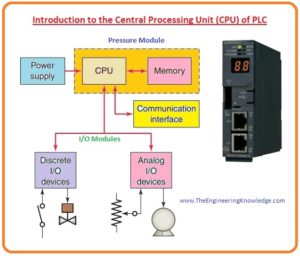
 Hi friends, I hope all of you are fine. As you already know we have started a series of PLC articles. In last lecture, we discussed detailed articles on the features of different plc inputs and output modules. In today’s tutorial, I am going to explain to you a detailed article on the Introduction to the Central Processing Unit (CPU) of PLC. CPU stands for the central processing unit. In plc, it is like a brain it performs a function like the human brain. It controls every activity of plc.
Hi friends, I hope all of you are fine. As you already know we have started a series of PLC articles. In last lecture, we discussed detailed articles on the features of different plc inputs and output modules. In today’s tutorial, I am going to explain to you a detailed article on the Introduction to the Central Processing Unit (CPU) of PLC. CPU stands for the central processing unit. In plc, it is like a brain it performs a function like the human brain. It controls every activity of plc.
CPU of plc is like a personal computer CPU, which controls all functions of a computer. From receiving a signal to sending or control and logic function. Similarly CPU of plc control every function and circuitry of plc. It is the core part of plc without it plc is nothing, as there is no control system then how other devices can work. So in today’s article, we will discuss details about it. So let’s get started with an Introduction to the Central Processing Unit (CPU) of PLC.
Introduction to the Central Processing Unit (CPU) of PLC
- The central processing unit of plc is constructed into a single-element fixed PLC controller while modular frame categories normally use a plug-in unit.
- A central processing unit, control system, and computer are all names used by different producers to signify a similar unit that performs similar tasks.
- CPUs differ in handling speed and storage choices.
- A computer unit can be distributed between two parts the central processing unit and the memory or storage unit.
- The central processing unit implements the programs and makes the decisions needed by the PLC to operate and communicate with other units.
- The memory unit by electronic means stores the PLC controller programs with other retrievable numerical data.
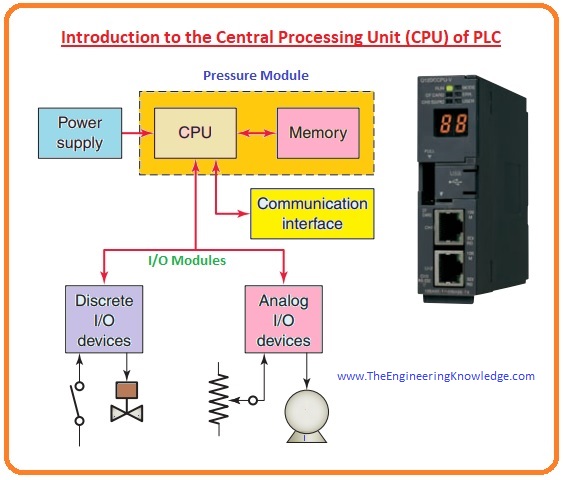
PLC Power Supply
- The PLC controller power supply delivers the essential power (normally five volts DC) to the CPU and input and output units connect into the back-plane of the frame.
- Power sources are existing in different ratings.
- The power source transformed 115V AC or 230V AC into the operating (direct current) voltage obligatory to the processor, memory or storage, and input and output electric circuits.
- PLC power source is usually built to endure temporary damages of power without upsetting the process of the PLC.
- The time for which plc can bear a loss of power is known as Holdup time, normally it ranges from ten ms to three seconds.
Difference Between PLC CPU and Computer CPU
| PLC CPU | Computer CPU |
| The program used in this processor is intended to simplify manufacturing control. | This CPU is constructed only for general mathematical and computing work. |
| This processor implements the functioning scheme, control storage, controls inputs, assesses the operator logic program, and make suitable outputs. | While this CPU do just arithmetic logic functions and simple control functions. |
| The CPU of a PLC scheme can be consists of more than one processor. Which enhances its overall working speed. | Cpu of the computer contains only one processor. |
| Every processor of plc CPU has its own storage and instruction, which work instantaneously and independently. | This CPU has only one processor which do many functions alone. |
| Due to having multiprocessors the scanning of every processor is equivalent and liberated thus dipping the retort time. | Due to a single processor, these parameters did not happen in this CPU. |
| Error tolerant PLC schemes sustenance double CPUs for serious procedures. These schemes permit the operator to arrange the scheme with two processors, which permits the transmission of a switch to the second CPU in the case of a CPU error. | we cannot use the CPU of a computer for such schemes. |
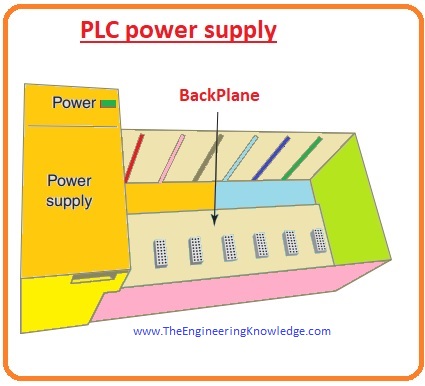
The function of key switch of the PLC CPU
RUN Position
- This mode of key switch converts the CPU in the Running condition.
- It Implements the ladder logic program and operates output instruments.
- It Stops you from doing online programming changes.
- It Stops users from using programming or operative interfacing components to change the CPU style.
PROG Position
- This feature of a key switch converts the CPU to the Program condition.
- It Stops the CPU from scanning or implementing the ladder programming, and the regulator outputs stop working.
- It Permits the operator to make program entrance and removal.
- It also Stops users from using a programming or operative interfacing instrument to change the CPU mode.
REM Position
- This feature of a key switch converts the processor in the distant style which can be either the Run, Program, or Test mode.
- It Permits us to alter the CPU mode from a programming or operative interfacing component.
- It Permits us to do online programming changes.
Features of PLC CPU
- These are important features of the PLC CPU that are explained here.
- The CPU also comprises circuits to link with the programmable device.
- Someplace on the unit, we will find a joint that permits the PLC to be linked to an exterior programmable expedient.
- The decision-making aptitudes of PLC CPUs go far away from the simplest logic process.
- The CPU executes other tasks like time, calculating, latching, associating, indication control and complicated mathematics tasks.
- PLC CPU has varied continually due to progress in computer equipment and larger responses from different applications.
- Nowadays, the CPU is quicker and has extra commands which are introduced in new models.
- As PLC are microchip constructed, they can be prepared to do jobs that a computer can also do.
- In count to their controlling purposes, PLC can interact with the (SCADA).
Precautions for PLC static devices
- Numerous electrical apparatuses establish in CPUs and other kinds of PLC units are subtle to electrostatic voltages which can damage their working or harm them.
- The following stationary control actions should be monitored when supervising and functioning with stationary-sensitive components and units.
- Be grounded physically by moving a conductive body before supervision of static-sensitive types of machinery.
- Always try to dress a wristband that offers a track to drain off any charge which can figure up through working.
-
- Be cautious not to trace or touch the backplane connections or connector pinouts of the PLC scheme (permanently grip the circuitry passes by the border if probable).
- Also, be cautious not to touch other circuitry machinery in a unit when you arrange or substitute its inner components.
- When not in working conditions stock units in its static-shield container.
- If accessible, use a stationary safe working place.
I also have uploaded some related articles to plc you must read them for further learning.
- Introduction to PLC
- Working of PLC
- Parts of PLC
- Input and Output Section of PLC
- PLC Discrete Input and Output Devices
- Analog Input and Output Devices of PLC
- plc special inputs and outputs
- Features of PLC Inputs and Outputs
Faqs
What is the introduction of PLC?
PLC can be defined as small industrial computes having modular components made for automated control processes. There are controllers used in all industrial automation
- The CPU is a hardware component that is a core computational unit in the server. Servers and other smart devices transform data into digital signals and do mathematical operations on them. The CPU is the main component that processes signals and make computing easy
- CPU is the brain of PLC having an octal or hexagonal microprocessor. Microprocessor-based CPU do not have timers, relays, and counters. The two types of processors single-bit or word processors can configured with PLC. A bit processor is employed for logic functions.
- The programmable logic controller is a small computer that can get data through at input points and send operating instructions at outputs. PLC’s main work is to control the functions of a system with the use of internal logic programmed
- PLC monitors machine input, makes proper decisions according to programs, and controls outputs for triggering machine and process automation. PLCs are created with input points or modules, output points or modules, and CPU.
- CPU interprets, processes, and applies instructions and mostly from hardware and software programs operating on devices. The CPU does arithmetic, logic, and other operations for transforming data input into accurate information output.
- The CPU executes the PLC program, and for running the PLC program, the CPU interfaces with the unit’s other components.
- PLC and industrial computers comes with CPU with input and output units and memory. But in PLC processors is lower power and made for executing repetitive logic style operations having dedicated calculation unit
- The main components of PLC are central processing unit (CPU), a power supply, a mounting rack, read-only memory (ROM), (RAM), input/output (I/O) modules,and a programming device.
That all about the CPU of PLC and everything mentioned in this tutorial. If you have a query can ask in the comments thanks for reading.







Can you please explain difference between processor and CPU? I thought they are same
Processor is PART of the CPU. Thus a CPU can have more than one processor.
can you explain what is the communication processor of plc and how do they work