 Hello, friends, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, I am going to explain Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator. The synchronous generator is such a device that transforms mechanical energy into the electrical energy delivered by the prime mover of the generator. It is also known as an alternator. It is called a synchronous generator because its rotation speed is equal to the rotating speed of the field at the stator of the generator called synchronous speed. In this generator, an external supply is provided to excite the generator which is the reverse of the induction generator. For excitation, the external DC source is connected to a synchronous generator.
Hello, friends, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, I am going to explain Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator. The synchronous generator is such a device that transforms mechanical energy into the electrical energy delivered by the prime mover of the generator. It is also known as an alternator. It is called a synchronous generator because its rotation speed is equal to the rotating speed of the field at the stator of the generator called synchronous speed. In this generator, an external supply is provided to excite the generator which is the reverse of the induction generator. For excitation, the external DC source is connected to a synchronous generator.
In today’s post, we will have a look at another type of synchronous generator called a permanent magnet synchronous generator. In this generator, there is no need for a separate DC source for the excitation of the generator. We will describe the working principle, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and some other related parameters of this generator. So, let’s get started with the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator.
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator
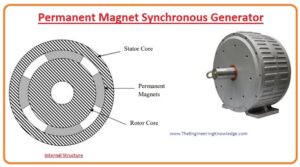
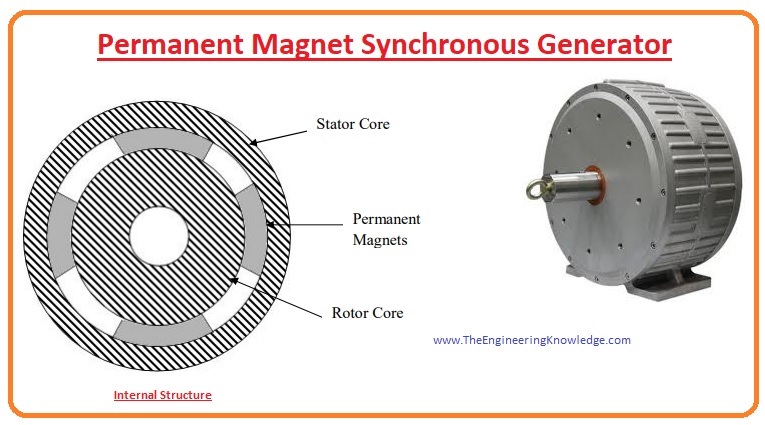
- The permanent magnet synchronous generator is called so because in this synchronous generator, excitation is provided with the permanent magnet instead of the external excitation source.
- Its rotor consists of the permanent that generates a field for excitation and replaces the external supply source for the generator.
- In most of generation power plants, the synchronous generator is used. In steam turbines, hydro turbines, and in gas turbines synchronous generator is used.
- Like other generators, the physical structure of this generator is the same it also consists of the rotor which also comprises of the permanent magnet with the shaft connected with it.
- Like the stator of other generators, this generator also has a stator that protects the internal structure from the exterior environment.
- In a permanent synchronous generator, there is no need of slip rings and carbon brushes, which makes the machine less expensive, and lightweight, and maintenance of the generator also decreases.
- But in high-rating generators, large-size generators are used to make machines somewhat expensive and increase the price.
- The generator attached to the power electronic conversion circuitry can work at less speed and so there is no need of the gearbox.
- The presence of gearboxes increases the price, energy losses, and cost of repairing the generator but without the gearbox price and weight of circuitry decreases it is also the best option for offshore applications.
- With the direction of flux lines, the permanent synchronous generator is divided into three categories: the radial flux permanent magnet synchronous generator, the second one is axial flux permanent magnet synchronous generator and the transverse flux permanent synchronous generator.
What is Synchronous Speed
- PMSG is called synchronous generators since the voltage produced frequency in the stator or armature calculated in the hertz is directly proportional to the rotation cycles of the rotor.
- The formula to find the synchronous speed is 120 (fe/P).
- In this equation, the fe is the frequency of the voltage induced at the stator.
- P is the no of a pole in the generator.
Working Principle of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator
- The working of the PMSG depends on the field produced by the permanent magnet attached to the rotor of the generator for the conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Like synchronous generators in PMSG, there are two types of windings first one is the armature that is wound on the stator and the second one is the field winding that is wound on the rotor.
- At the generator’s stator, 6 soils of copper and windings are wound and fixed at their respective places.
- The rotor that has a permanent magnet is connected to the bearing rotating on the shaft. In this generator, there are 2 rotors; the first one is behind the stator, and the second one is at the exterior side.
- Both of these are connected through the long studs moving by the hole in the stator.
- The blades are also surfaced on these studs that connect the rotors.
- These blades rotate the rotor for the production of electrical energy.
Applications of Permanent Synchronous Generator
- These are some applications of the permanent magnet synchronous generator.
- It is used to provide the power for the excitation of the high-rating synchronous generator.
- During the short circuit, these generators provide the power to the generator connected in the system to maintain the required voltage for the system.
- It is also used in such power generation systems where wind turbines are used.
Advantages of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator
- reliability
- compact size
- loss reduction
- higher power density
- optimal efficiency
Disadvantages of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator
- Permanent magnet generators (PMGs) or alternators (PMAs) do not need a DC supply for the excitation circuit, and not they needed slip rings and contact brushes.
- The main disadvantage is that there is air gap flux is not controllable so the voltage of the generator is not easily regulated.
Difference between a permanent magnet motor and a permanent magnet synchronous motor?
- AC motors are not used without VFD for driving the pump or fan but are connected with variable frequency drives in the pump system or fan system for enhancing system efficiency. Permanent agent synchronous motor needed drive for operation.
Construction of Permanent Magnet Generators
- This generator comes with 3 main parts stator, rotor, and air gap. The air gap exists between the stator and the rotor. The air gap works as a path for the transfer of magnetic flux from the rotor to the stator and controls direct direction between the rotor and stator
The difference between a permanent magnet alternator and a regular alternator
Contrary to car alternator that uses field coils that energize through current and turn on or off in a charging system for regulating voltage permanent magnet-operated alternators do not have features to on and off.
Faqs
- The permanent magnet synchronous generator uses permanent magnets on roots rather than an external excitation source. it comes with a simple design without slip rings or brushes. These generators are used with wind turbines, gas turbines, and hydro turbines.
What is the working principle of a permanent magnet synchronous machine?
- Working of PMSM based on the rotating magnetic field of the stator and constant magnetic field of the rotor. The permanent magnets are used as rotors to make constant magnetic flux, work, and lock at synchronous speed. These motors are like the brushless DC motors.
What is the purpose of using a permanent magnet in synchronous motors?
- Permanent magnet synchronous motors are used for high-performance and high-efficiency motor drives. High-performance motor control has featues of smooth rotation over a complete speed range of the motor, full control for zero speed, and fast acceleration and deceleration.
What is the permanent magnet synchronous motor control method?
- Use a field-oriented control method for controlling the speed of 3 3-phase permanent magnet synchronous motors. The FOC needed rotor position feedback that gets through the quadrature encoder sensor.
What is the working principle of PMG?
The permanent magnet is configured on the driven side of the generator shaft. PMG provides isolated power to AVR when shafts rotate. The AVR uses more power when provides a non-linear load like the starting of motors.
How does a PMSM work?
- The permanent-magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) comes with magnets configured in rotors for generating a constant magnetic field. The stator has windings connected with AC supply to generate the rotating field.
What are the applications of permanent magnet synchronous machines?
- Permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) comes in different uses such as vehicles, robots, servo systems, and aerospace applications due to its simple structure, and high energy density
Related posts
Synchronous Generator Equivalent Circuit
Synchronous Generator Phasor Diagram
Synchronous Generator Power and Torque
Synchronous Generator Parameters
Synchronous Generator Operating Alone
Synchronous Generator Parallel Operation
Synchronous Generator parallel with Large Power system
Synchronous Generator Parallel with same Size Generator
Synchronous Generator Capability Curves
Synchronous Generator Transients
So, friends, that is the detailed post on the permanent magnet synchronous generator I try my level best to simplify this article for you and explain every parameter related to the generator. If you have any further queries about this post as in the comments. I will guide you further. See you in the next tutorial. Thanks for reading.





I like what you guys are usually up too. Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I’ve included you guys to blogroll.
Hello, Great to read your articles and discussions about Permanent Magnet Generators. Thank you for those.
I am an “inventor” with a multitude of practical and theoretical skills.
I am building a micro hydro water turbine in the hills to produce 3 – 5 Kw of electricity off grid.
The hydraulic system is in place and I have purchased a three phase 380v Permanent Magnet Alternator. The system is to run into purpose designed house heating system consisting of a 1.5kW heat pump and switched domestic heaters. These were to 240v. Single phase to be derived from rectified three phase to 380v DC into a 3 and 2 kw sine wave inverters. to 240v AC.
So I need controllers. to maintain the speed of PMA rotation to the given voltage output.
Then the challenge for the design. Resistive load present no real problem but the heat pump compressor will present on starting- loading issues particularly if in single phase.
So now I am thinking about using a three phase compressor. (A local refrigeration company are to construct a bespoke machine).
If I stay in three phase I will have less losses and the system should be the most resilient to the high milli second loading currents and not stress the sine wave inverter.
If I were to change generator to use a synchronous induction generator with AGC the output voltage and frequency would be automatically controlled and maintained.
But I already have the PMA (suitable for a wind turbine etc) which is classic in internal wiring configuration Star / Delta.
So thanks for reading the long introduction. So at last here is the real question.
Can this alternator be controlled with any kind of constructed AGC with feed back to maintain the frequency as well as the output voltage particularly in the miili-second compressor start up times.
I don’t think the speed variation controller that I will build to switch solid state relays to the resistive loads will react fast enough due to the flywheel effects of the hydraulic system.
I really welcome your advice if you can.
Many thanks.
Very interesting, I need a generator domestic use to provide dc generation supplying a battery pack holding a 20kw capacity via inverter. Where can I buy these ? Any different sizes?