 Hi friends, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we are gonna have a look at Introduction to Induction Motor. In 1824 French nationalist scientist Francois Arago found the phenomena of the rotatory electromagnetic field. That is recognized as Arago’s rotation. After almost fifty-four years of Francois’s work another scientist of America, Walter Baily proved this concept by physically on and off the switch, with the first time the base of the induction motor was created. The first induction motor was invented by an electrical engineer of the Hungry Otto Blathy, this motor was working on the 2-phases and do not have commutators.
Hi friends, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we are gonna have a look at Introduction to Induction Motor. In 1824 French nationalist scientist Francois Arago found the phenomena of the rotatory electromagnetic field. That is recognized as Arago’s rotation. After almost fifty-four years of Francois’s work another scientist of America, Walter Baily proved this concept by physically on and off the switch, with the first time the base of the induction motor was created. The first induction motor was invented by an electrical engineer of the Hungry Otto Blathy, this motor was working on the 2-phases and do not have commutators.
After Blathy’s invention, in 1885 the Galileo Ferraris (who was an engineer of Italy) and Nikola Tesla (an engineer of America) invented the three-phase induction motor, it was also without the commutator. After both scientists’ inventions induction motors became very common to our use and different companies start to manufacture different motors with different construction techniques. In today’s post, we will have a look at its construction, working, parts, and other terms of the induction motor. So, let’s get started with an Introduction to induction motors.
Introduction to Induction Motor
- The alternating current motor that uses the phenomena of electromagnetic induction to produce the current and flux in the rotor to produce torque is recognized as the induction motor. It is also is known as the asynchronous motor.
- Due to the use of the phenomena of electromagnetic induction (this phenomenon depends on Faraday’s law), there is no electrical connection between the rotor circuitry and stator circuitry of the motor like the transformer.
- There are 2 main types of induction motors according to the construction of the rotor of the motor, The first one is the squirrel cage motor because its rotor structure is like the squirrel and 2nd wound rotor motor.
- In industries, homes or for power generation purposes the 3-phase squirrel induction motor is mostly used, due to its reliability, less cost, and self-stating properties.
- The induction motor that has a Single phase is used for the light load, so it is mostly used in houses, like fan motors.
What is Synchronous Speed
- It is the speed of the revolving magnetic field in the stator of the induction motor.
- Synchronous speed depends on the number of poles of motor and the frequency of input voltages
- The formula of synchronous speed is:
Ns =120fe/P
- In this equation Ns represents the synchronous speed fe is frequency and P is no of poles of the induction motor.
- The rotor speed of the induction motor is always less than the synchronous speed, so the motor always runs at a speed less than the synchronous speed.
- The revolving field in the static part of the motor will caucus flux change in the rotor which causes it to move, with a speed less than the synchronous speed.
What is Slip
- Slip can be explaining as it is the difference between the two speeds. The first one is the speed of the rotatory magnetic field and the other is the induction motor rotor speed of rotation.
- Rotor speed is less than the speed of the rotatory magnetic field, which also known as synchronous speed (Ns).
- Slip is measured in percentage its formula is given as.
% Slip = (Ns-N)/Ns x 100
- In this equation, the Ns is the speed of the stator’s field and N is the speed of the rotor.
- The value of the slip will be ‘0’ when the motor is working at the synchronous speed and will be ‘1’ when the motor is stopped or not working.
- Slip is a very important factor in the operation of the induction motor as the torque of the induction motor depends on the slip.
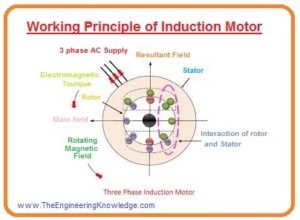
Working Principle of Induction Motor
- The main working of the induction motor depends on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
- When the alternating current is provided to stating part of the either synchronous or induction motor, it produces the rotating magnetic field in the stator of the motor.
- The speed of the rotating of the rotor is equal to the field speed in the stator in the synchronous motor so it called synchronous but in the case of the induction motor, the speed of rotor rotation is less than the revolving magnetic field.
- Like the transformer function, the field in the stator also produced current in the rotor due to the changing of the flux.
- This current produces the magnetic field that interacts with the field of the stator.
- According to Lenz’s law, the direction of the field in the rotor will be opposite to the stator’s field direction. As Lenz’ law says that any effect opposes its cause.
Power Factor of Induction Motor
- The value of the P.F of the induction motor depends on the load connected with the motor, if the motor is connected with the full rated load its P.F will be from 0.85 to 0.95, and if there is no load is connected with it, its power factor will be 0.2.
- In some certain cases if its power factor is not for the working situation it can be improved by connecting capacitor banks with the motor.
What are the Parts of the induction Motor
- There are two main parts the induction motor first one is the stator which is the static part of the induction motor and supply voltages are provided at those parts.
- The second main part induction motor is the rotor, it is the rotating part of the induction motor.
- Now we discuss these two main parts and some sub-parts of induction motor with the details.
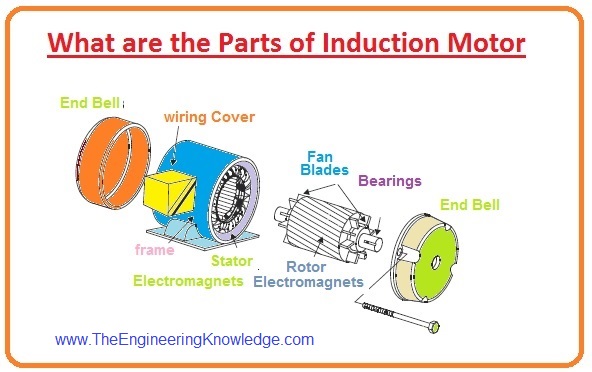
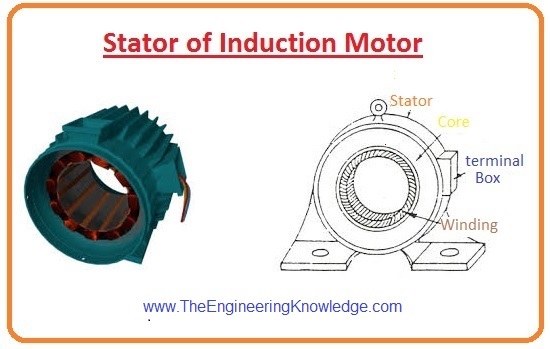
Stator of Induction Motor
- The stator is the static part of the induction motor, at this part revolving magnetic field is produced when supply is provided at its point.
- The revolving magnetic field of this part connects with the rotor and generates a field in this part (rotor) and it starts to rotate.
- The stator is created by cast iron material, and it has different slots to carry the stator wingdings.
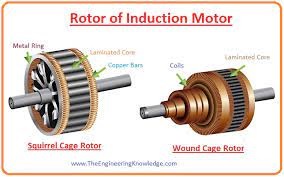
The Rotor of the Induction Motor
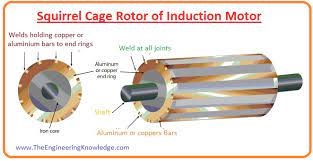
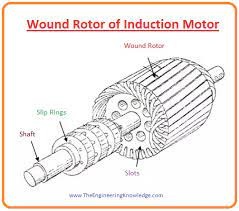
- The rotor is the revolving part of the induction motor. There are two types of rotor which are used in an induction motor. The first one is the Wound rotor and the other is a squirrel cage rotor.
Squirrel Cage Rotor
- This rotor is known as squirrel cage because its construction is like a squirrel. Its shape is similar to the cylinder which has laminated slots as a conductor.
- Every slot consists of copper (Cu), Aluminum (Al), or other conductive material, but it mostly consists of aluminum.
Wound Rotor of Induction Motor
- In this kind of rotor, windings are linked with the exterior resistors by the slip ring.
- By varying the value of resistance, we can vary the torque of the motor.
- Wound rotor induction motor can start its operation by the less starting current, by introducing higher resistance (R) in the rotor circuitry, when the motor rushes, the resistance (R) can be reduced.
Types of Induction Motor
- There are two main types of induction motors one is single-phase induction motor and the second is a three-phase induction motor.
- These two motors are further divided into many types.
Single Phase Induction Motor
- Single-phase motor has a single-phase winding this winding is wound on the stating part of motor and its cage winding is wound on the motor’s rotating part which is rotor.
- When a single-phase is applied to this motor then the revolving magnetic field is created.
- There are many types of single-phase induction motor.
- Split-Phase Induction Motor
- Shaded Pole Induction Motor
- Capacitor Start and Capacitor Run Induction Motor
- Capacitor Start Induction Motor
Three-Phase Induction Motor
- Three-phase motors are a self-start and as we studied in a single-phase induction motor article it need capacitors to start its operation.
- In our industries and household, 3 phase induction motors are used.
- This motor is further divided into 2 types first one squirrel cage and other is wound rotor.
- Squirrel cage motors are generally used due to their rugged construction and simplest enterprise.
- Wound rotor motor needs exterior resistances to have higher initial torque.
Induction Motor Features
- The assembly of the induction motor is very simplest.
- It is a less costly motor and its repairing cost is very less.
- It is highly reliable and has an adequately higher ability.
- There is no need for a special motor to start an induction motor like the synchronous motor.
- In our industries and in households it is mostly used.
Applications of Induction Motor
- There is a lot of application of induction motors. It is the most commonly used motor in our houses and industries.
- It is used in different pumping devices.
- It is used in compressors.
- An induction motor is used in little fans.
- It used in different juicer machined.
- Induction motor is also used in toys and robotic devices.
- It used in Higher-speed cleaners
- It used in Electric razors
- It also used in different Drilling machines.
Induction Motor Advantages
- There are many advantages of the induction motor which is mentioned here in detailed.
Less Cost:
- Induction motors are less expensive than other motors like direct current and synchronous.
- It is less expensive because its construction is very simple. Consequently, these motors are overpoweringly favored for static speed submissions in manufacturing and for local submissions where alternating current line power can be effortlessly linked.
Less Repairing Price:
- The repairing cost of the induction motor is very less. This is due to that its construction is very simple.
Easy to Operate:
- The working of induction motors is very modest because there is no need for a special motor to start it.
- Induction motors are self-starting motors. Which reduces its starting process construction which is needed in other motors.
Speed Variation:
- The speed alteration of the induction motor is almost persistent. The speed classically fluctuates merely by an insufficient percent.
Higher starting torque:
- The starting torque of this motor is very higher which makes it the best choice for heavy loads.
- In three-phase inductions, motor the starting torque is self-starting while in case of a single-phase induction motor there is no self-starting torque. It needs some other devices like starting a winding or capacitor to start its operation.
Durability of the Induction Motor:
- The additional main benefit of an induction motor is that its strength or durability. Which marks it the perfect apparatus for countless usages.
- Due to this feature, it works for many years without any serious damage.
Induction Motor Disadvantage
- As we know the speed of an induction motor is contingent on the frequency of the AC which energies it, and works at a constant speed till we usage an adjustable frequency driver.
- The simple induction motor is heavyweight.
It is a detailed and comprehensive article about the induction motor, I have explained each everything about the induction motor. If you want to know something more about it ask in comments. I will explain you more about it. See you in the next tutorial of the three-phase induction motor. Take care until the next tutorial.
You can also read some related articles to the induction motor. That is described here.
- Introduction to Induction Motor
- Introduction to Three Phase Induction Motor
- Equivalent Circuit Induction Motor
- Induction Motor Torque-Speed Characteristics
- Variations in Induction Motor Torque-Speed Characteristics
- Power and Torque in Induction Motors
- Induction Motor Design Classes
- Induction Motor Design
- Equivalent Circuit of Induction Motor
- Maximum Pullout TOrque of Induction Motor






Thanks for the information, nice article,