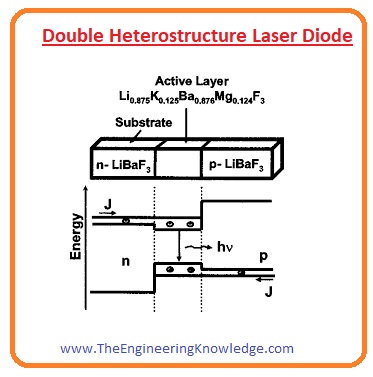
Double Heterostructure Laser Diode:
- This diode is manufactured with sandwich-like arrangements in center a substance of less bandgap is placed and both sides material of high bandgap is assembled.
- Due to different layers of different material, it makes 2 heterojunctions. Normally used substance are Gallium Arsenide, and AlGaAs.
- The benefit of double heterojunctions is that the portion where electrons and holes are present together is constrained the thin central layer.
- It provides more electrons and holes pairs for the amplification process.
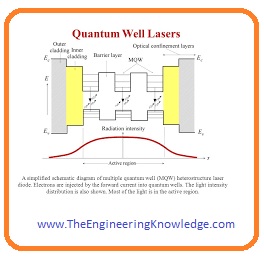
Quantum Well Laser Diode
- This diode has a thin central layer that works like a quantum well ( quantum well is potential well that have discrete energy values).
- As the quantum well is square-like shape so it confine electrons at energy levels that are necessary for laser operation and it also enhances the efficacy.
- With the single quantum well diodes, multi-quantum well diodes are also available that enhances the overlapping among the gain portion and optical waveguide mode.
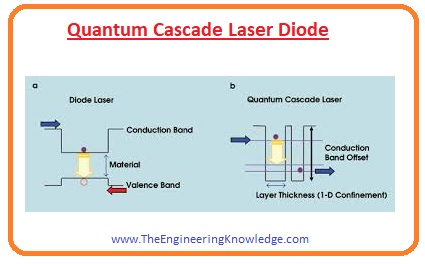
Quantum Cascade Laser Diode
- Quantum cascade laser diode is a hetero junction diode that uses alteration among the good energy levels to help the production of a laser light beam.
- It produces the wave of larger wavelength and product wavelength can be controlled by varying the thickness of the diodes layer.
Separate Confinement Heterostructure Laser Diode
- This type of laser diode is being mostly used from the year 1990. It resolves the problems that occur in other diodes.
- In other diodes due to thin central light no confine properly but these diodes confine light effectively.
- For confinement of light into the diode, this diode has 2 exterior layers with the less refractive index value.
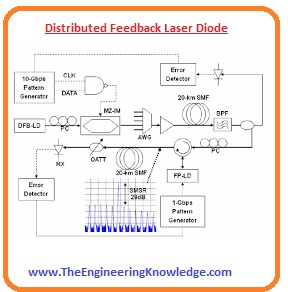
Distributed Feedback Laser Diode
- This diode is mostly used in signal transmission systems such as in optical fiber.
- The problem is that the wavelength of this diode effected through the external environment temperature, etc.
- To stable, the wavelength of the beam diffracting grating is placed near to the PN junction of this diode.
- This grating work like an optical filter directs the single wavelength of to gain a portion of the diode.
- So the grating delivers the feedback that is necessary for the lasing action of the laser.
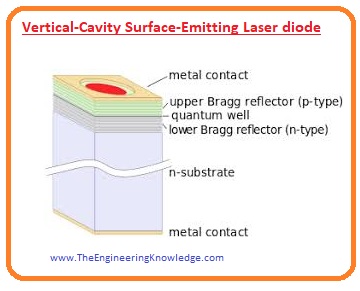
Vertical-Cavity Surface-Emitting Laser diode
- This diode emits waves from the surface at an angle of ninety degrees and provides some mWs with high beam quality.
- The length of an active part of this diode is less the lateral so waves come out through surface then the from the edges.
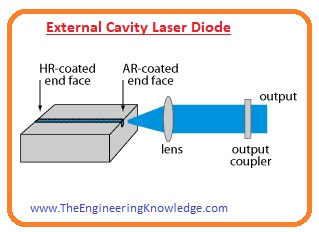
External Cavity Laser Diode:
- This diode comprises a laser diode having a larger laser cavity as a gain medium.
- This diodes is a wavelength variable and display less size spectral lines.
So friends that is the detailed post on the laser diode I have mentioned each and every parameter related to laser didos. I tried my level best to make this post simpler for you if you still have any questions ask in comments. I will solve your queries. Thanks for reading. See you in the next tutorial. Have a good day.