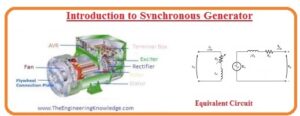
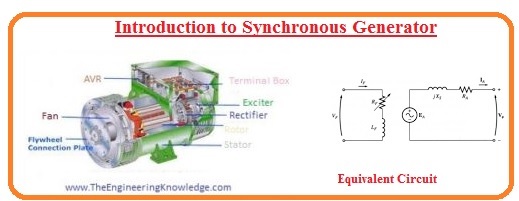
 Hi friends, I hope all of you are fine. In today’s tutorial, we are gonna have a look at Introduction to Synchronous Generator. In electrical engineering particularly in power production, there are 2 main sources of energy conversion, first is the motor and the other is generator. The generator is a device that produces electrical energy and motor produces mechanical power. The motors and generators are further divided into AC and DC motors and generators according to their power generation and use.
Hi friends, I hope all of you are fine. In today’s tutorial, we are gonna have a look at Introduction to Synchronous Generator. In electrical engineering particularly in power production, there are 2 main sources of energy conversion, first is the motor and the other is generator. The generator is a device that produces electrical energy and motor produces mechanical power. The motors and generators are further divided into AC and DC motors and generators according to their power generation and use.
The synchronous generator is a type of AC generator. For energy generation in wind turbines, a steam turbine or hydro turbines synchronous generator is used. In today’s post we will have a look at its construction, working, excitation method, etc. so let’s get started with the introduction to a synchronous generator.
Introduction to Synchronous Generator
- The synchronous generator is also known as an alternator, it converts mechanical power into electrical.
- The electric energy we used in our homes or industries is mostly produced by the synchronous generator.
- There are many sources of energy conversion in the world but most of the energy is converted by the synchronous generator.
- They convert mechanical energy into electrical energy up to 1500 megawatts.
- The synchronous generators used in our industries are constructed by a static or rotating magnetic field.
- The construction of the synchronous generator built by the static field is like the DC generator.
- In the rotating magnetic field generator, the static armature is known as the rotor.
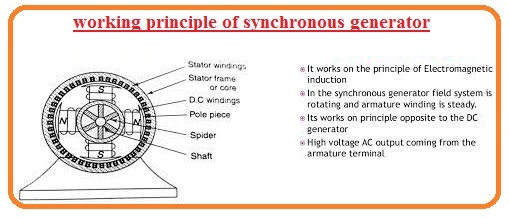
Working Principle of Synchronous Generator
- The working of a synchronous generator is based on Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction.
emf= dΦ/dt
- This law says that the rate of change of flux in any device will produce emf in that device. If a device is static and the field is rotating it will also produce field in the device.
- In case of a synchronous generator, the rotor is rotating, and it produces field in the stator.
- For an understanding of emf induced in any device study the article on the voltage induced in the loop
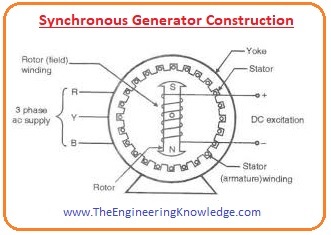
Synchronous Generator Construction
- In a synchronous generator, there is no residual magnetism to produce self-excitation like the induction motor and induction generator.
- The external direct current supply is given to the rotor and it produces field in the rotor. When we rotate the rotor by a mechanical way, its field link with the stator windings and produce a voltage in the stator.
- There are 2 terms we use to represent windings in the machines first one is armature winding and the other one is field winding.
- The windings that produce the main field in a machine called field winding and the windings that produce voltage is called the armature.
- In case of the synchronous generator, the field windings are the rotor windings and the stator windings are the armature windings.
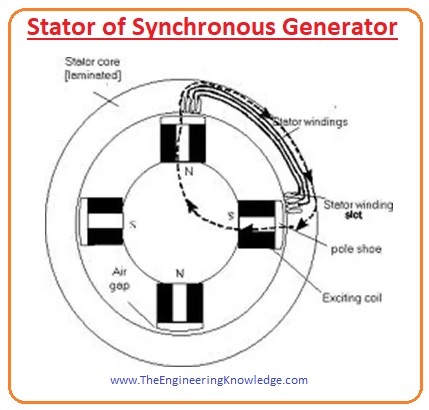
Stator of Synchronous Generator
- The stator is the static part of the generator it provides the covering for the internal construction of the machine.
- It is constructed by laminated sheets of aluminum, there are slots at its inner periphery which used to hold the windings.
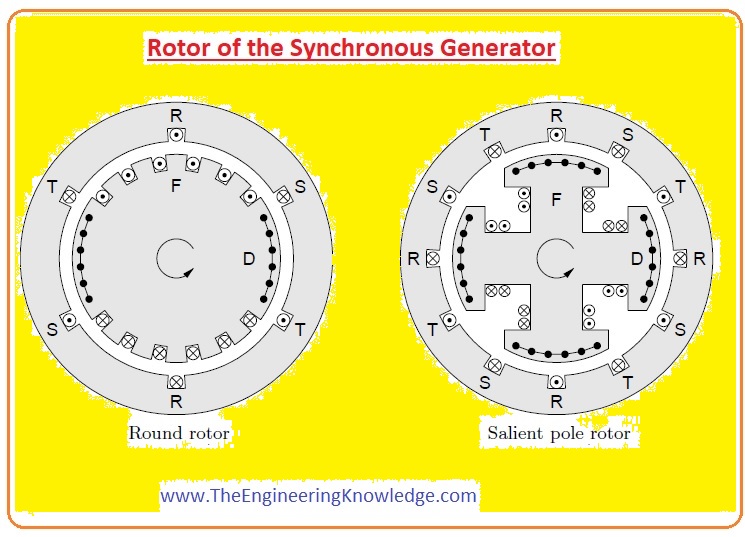
Rotor of the Synchronous Generator
- The rotor of the generator is an electromagnet, it is connected with the external DC source. The external source produces a voltage in the rotor, the field of the rotor induces a voltage in the stator.
- There are 2 main types of synchronous generators.
- Salient Pole Rotor
- Non-Salient Pole Rotor
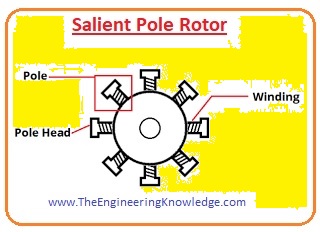
Salient Pole Rotor
- This type of rotor has many no of poles that are manufactured on wheel-like arrangements.
- These poles are constructed from steel and are laminated.
- The windings of the rotor are wound on these poles and at the corners, windings are controlled by the pole shoe.
- The dia of the salient pole rotor is higher and its axis is short.
- The salient pole rotor has 4 or large no of the pole.
- The given diagram shows the salient pole rotor.
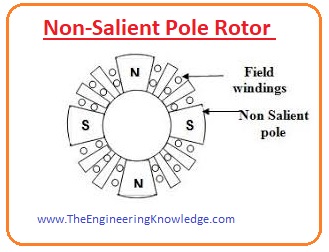
Non-Salient Pole Rotor
- The word ‘salient’ means to stick out, Non-salient pole is such a pole that is manufactured with the surface of the rotor they are not out of the surface like the salient poles.
- This type of rotor is used where 4 or more poles are required at the stator.
DC Excitation of Synchronous Generator
- As we discussed that the synchronous generator is not a self-start machine. It must connect with the external source.
- To excitation of the generator, the DC supply is connected with the circuitry of the rotor.
- As the rotor rotates so there is some precaution that we should keep in mind, connecting the rotor with the DC source.
- Try to connect the windings of the rotor with the DC source through the slip ring and graphite-made brushes, if you connect the windings directly with the dc source, it causes serious sparks and the motor will damage.
- Connect such dc source with the generator that remains permanently connected to the rotor.
- The slip ring is rings made by some metal, they are mounted on the shaft of the generator and have some insulation.
- Every end of the rotor’s windings is joined with the slip rings and the static brushes are mounted on the slip rings.
- The brushes are always mounted on the slip ring because they are made from graphite which has less resistance.
- If one terminal of the DC source is joined with one carbon brush, then the other will be connected with the second brush.
- The important thing you should note is that the dc voltage you provided to the generator should have the same value irrespective of the variation in the speed and angular position of the generator.
Problems of Slip Ring and Brushes in Synchronous Generator
- As we discussed that we use slip rings and carbon brushes to provide the dc supply to the windings of the rotor. These two components cause some difficulties.
- As the brush is made from carbon which is a soft material of nature, so their condition must be monitored after some time and maybe they should be replaced after some time. This process increases the maintenance cost of the machine.
- There is some loss of voltage at the brushes which increases the field current and power loss at the field windings.
- For a smaller synchronous machine, this method of voltage is used because it is a cheap method for these machines.
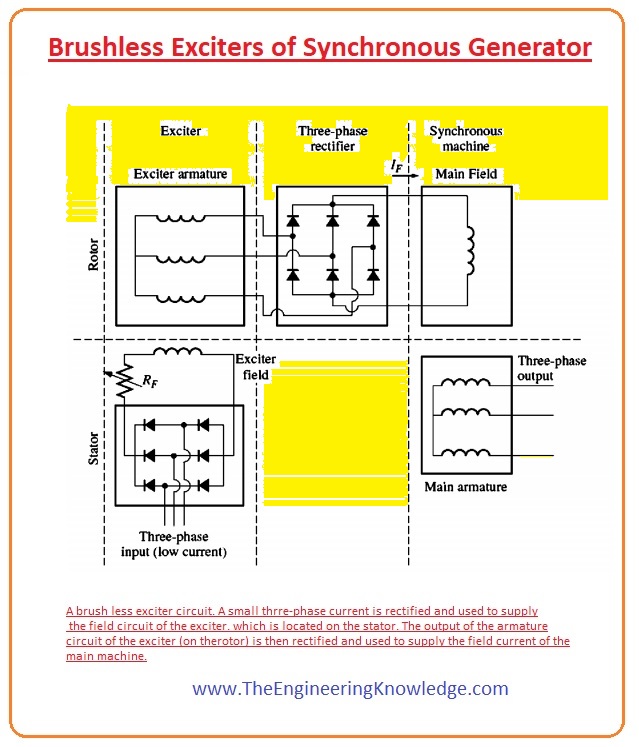
Brushless Exciters of Synchronous Generator
- The slip ring and brush technique do not work for the larger motor and generator. For dc supply to the rotor, they used brushless exciters.
- The brushless exciter is itself an ac generator, as any machine has 2 circuitries, first is the armature and the other is field.
- When this exciter relates to any synchronous machine, its field circuitry resides on the static part of the synchronous machine and armature circuitry is mounted on the shaft of the machine.
- As the output of the exciter is 3-phase ac which is then converted to dc by the rectification, this rectification circuitry is also connected on the shaft of the synchronous generator.
- Then the output of the rectifier sent to the field circuitry of the rotor. By varying the field current of the exciter, we can easily control the field current of the synchronous generator.
- As there is no physical connection between the stator and rotor of the generator, so the exciter needs a very lesser amount of repairing the slip rings and brushes.
- The arrangement of the brushless exciter with a generator is shown in the given diagram.
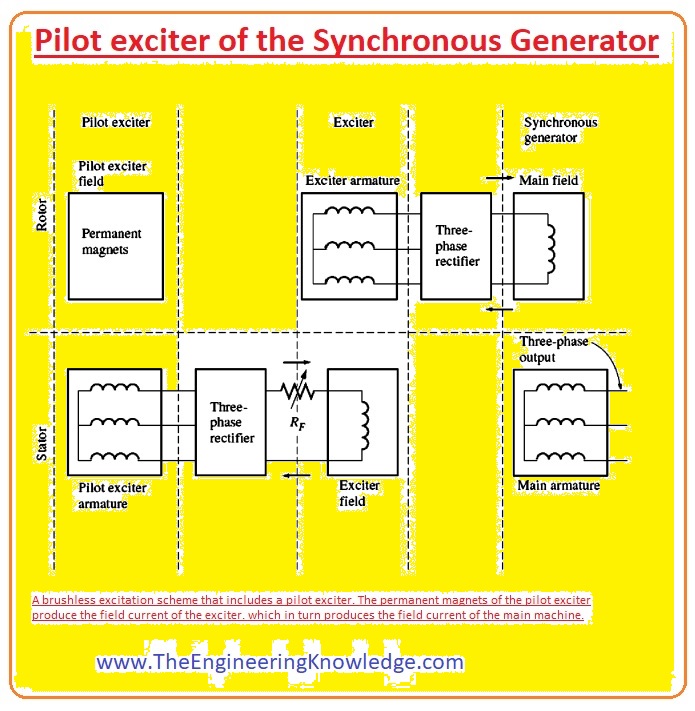
Pilot exciter of the Synchronous Generator
- A pilot exciter was introduced on the machine to make the construction of the synchronous generator simple and the excitation of the generator independent from the exterior circuitry.
- The pilot exciter is also an alternating current generator it has a permanent magnet instead of the armature circuitry which is connected with the shaft and its 3 phase windings are joined with the stator.
- It generates the power for the exciter’s field circuitry, this power then governs the field circuitry of the generator.
- If a pilot exciter relates to the shaft of the rotor, then the exterior power supply will not need to operate the generator.
- Most of the synchronous generator also has a slip ring and brush with the brushless exciter, in case of an emergency backup power supply.
- A given diagram shows the pilot exciter circuit.
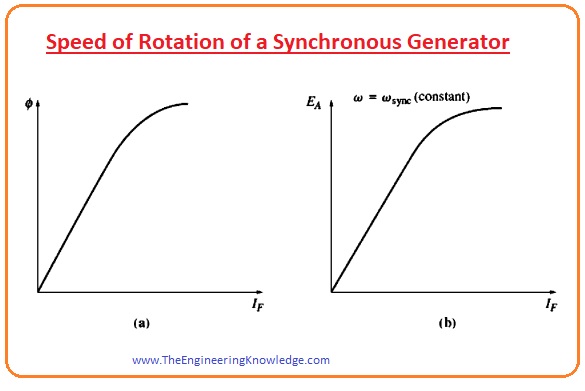
Speed of Rotation of a Synchronous Generator
- As we have discussed the rotor of the synchronous generator is an electromagnet, it joined to the DC source.
- The direction of the field of the rotor will be the direction of the rotation of the rotor.
- The speed rotation of the field in the ac machine has a relation with the frequency at the stator, is given as.
fe =nmP/120
-
- fe in this equation is the frequency of the stator.
- nm it is the speed of the field.
- P is the no of poles
- As the speed of the rotation of the rotor is equal to the speed of the field, this equation shows the relation of the rotor speed to the frequency of the stator.
- The electrical energy is generated at the fifty or sixty-hertz frequencies, so the generator should move at a constant speed.
- For example, to produce the sixty-hertz energy in a 2-pole machine the speed of the rotor should be 3600 revolutions per minute.
- And to produce the fifty-hertz energy in a 4-pole machine the speed of the rotor should be 1500 revolution per minute.
Synchronous Generator vs Induction Generator
- These are some similarities and dissimilarities between synchronous and induction generators that are described here.
- In a synchronous generator, the speed of rotation of the rotor is equal to the speed of the rotation of the field at the stator.
f = (Nx P)/120
- But in the case of a synchronous generator, the frequency of output voltage is controlled by the power system with which it is linked.
- The synchronous generator is not self-excited there is a need of a special direct current source to connect with it.
- There is no need of a special external source for the induction generator, as it is the self-start machine.
- The presence of carbon brushes and separate dc sources make the complicated construction of a synchronous generator and increase its price.
- But the induction generator is self-start and there is no need of carbon brushes and slip rings so its construction is simplest and its maintenance price is also less.
Cooling of Synchronous Generator
- When the generator is operated at a heavy load a huge amount of heat is produced in the generator which can cause of dangerous for the internal structure of the synchronous generator.
- To reduce or minimize heat in the generator there are several methods are used that are described here.
Radial Flow Ventilation System
- In this type of colling method cool air is passed through the stator with the ducts and from another side of the stator it comes out.
Advantages of Radial Ventilation
- In this method of colling power losses for ventilation is less.
- It can be used for both less ratings and high-rating generators.
Hydrogen Cooling of a Synchronous Generator
- In this method, hydrogen is used for the colling of a generator. Before its use for colling its ratio with air must be controlled and keep (9/1) hydrogen to air.
- As if the air exists in environments where hydrogen is performed it can create expulsion.
Difference between Synchronous Motor and Synchronous Generator
- The synchronous generator is such a device that transforms mechanical energy provided by the prime mover to electrical power, but the motor transforms electrical into mechanical energy.
- But these to the motor are similar in physical structure.
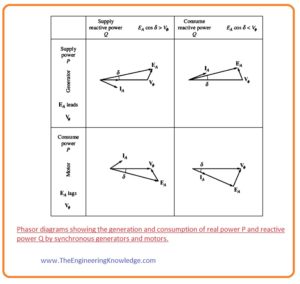
- Any synchronous machine either a motor or a generator can provide active power to or get active power from a system connected and provide reactive power to and get reactive power from the system.
- All these 4 possibilities of these machines are shown in a given figure in the shape of the phasor diagram.
- You can note from the given figure that.
- The unique feature of a synchronous generator (providing P) is that internally generated voltage EA lies ahead Vø, but in the case of a motor internally generated voltage, EA lies behind Vø.
- The different feature a machine (either generator or motor) providing reactive power Q is that EAcosδ> Vø, irrespective of whether the machine is acting as a generator or as a motor. A machine that is taking Q has EAcosδ< Vø.
Synchronous Motor vs Synchronous Generator
Synchronous motor transforms electrical enegy into mechanical energy.
Synchronous generators have DC provided at rotor winding that generates a rotor magnetic field. The rotor is rotated with a primer mover and rotating magnetic field procedures in the machine.
The main working of a synchronous generator is to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy
Applications of Synchronous Generator
- These are some applications of synchronous generators that are described here.
- It is mostly used in such a system where constant speed is required.
- They also maintain the power factor of the system.
- Almost all power generation plants use synchronous generators due to the constant frequency providing the capability.
Faqs
What is the construction and types of synchronous generator?
- Synchronous generators come with 2 main parts stator and rotor. The stator is a static part that comes with the armature winding where voltage is produced. The output of the generator is taken out from the stator.
- The 3-phase AC synchronous generator is the main component of a power system having two synchronous rotating fields. One field is generated with rotor operating at synchronous speed and excited with DC current.
- Synchronous generators are used as power factor correction devices. In industries, they are used to enhance the power factor of the system.
- The working of a synchronous motor is based on the synchronism principle. Where rotation of the rotor is synchronized with the frequency of alternating curent of AC supply. Like the AC motors, synchronous motors also come with the stator
- The generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction defines that change in the field of conductors produces an electric current in a circuit. When the coin rotates in a magnetic field curent induces the coils.
You can also read some related topics to a synchronous generator that are listed here.
Synchronous Generator Equivalent Circuit
Synchronous Generator Phasor Diagram
Synchronous Generator Power and Torque
Synchronous Generator Parameters
Synchronous Generator Operating Alone
Synchronous Generator Parallel Operation
Synchronous Generator parallel with Large Power system
Synchronous Generator Parallel with same Size Generator
Synchronous Generator Capability Curves
Synchronous Generator Transients
So, friends, it is a detailed article on the synchronous generator I have mentioned each and everything related to a synchronous generator in this tutorial. See your next tutorial Equivalent Circuit of Synchronous Generator.






After checking out a number of the blog posts on your blog, I seriously like your way of blogging. I book-marked it to my bookmark site list and will be checking back in the near future. Please check out my web site as well and tell me your opinion.
Hi, the Introduction to Synchronous Generator article it is well written and was
a pleasure to red it. 🙂 Many Kisses!
Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It really useful & it helped me out much. I hope to give something back and aid others like you aided me.
I’m not that much of a internet reader to be honest but your blogs really nice, keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your website to come back later. Many thanks
I’m not that much of a online reader to be honest but your blogs really nice, keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your website to come back down the road. Many thanks