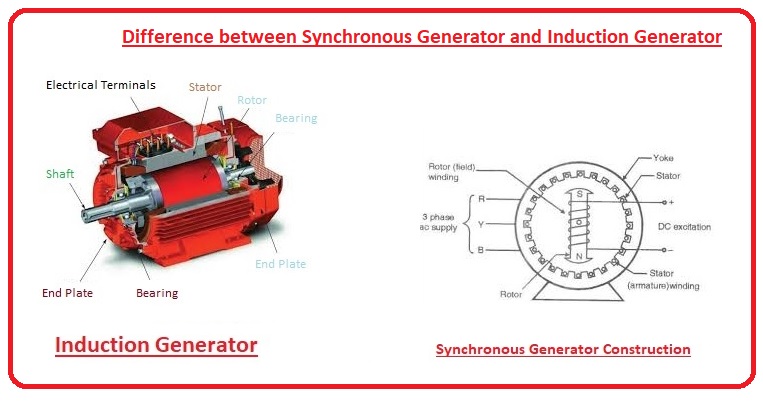
 Hello, readers welcome to the new post. Today we will discuss the Difference between Synchronous generators and Induction generators. In electrical engineering, especially in electricity generation, there are 2 main sources of energy conversion, first is the motor and the second is the generator. A generator is a device that produces electrical energy and a motor produces mechanical energy. Motors and generators are further divided into AC and DC motors and generators according to their power generation and usage.
Hello, readers welcome to the new post. Today we will discuss the Difference between Synchronous generators and Induction generators. In electrical engineering, especially in electricity generation, there are 2 main sources of energy conversion, first is the motor and the second is the generator. A generator is a device that produces electrical energy and a motor produces mechanical energy. Motors and generators are further divided into AC and DC motors and generators according to their power generation and usage.
A synchronous generator is a type of alternating current generator. A steam turbine or a water turbine synchronous generator is used to generate power in wind turbines. Here we will discuss different points to find the difference between synchronous generators and induction generator
Introduction to Synchronous Generator
- A synchronous generator is also known as an alternator, it converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- The electricity we use in our home or industry is mostly produced by a synchronous generator.
- There are many sources of energy conversion in the world, but most of the energy is converted by the synchronous generator.
- They convert mechanical energy into electrical energy up to 1500 megawatts.
- Synchronous generators used in our industry are constructed using a static or rotating magnetic field.
- The construction of a synchronous generator built by a static field is like a DC generator.
- In a rotating magnetic field generator, the static armature is known as the rotor.
Working Principle of Synchronous Generator
- The operation of a synchronous generator is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
emf= dΦ/dt - This law states that the rate of change of flux in any device will cause an emf in that device. If the device is static and the field is rotating, it will also create a field in the device.
- In the case of a synchronous generator, the rotor rotates and creates a field in the stator.
To understand the emf induced in any device, read the article on the voltage induced in a loop
Introduction to Induction Generator
- An AC generator that has work phenomena similar to induction motors is called an induction generator.
This generator works mechanically because the rotation speed of the generator is higher than the synchronous speed.
A normal induction motor usually works as a generator without any special changes in its circuits. - Induction generator is mostly used in hydel power plants, wind power generation and they have the ability to reduce higher air pressure to lower pressure because they have the ability to recover energy in the easiest way.
An induction generator has many limitations. Because it has no external excitation circuits and cannot generate reactive power (Q).
- Since this generator uses reactive power, there should be an external source of reactive power connected to it to provide a field on the stator.
- This separate supply also regulates (controls) the output voltage of the generator, this generator does not have the ability to control its terminal voltages.
- Usually, the voltage of the generator is controlled by an external power source connected to it.
- The main advantage of this generator is that its construction is very simple and there is no need to constantly move at the same speed, and it also does not have special field circuits.
Difference between Synchronous Generator and Induction Generator
- Some of the similarities and differences between synchronous and induction generators are described here.
In a synchronous generator, the speed of rotation of the rotor is equal to the speed of rotation of the field on the stator.
f = (N x P)/120 - But in the case of a synchronous generator, the frequency of the output voltage is controlled by the power system to which it is connected.
- The synchronous generator is not self-excited, it is necessary to connect a special direct current source to it.
- Although there is no need for a special external source for the induction generator as the machine is self-starting.
- The presence of carbon brushes and separate DC sources complicates the design of the synchronous generator and increases its cost.
- However, the induction generator is self-starting and does not need carbon brushes and slip ring, so its construction is the simplest and the maintenance cost is also lower.
Working principle of Induction generator
- An induction generator generates electrical power when the speed of rotation of the rotor is greater than the synchronous speed (this is the speed of rotation of the field in the stator).
If we have a normal 4-pole induction motor that runs at 60 Hz, it will have a synchronous speed of 1800 RPM (revolutions per minute).
According to this formula, we can find the synchronous speed. - nsyn = 120fe/P
- In this equation,
nsyn is the synchronous speed. - fe is the electrical frequency.
- P is the motor pole number.
- If we have another similar number of pole machines operating at fifty hertz frequencies, then it will have a speed of 1500 revolutions per minute.
- The motor rotation speed is less than the synchronous speed (nsync).
The difference between the rotor speed and the synchronous speed is known as slip.
Suppose the motor rotates at 1450 rpm and has an Nsync (synchronous speed) of 1500 rpm, then its slip is (+3.3) percent.
In the normal operation of an induction motor, the synchronous speed is greater than the rotor speed.
It allows the rotor flux to produce a current in the rotor, and this current produces a flux in the stator whose polarity is opposite to the stator flux.
In this way, the rotor followed the stator flux, with currents in the rotor being induced at the slip frequency.
In the case of a generator, the prime mover (which supplies mechanical power to the generator) drives the rotor at a speed that is higher than the synchronous speed.
In the case of a generator, the stator has also induced a current in the rotor and produced a flux because the opposite rotor flux now joins the stator, a current is formed in the stator and the motor now works as a generator as it produces electrical power.
That is all about the Difference between a Synchronous Generator and Induction Generator all details has explained. IF you have any questions ask them here