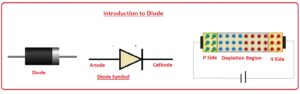
 Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at Introduction to Diode and its practical implementation. It is an electronic device has two terminal first is positive and second is negative. A diode allows the current to flow only in a single direction as it shows a high value of resistance in one direction and less resistance in other direction. Diode first time was created with the crystals of minerals and known as Cat’s Whisker diode.
Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at Introduction to Diode and its practical implementation. It is an electronic device has two terminal first is positive and second is negative. A diode allows the current to flow only in a single direction as it shows a high value of resistance in one direction and less resistance in other direction. Diode first time was created with the crystals of minerals and known as Cat’s Whisker diode.
There are numerous types of a diode are available in the market and used in different electronic projects and devices. The main function of a diode is the conversion of ac current into dc as some device required dc for their operation. So diode is used to operate these devices with the AC at the input terminals. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at its construction, working, types and some practical use in different projects. So let’s get started with the introduction to Diode.
Introduction to Diode
- The diode is an electronic component that converts ac into dc by the rectification process and allows current flow only in one direction.
- The operation of a diode is similar to the check valve that allows the liquid to flow only in a single direction similarly current flows through the diode in only one direction.
- The diode is made with the combination of two different semiconductor material P and N.
- P side of the semiconductor is positive and called the anode and N side of the diode is negative is called an anode.
- Due to high-temperature bears, the silicon is used in the construction of diode but also germanium is used for diode production when less value of voltage loss is needed.
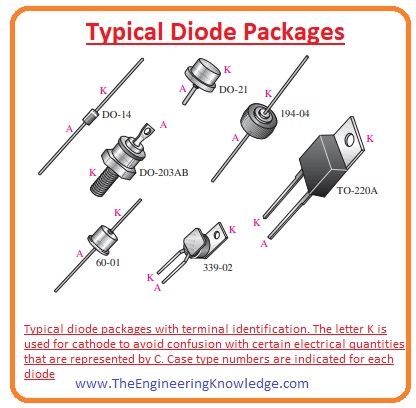
Typical Diode Packages
- There are numerous packages of diodes are available in the given figure different packages are shown.
- The anode and cathode are defined through numerous ways.
- Depending on the features cathode is defined as a band or tab. In such arrangements of diode structure where is only when lead is existed than the casing of diode behaves as a cathode.
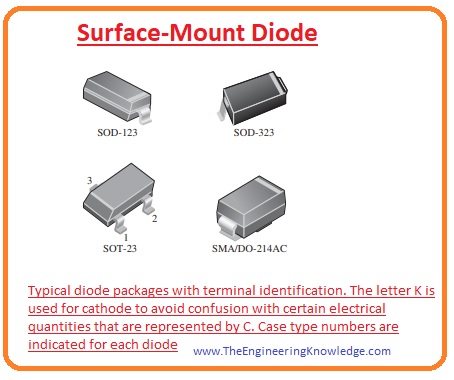
Surface-Mount Diode
- There are numerous diode packaging for surface mounted on the PCB board is shown in a given figure.
- In the figure there are 2 packagings are shown first one SOD (Small Outline Diode) and the second one is SOT (small outline transistor).
- The leads in the structure of casing SOT and SOD are like the gull wing.
- While in SMA casing the leads are like the L shaped which are bent in the casing.
- The one point of SOD and SMA is bent that works as a cathode.
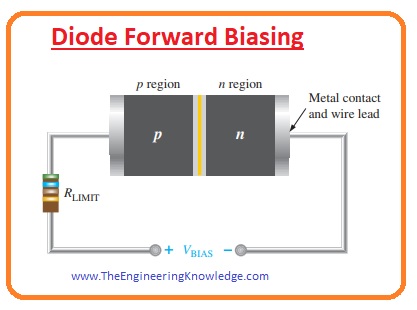
Diode Forward Biasing
- Biasing is a process in which input supply is provided at the terminals of diode.
- In forwarding biased condition current flows due to movement of electrons and holes across the PN junction.
- In given figure, you can see that diode is attached with the dc voltage source in the forward-biased direction.
- The voltage biased provided by the external dc source is represented as Vbias.
- You can see that in the circuit resistance is connected in series with battery and diode it is for limit the value of current and known as current limiting resistance.
- There are 2 conditions should be followed for the forward biased condition.
- The first is to connect the anode of a diode with the positive terminal of the battery and cathode with the negative terminal of the battery.
- In the second condition, the value of the voltage source connected with the diode should be larger than the potential barrier.
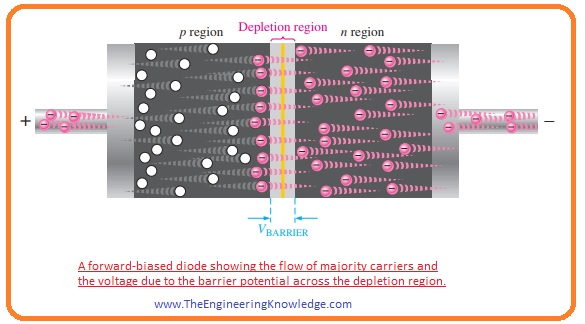
- The behavior of diode after forward biasing is shown in a given figure.
- As we know that similar charges oppose each other so negative terminal apply force on the electrons in N region and they start to move towards the PN junction.
- Due to the movement of electrons current flows through the electrons.
- As the negative terminal of the battery continuously providing energy to the electrons so they have enough energy to cross the potential barrier and enters in the P region and combine with the holes after losing their energy.
- As opposite charges attract each other so positive terminal of battery also attracts the electrons in P region an electron starts to move towards that terminal.
- As electron moved from N-region to P Region so holes also created in the N region that moves towards the negative terminal of the battery.
- In this process, we can conclude that current in forwarding biasing condition flows due to the flow of electrons and holes.
Effect of forwarding Bias on the Depletion Region
- As depletion region is a combination of positive and negative ion.
- In forwarding biased as a quantity of electrons coming in the depletion region increases so they combine with the positive ions existing in the depletion region and holes coming from the P side combine with the negative ions.
- Due to a combination of ions with the holes and electrons reduces their quantity as potential barriers are comprised of ions, so due to decrement in the ions the area of potential barries is also reduces. It is shown in a given figure.
Effect of the Barrier Potential During Forward Bias:
- Above we discuss that depletion region is consists of the positive and negative and these are linked with each other through the electric field.
- And this field makes an energy barrier for electrons and holes to cross the depletion region this energy barrier is called a potential barrier.
- When the diode is connected with the forward biased condition then the electrons get the energy to cross the barrier to move the P side.
- The energy provided battery is equal to the potential barrier.
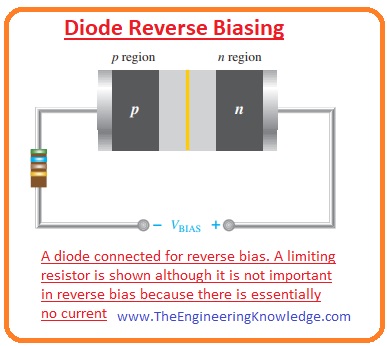
Diode Reverse Biasing
- In reverse biased conditions, current does not flow or very less amount of current flow.
- In reverse biasing situation, the positive terminal of the battery is attached with the cathode and a negative terminal is attached wit the anode of the diode. It is shown in a given figure.
- The voltage source connected in this reversed biasing is denoted as Vbias.
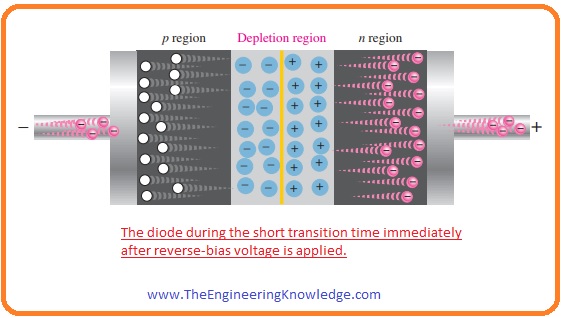
- In the above figure, you can see that the area of the depletion region is wider than the depletion region of forward biasing.
- The process of reverse biasing is discussed with the detailed in the given below figure.
- As opposite charges attract each other so the positive terminal of battery attracts the electrons in the N regions so due to the movement of electrons further positive ions are created and the area of depletion region increases.
- Similarly, electrons prived by the negative terminal in the P region of diode combine with the hole and make negative ions increases the area of the depletion region.
- With the increment in the area of the depletion region, the quantity of majority carriers in P and N region decreases.
- Due to large area of depletion region and ions strength of the electrical field is also increased and there is no option for the flow of current but very small amount of current flow due to some minority carrier but can be neglected.
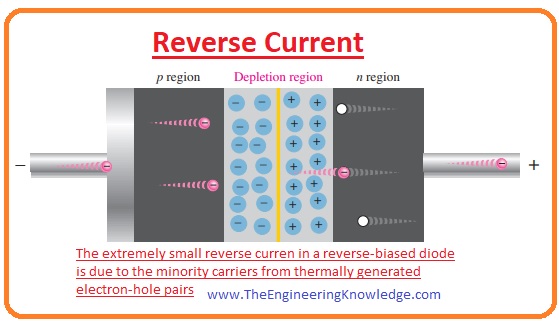
Reverse Current
- This current flows in reverse biasing conditions due to minority carriers existing in the P and N regions.
- A small number of electrons present in the P region repelled by the negative terminal of the battery and moved towards the PN junction.
- When the electrons reach the depletion region they cross it and move to the P region due to this movement small amount of current flows this current is called reverse current as it flows through the N to P side of the diode.
- The given below figure explains the movement of reverse current in the opposite direction.
Reverse Breakdown
- Usually, the reverse current is very less and not take into consideration but if the input voltage is provided at the level known as breakdown voltage then the reverse current flows very largely.
- After getting energy from the voltage source minority electrons in the P regions moves towards the potential barrier during their movement they collide with other atom releases the valence electrons from that atom.
- The released electrons also further collided with other atom and further electrons are released.
- So this process makes minority electrons into the majority and they move to the N region after crossing the potential barrier.
- The increment in the numbers of free electrons is called the avalanche effect so the quantity of reverse current increases due to the avalanche effect.
- If this reverse current is not in the limited condition it can damage the diode.
Difference between Diode and LED
- Now we discuss the difference between diode and LED with the detailed.
| Diode | LED |
| A diode is used to provide rectification and operate only in one direction. | LED stands for light-emitting diode. When a voltage source is connected with it emit light. |
| It manufactured with silicon and germanium. | It manufactured with the GaAs and GaP. |
| It transforms energy into heat. | It transforms energy into the light. |
| Its reverse breakdown voltage is large. | Its reverse voltage is less. |
| It starts operation at 0.7 incase of silicon and 0.3 in case of germanium | It operates at 1.2 to 2 volts. |
| It used to rectifier ac into dc. | it used to produce light |
| It used as rectifies, clamping circuits, etc | It used as a light source, as an indicator in the seven-segment display. |
Difference between Diode and Photodiode
- Now discuss the comparison between diode and photodiode.
| Diode | Photodiode |
| It operates only in forward biasing. | It operates in reversed biased mode. |
| It operates as a switch | It transforms light into electrical current. |
| Constructed with the silicon and germanium | It also constructed with germanium and the coating of silver nitride is used as anti-reflective. |
| It used for rectification, clamping circuits, etc. | It used in optical devices like cameras, etc. |
Difference between Diode and Zener Diode
- These are some differences between diode and Zener diode.
| Diode | Zener Diode |
| It operates only in forward biasing. | Zener diode operates in forward and reverses bias conditions. |
| If it operates in reverse biased condition it will damage. | It will operate in reverse biasing without any damage. |
| The doping level in general diode is less as compared to the Zener diode. | I this diode is doping level is large to get a high value of breakdown. |
| It used for rectification, clamping circuits, etc. | It used in voltage regulation circuits. |
Difference between Diode and Transistor
- These are some differences between the diode and the transistor.
| Diode | Transistor |
| A diode is 2 terminal device used to flow current in a single direction. | A transistor is 3 terminal device through which current flows from high resistance area to less resistance area. |
| In the construction of diode, only two semiconductor materials are used P and N. | In diode three layers of semiconductors are used one is between two semiconductor material either P or N and makes a combination of NPN or PNP transistor. |
| In diode is only a single depletion region | Transistor has 2 depletion regions. |
| A diode has only a single junction among P and N material. | It has 2 junctions first is between emitter and base and second between base and collector. |
| A diode has 2 terminals positive called anode and negative called cathode. | Three terminals in transistors, known as emitter, base, and collector. |
| It can be work as a switch. | It can be operated as a switch and amplifier. |
| It operates as a switch, in clamping circuits and rectifier. | It operas as amplifiers and oscillators. |
Types of Diode
- There are numerous types of diodes lets discuss them with the detailed.
Avalanche diodes
- The operation of these diodes occurs when the reverse-biased voltage crosses the breakdown voltage.
- The operation of these diodes is almost similar to the Zener but with some differences in the break down effect that is an avalanche effect.
- It occurs when revers voltage provided cross the potential barrier than current start to flow in large amounts like an avalanche.
- The structure of these diodes that do not allow them to damage at the reverse biased condition.
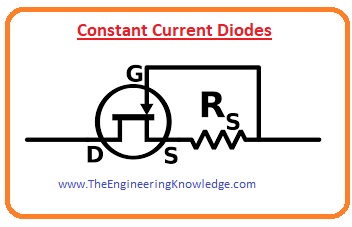
Constant Current Diodes
- This diode is also known as Junction field-effect transistor (JFET) its gate terminal is attached to the source.
- So it operates like the voltage limiting Zener diode.
- This diode is also known as CLD (constant current diode) due to the linking of transistors.
Crystal Diode
- This diode is also known as point contact diode when the first time it constructed for the use in the receiver of microwaves.
- The working of this diode relies on the pressure between point and semiconductor substances used in its construction.
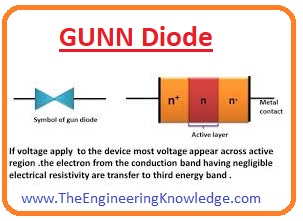
Gunn Diode
- This diode is also known as a transferred electron device (TED) it has negative resistance with the 2 terminals.
- It used in such electronic projects where the high frequency is required.
- It used for the generation of microwaves in the electronic oscillators.
- Due to microwave generation, it is employed in RADAR, microwaves and automatic door openers.
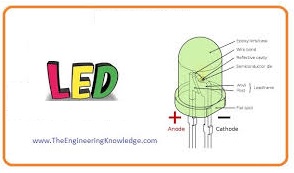
LED
- A led stands for light-emitting diode it releases light when input supply provided to its terminals.
- The process of light-emitting accomplished when the electrons move from the N side to the P side and combine with the holes.
- When electrons combine with the hole they release their energy and this energy is emitted in the form of light.
- The color of the emitted light depends on the semiconductor material used for the construction of LED.
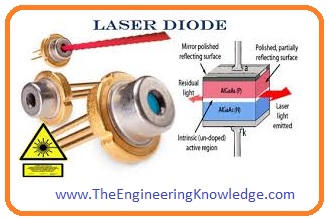
Laser Diode
- Laser (light amplified by the stimulated emission) diode also called injection laser diode.
- It also emits light similar to the diode but in this emission process is different. It uses the spontaneous and stimulated emission process for the emission of light.
- The working of a laser diode is mentioned in previous you also read it with the detailed. Laser Diode
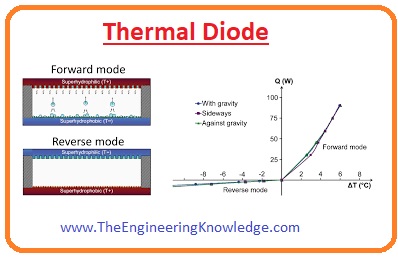
Thermal Diode
- This diode is similar to a normal diode and flows energy in only one direction like current flow in a normal diode.
- It used in a heat engine, refrigeration and some other heat transfer-related applications.
Photodiode
- The type of diode transform light into the current. The photons of light collided with the photodiode converted into the current.
- With the increment in the surface area, its response time decreases. The practical example of a photodiode is a solar cell that uses numerous photodiodes for the conversion of light into the current.
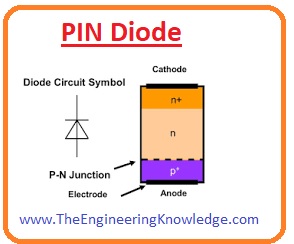
PIN Diode
- The operation photodiode is alike to the photodiode that transforms the light into the current.
- There are 3 main parts of PIN diode first is P, second is I (intrinsic) and third is N region.
- The intrinsic region is sandwiched between the P and N that are heavily doped semiconductor materials.
- A PIN diode is used in different switching circuits, phot detecting devices, and large power-consuming electronics instruments.
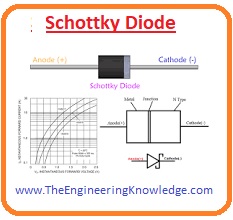
Schottky Diode
- This diode is manufactured with the metal and semiconductor material. The forward biased voltage drop of this diode is less as compared to the general PN junction diode.
- The value of forwarding voltage loss at a current of one milliampere is in the range of 0.15 volts to the 0.45 volts, due to this feature it used in clamping circuits.
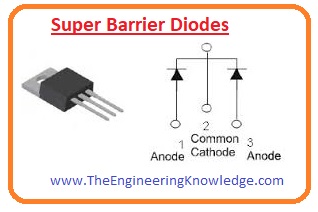
Super Barrier Diode
- This diode is used in rectifier circuits were due to less value of forwarding biased voltage loss and better surge handling capacity.
- It also has less value of reverse leakage current than the general diode.
Gold Top Diode
- In this diode, gold is dopant material in some diode platinum is also used as a dopant material.
- The use of gold increases the movement of electrons from the N region to P region.
- The operation of a gold diode is fast than the other diode but less than the Schottky diode.
- The value of leakage current is less than compared to the Schottky diodes.
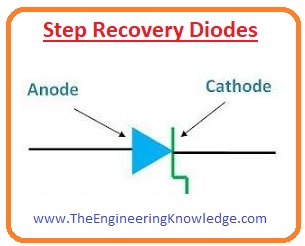
Step Recovery Diodes
- This diode is also called a voltage-dependent variable capacitor. Its doping level is very less close to the PN junction.
- Also, the quantity of carriers is little nearer to the junction.
- This diode operates very fast at less frequency value so it also used as a charge controlled switching circuit.
- It operates in forward biasing and not operate in a revered biasing circuit.
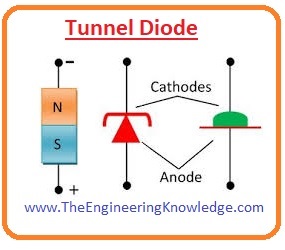
Tunnel Diode
- This diode has features with which the increment in the voltage-current decreases.
- It used in the computer due to fast switching and also used in high-frequency amplifier circuits.
- The other name if this diode is Esaski diode due to its creator name.
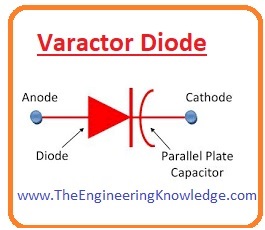
Varactor Diode
- The word varactor derived from the variable capacitor. This diode only in reverse biasing.
- It is similar to the variable capacitor during its reverse biasing.
- There are some other names of this diode like varicap tuning, variable capacitance diode.
Applications of Diode
- Friends I hope till now you have become well aware of the diode, now let’s discuss practical applications of diodes with the detailed.
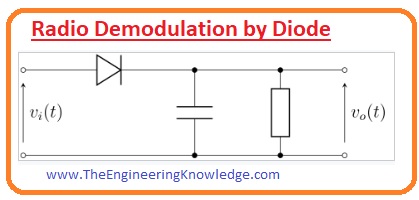
Radio Demodulation
- The first time diode was used in the circuit for the demodulation of AM radio signal.
- Amplitude modulated or AM wave comprises of the positive and negative peaks of radio waves as a carrier, the magnitude of this wave is equal to the audio.
- The diode only rectifies the amplitude modulation radio signal.
- After that sound is separated from the carrier signal by using a filter and provided to the transducer to conversion into a sound signal.
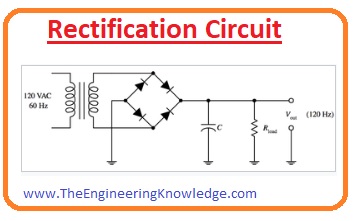
Power Conversion
- The diode used as a rectifier in which it transforms the AC signal into DC this process is called rectification.
- The given circuit shows the rectification process of the diode.
Logic Gates
- Diodes are used to construct logic gats by combination with other instruments.
Temperature Measurement Devices
- The diode is also used as a temperature computing device, a forward voltage drop of diode rely on the temperature.
Related Posts
- Current Regulator Diode
- Zener Diode
- Step Recovery Diode
- PIN Diode
- Schottky Diode
- Photodiode
- Varactor Diode
- Diode
- Zener diode Applications
- Laser Diode
- LED
So friends that is the detailed post on the diode I have each and every parameter related to the diode. I tried my level best to make simpler and easy this post and describe every aspect of a diode. If you have any queries about diode ask in comments. See you in the next interesting tutorial. Have a good day. Thanks for reading.