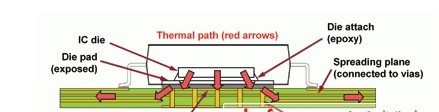
Hello readers, welcome to the new post. Here, we will learn PCB Heat Dissipation Techniques. Electronic devices are important to use. From mobile phones to laptops and complicated machines, PCB boards are used as building blocks of devices. However electronic components come in small sizes and increasingly difficult to manage heat due to complex structure. In this post, we will discuss different PCB heat dissipation methods mostly used in electronic devices and projects. So let’s get started with PCB Heat Dissipation Techniques.
Introduction
Printed circuit boards are the main component of electronic devices that provdies working conditions for the interconnection of electronic components. These components are high power generated high heat. Heat causes operation issues, reduces working life, and affects the structure. To avoid these problems, there is different dissipation technique used to make sure the board work in proper conditions
Understanding Heat Generation in PCBs
Heat is a natural byproduct of electrical resistance and power dissipated by electronic components. where and how heat is produced in the board is the first phase in effective heat management. Components like voltage regulators, microprocessors, and amplifiers are the main sources of heat
Conduction: Spreading the Heat
It is a method to dissipate heat. It uses thermal conducting, such as copper, to spread heat from hotspots. Accurate configuration of copper traces helps to dissipate heat on board
Convection: Cooling Through Air
It is based on the condition of air to carry heat from the board. Fans and heat sinks are used here. Accurate airflow and effective heat sink design are good for an effective convection cooling process
Radiation: The Invisible Coolant
Each particle released infrared radiation also board. Boad design with radiation should increases their featues to remove heat in a neighboring area.
Heat Sinks: Keeping it Cool
There is a heat sink used for heat dissipation from high-power components. Metal structure provdies a larger area for heat transfer and paired with fans to have good cooling. Correct side and mounted heat sinks helps to reduce overheating.
Thermal Vias: Conductive Pathways
Thermal vias are small size holes of boards that flow heat from one layer to another. Best for conducive heat away from components that are mounted on board
PCB Material Selection
The use of board material affect heat dissipation. FR4 and metal core pcb board have different thermal features and are used based on certain projects need
Component Placement and Layout
The component configuration on board affects heat dissipation. Putting heat generated component in the proper way decreased chances to overheating.
Optimizing Traces and Planes
Design of copper traces and ground planes affect board features for heat dissipate. Wider races and larger planes can handle high heat from component
Thermal Analysis Software
Advanced thermal analysis software tools stimulate heat flow in the board. These tools optimize desing to have high heat dissipation
WHY HEAT IS A PROBLEM IN PCBS
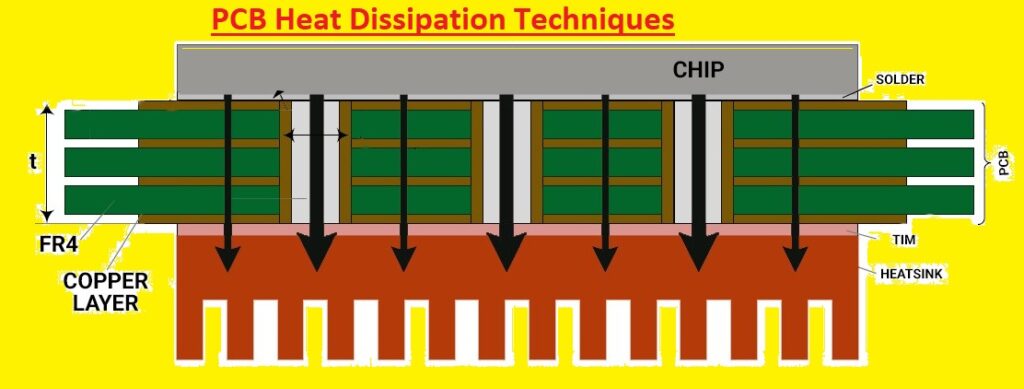
Heat is an issue in PCBs since it can cause a different problem, like
- When components have temperature their properties change, which results in less operation or damage. Such as, solder joints that connect a component to older ones get weak structures and broken, and the plastic insulation of component get melted
- The board layer is made with material tha expands and contracts with temperature variations. If the board is at a high temperate can deform and damage component
- High temperate increases the process of the board, that results in premature failure.
- The board becomes overheated and catches fire. it is a risk for boards that are used in high power uses or have high-temperature
How to dissipate heat in PCB
Thermal Via Arrays
it can be board converted in a board heat sink by connecting an array of vias on copper-filled areas. it helps to float away from component to copper areas and dissipate from vias. Normally, thermal vias array is used for power managing modules and components with thermal pads.
When connecting the thermal via array, note that it needed a certain value of dia about 0.1mm for heat dissipation properly. Also, make sure vias are not thermal removing pads but padded holes connected to copper areas. Increases the number of thermal vias to heat dissipate
Use Wider Traces
Copper traces cause high current and heat as a result, So it is good to increase width traces to increase heat dissipation to air. With this minimize thermal resistance of traces and minimize heat areas
3. Use Heatsinks and Cooling Fans
Passive heat dissipation methods such as thermal vias array are enough if the board creates high heat that dissipation. In these conditions, add heatsinks and fans.
Heatsinks are connected that produce heat highly normally voltage regulators, MCU, CPU, and power transistor. Heatsinks are connected to the board or left open. In the enclosed design cooling fan is connected to displace hot air in environment
What are PCB Heat Dissipation holes?
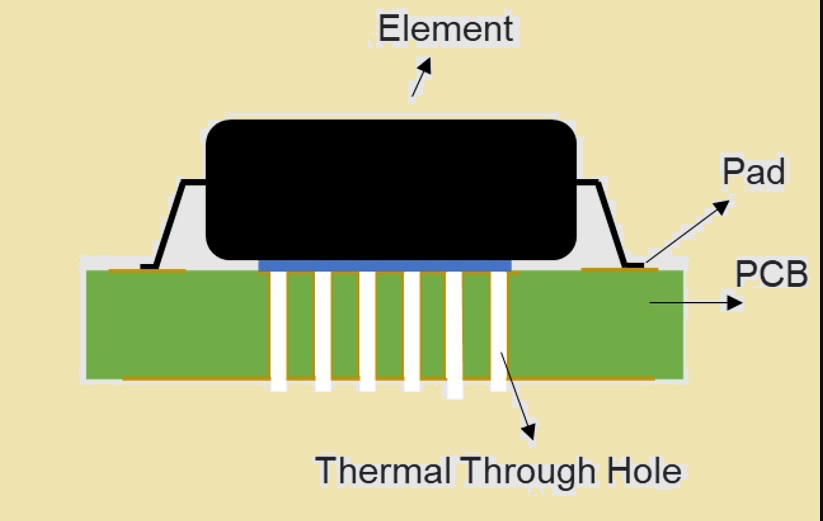
PCB heat dissipation holes, known as PCB thermal vias, are employed to dissipate heat at the back end with the use of through holes that pass in the board. They are connected as directly as possible to the generating component.
Thermal vias work by offering a direct path to heat flow from the component to cool backside of the board. Copper in vais operate heat away from component and air on the backend of the board helps to reduce heat.
Therma vias are best to increase the heat dissipation of the board. They used other heat dissipation methods such as heat sinks and fans
parameters to consider when designing PCB heat dissipation holes
- Size and number of holes: The number of holes and size based on the heat that dissipated
- location of the holes: Holes should place directly under or close to the generating component
- material of the holes: Holes should made with materials that have high thermal conductivity such as copper.
- filling of the holes: In holes, high thermal conductive material filled like solder or epoxy for heat transfer
Seven tips for heat dissipation of PCB
- Accurately connect components on board. That makes sure hat dissipates smoothly and effectively. Avoid putting heat generating component to close each other and ensure there is enough airflow.
- Note that there is accurate airflow close to the board. it can be done with the use of fan or heat sink. This board has open spaces and vents.
- Use convection air to dissipate heat. It is done by putting the board in a good ventialted area for using a fan.
- The use of heat-generating components at the point where heat disaiption is good. Such as we need to put it close to the edges of the board or lower of the board
- Apply heat-emitting degrees of each component for board design. It will avoid overheating components.
- Use correct wiring design to dissipate heat. That uses thick traces and vias preventing bends in wire.
Faqs
-
What are the methods of heat dissipation?
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
- Evaporation
- Phase change
-
What is the heat dissipation process?
- The process of heat dissipation involved low heat from hot bodies to cold body..
-
What is the application of heat transfer knowledge in the engineering field?
- Heat transfer knowledge is used in different engineering fields, like
- Electrical engineering
- Mechanical engineering
- Chemical engineering
- Civil engineering
- Aerospace engineering
- Automotive engineering
- Industrial Engineering
- Heat transfer knowledge is used in different engineering fields, like
-
What is the purpose of heat dissipation?
- Heat dissipation reduces heat from components to have proper working of the system
-
What is the process of dissipation?
- It is a method to spread heat. so it continue to flow to the system smoothly not affect certain point
-
What materials are used for heat dissipation?
- Materials that are good at heat dissipation are:
- Metals such as copper and aluminum
- Graphite
- Ceramics
- Plastics
- Materials that are good at heat dissipation are:
-
What is the unit of heat dissipation?
- The unit of heat dissipation is the watt (W).
-
What is the formula for heat dissipation?
- The formula for heat dissipation is:
- Q = ∆T x R
- Q is the heat dissipation rate, where Q is the heat dissipation rate ∆T, the difference between temperatue of hot and colored bodies, and R is thermal resistance.
- The formula for heat dissipation is:
-
What is the heat dissipation rate?
- Heat dissipated per unit time is the rate of heat dissipation
-
What is the heat dissipation time?
- When the system is heated time taken to reach a steady state condition
-
What is the heat dissipation limitation?
- The heat dissipation limitation is the highest heat value that can dissipate.