Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will have a look at What is a Digital Voltmeter. Electrical measurements are commonly made with digital voltmeters, which offer a higher value of correctness and simpler use than devices. In this post, we’ll look cover digital voltmeters and related parameters. So let’s get started with Introduction to Digital Voltmeter
Introduction to Digital Voltmeter
Accurate measurement of electrical parameters is important. Digital voltmeters are used to provide correct results of voltage measurement. They are now considered as best tool for industries such as engineering, electronics, power production, and automobiles. A voltmeter is a device that is used for measuring the potential difference between two points.
The voltage measured can be AC or DC. Two types of voltameter are normally used analog and digital. Analog voltmeter comes with a dial and needle-moving accordion to measure and show value. Analog meter replaced to digital voltmeter based on features. Digital voltmeter shows value of AC or DC voltage measured in discrete numbers then pointer deflection on continuous scale as shown in analog.
What is Voltmeter
The voltmeter also called the voltage meter that is device measures the voltage or potential difference between two points of the circuit. Normally voltmeter is employed for AC curent measuring or circuit. Radiofrequency voltage is also used for measuring with specialized voltmeters.
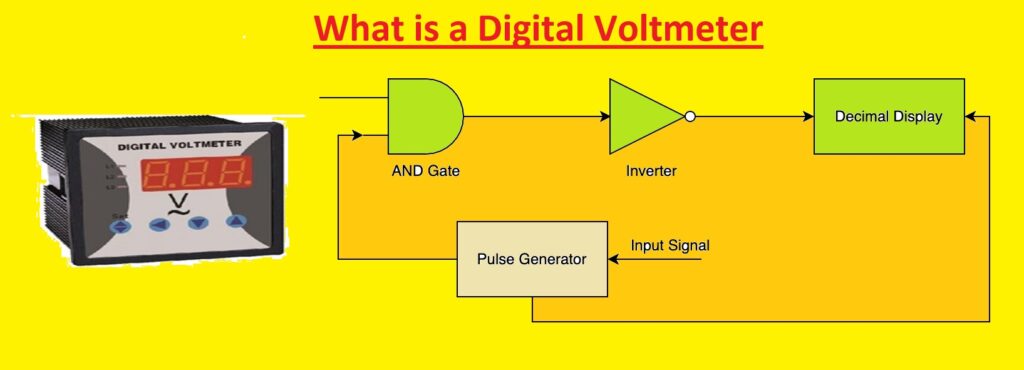
How Does a Digital Voltmeter Work?
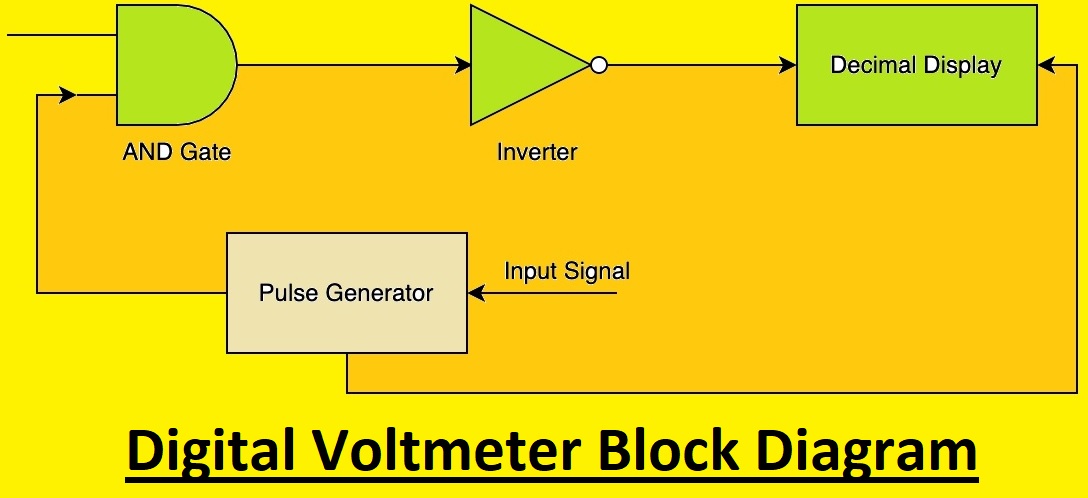
- In its working principle input signal is given as input to the pulse generator. The pulse generator produces rectangle-shaped pulses having the same width as the input signal.
- The output of the pulse generator works as input for the AND gate and another input of this gate is pulse series. it makes a positive-triggered switch resulting in a triggered sequence of pulses with the width same as the produced pulse of the pulse generator.
- The output of the AND gate that is positive triggered pulses is given to the inverter that inverts output of the AND gate.
- The output of the inverter is given to the counter at the input point that counts total pulses and the duration between pulses.
- in the last accurate output is shown on LED and the reading value in volts is shown.
Digital Voltmeter Block Diagram
The voltmeter measures voltage values in volts, millivolts, and kilovolts. For measuring voltage voltmeter is connected with the parallel combination. This configuration is used since the same voltage exists in a parallel combination.
The voltmeter also comes with a high value of inner resistance. it is added since used for measuring the potential difference between circuits’ two points. The current of measuring devices is the same. in simple words, the high resistance of the voltmeter impedes the current flow. It helps to get an accurate value of voltage.
The main parts of a digital voltmeter are:
- Input: At this point voltage measured connected
- Attenuator: It reduces voltage value at input to a value that is in the range of the analog-to-digital converter.
- ADC: The ADC converters analog input to digital signal
- Digital display: The digital display has input volts in digital format.
The operation of a digital voltmeter is explained here
- Input volts are provided to the input terminal of the meter
- The attenuator makes the value of input volts for ADC.
- ADC transfers the analog input voltage to a digital signal.
- The digital signal is shown on the digital display.
What is a Digital Voltmeter?
Definition and Purpose
A digital voltmeter is an electronic device used to calculate electrical potential differences or voltage. It transforms the analog voltage signal into digital values and shows output on a digital screen or panel. Digital voltmeters have many benefits like faster response time, high accuracy, ease of reading, and advanced level features.
Analog Voltmeters Vs Digital voltmeter
| Feature | Analog Voltmeter | Digital Voltmeter |
|---|---|---|
| Display | Moving pointer across a scale | Numerical display on an LCD screen |
| Output signal representation | Potentiometric deflection | Digital |
| Types | true RMS reading, Average reading, sampling type | Ramp type and integrated type |
| Overload indication | No | Yes |
| Resolution | Lower | Higher |
| Programming | Cannot be programmed | Can be programmed |
| Sensitivity | Less | More |
| Speed of operation | Slower | Faster |
| Digitization of signal | Not required | Required |
| Measurement range | Fewer | More |
Types of Digital Voltmeters
Ramp-Type Digital Voltmeter
In this meter circuit produces an output signal in a ramp shape. Volterme is used for measuring such ram signal called Ramp type digital voltmeter. Timing is important for these signals this meter name due to the measuring ramped-up signals.
In this meter, voltage is measured by giving an unknown input signal to range and attenuation. Based on requirements signal is attenuated by amplification. The ramp generator generates a positive or negative ramp and the unknown signal is compared with it. The comparator compares the input signal with the ramp signal. if the input voltage is the same as the ramp voltage then gate is opened through the pulse and then the ramp signal becomes zero gate is closed. The tom between two occurrences is known as a gating time interval.
Integrating-Type Digital Voltmeter
This meter measures the accurate value of input according to constant time. This circuit normally uses a voltage-to-frequency converter device that operates on a feedback control system. The main featues of this device is that output from the integrator is compared with the fixed-level voltage used as a reference.
Dual-Slope Digital Voltmeter
it gets input voltage by integrating the input signal for a certain duration in one direction and then for the same duration in the opposite direction. By comparing the 2 integrator output values, it measures the input voltage.
Successive Approximation Digital Voltmeter
In this meter, the output of digital to digital-to-analog converter is taken with a certain unknown reference voltage. This meter can measure about 100 readings in one second. The voltmeter uses an amplifier for the selection of the required input voltage range and reduces noise that can casues distortion.
Applications of Digital Voltmeter
- it is part of labs and laboratories for measuring correct voltage value over different devices like resistors, diodes, and capacitors
- it is also used to measure unknown values. It helps to measure voltage and when voltage level is known we can measure the current in the circuit also.
- It is used for verification purposes such as in cathode ray tubes for verification of accurate values. it helps with circuit inspection.
- With use of the tree ammeter technique, 3 voltmeter is used for measuring power. it is used for measuring power factor at a certain load.
- it is used for prototype and circuit design. That helps to measure and verification of voltage at different points.
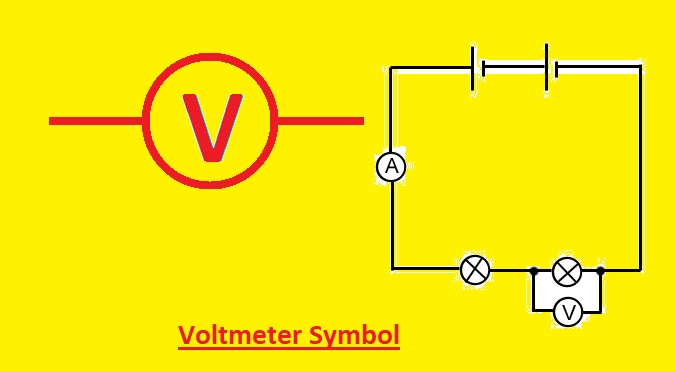
Symbol of Digital Voltmeter
A horizontal line with a V-shaped notch on the left side is the symbol for a digital voltmeter. With the proper unit, such as V for volts, the letter V is frequently used as a shorthand notation for voltage.
Digital Voltmeter Advantages
- It does not measure reading with a pointer, it reduces the chance of human error that is due to reading at an angle. it is a gross error and removed by giving accurate results
- it is a more reliable and stable device than an analog meter tha is unreliable for measuring values.
- its output is given to memory devices for storage use. it means we can store results obtained from the digital meters in flip-flops.
- It does not need any extra manuals for the use of the meter since it easily gets and check
- it is more durable than an analog meter and has correct readings without affecting different factors like atmosphere, temperature, and moisture.
Disadvantages of Digital Voltmeter
- it is more fragile than an analog meter and requires handling properly. it can get heated for long use and also has a chance of wrong reading.
- its speed is based on a digitizing circuit. it can minimize the operational speed of the voltmeter for reading.
- There is a certain threshold value for a digital meter and crossing that value can affect the meter.
- If there is fluctuation in the output digital meter not measures them and provides incorrect values for output
- its design is such that not measure transient voltage with the use of the device. So measuring transient spikes in this meter is not easy
Read our latest Electronic Guides:
What is 12v Digital Voltmeter Gauge
A 12V digital voltmeter gauge is an electronic instrument used to find the voltage in a 12-volt electrical system. it has a simple and correct technique to measure voltage value helps to have the correct function and condition of the system. it is made to operate for the system that has 12 volts voltage that is used in marine, vehicles, and recreational vehicles.
The working principle of a digital voltmeter gauge is based on internal circuitry and sensors to measure voltage. Connected to a 12-volt power source, the gauge measures the voltage signal and transforms it into a digital value for display.
This device uses an ADC converter to convert continuous analog voltage signals into discrete digital values.
Features of a 12V digital voltmeter gauge:
- Measures voltage from 8V to 16V
- 3-digit LED digital display
- Simple connection, easy to use
- Waterproof
- Widely used for cars, motorcycles, bikes, substation automation, distribution automation, test equipment, voltage regulator, etc
- Displays “LLL” when the voltage is less than the measuring values; displays “HHH” when the voltage is high than the measuring values
What is the symbol of the voltmeter and its uses?
The symbol for a voltmeter is a circle with a capital V inside. Voltmeters are used to measure the voltage, or potential difference, between two points of an electrical circuit.
What is the symbol of the voltmeter?
Voltmeters are represented as a circle with a capital V within. In electrical circuit diagrams, a voltmeter is represented by it. The locations in the circuit where the voltage is to be measured are connected in parallel to the voltmeter. The voltmeter has an extremely high resistance, thus it barely affects the circuit’s current.
What are the 2 types of digital voltmeters?
- True RMS DVMs: This meter calculates the voltage’s actual root mean square value. This DVM is the most precise.
- Non-RMS DVMs: These meters calculate the voltage’s average value. True RMS measurement is accurate, but this is commonly used and less expensive.
How does voltmeter work?
DC Voltmeter and Ammeter in Proteus
A device called a voltmeter is used to measure voltage, which is the difference in electrical potential.
This device works by connected in parallel combination with a circuit where voltage is measured. Voltmeter comes with high resistance so it does not affect the current of the circuit
A coil on the voltmeter is connected to the pointer. A magnetic field is generated when coils have voltage. The permanent magnet in the meter interacts with the magnetic field, moving the pointer as a result. The voltage of the coil determines how much the pointer moves.
What are the types of Voltmeters?
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Analog voltmeter | Has a needle that moves across a scale to indicate the voltage. |
| Digital voltmeter | Displays the voltage as a number. |
| Amplified voltmeter | Has a built-in amplifier that increases the voltage signal, it measures very low voltages. |
| High-impedance voltmeter | Has a very high input impedance, which prevents it from affecting the circuit it is measuring. |
| True RMS voltmeter | Measures the true (RMS) value of the voltage, which is the most accurate way to measure non-sinusoidal waveforms. |
What is the SI unit of the Voltmeter?
Volt (V) is the volt as defined by the SI. It bears Alessandro Volta’s name, an Italian physicist. The definition of a volt is the difference in potential between two points in a circuit that, in the absence of resistance, will result in the passage of one ampere of current.
What is the Formula for a Voltmeter?
The formula for a voltmeter is:
V = I * R
where:
- V is the voltage measured by the voltmeter
- I is the current flowing through the voltmeter
- R is the resistance of the voltmeter
What is Analog to digital convertor? How is it similar to DVM?
Analog to-digital converter is used for conversion of the analog signal in a digital signal with use of circuits. its working is like DVM since it converts analog input signal in a sequence of pulses.
What is the range of digital voltmeters?
The range of input voltage is from 1 to 1000 volts. it comes with an automatic range or an overload indication.
What are the characteristics of a digital voltmeter used in a typical digital multimeter?
The digital voltmeter is a voltage measuring device and when used in any device, it has voltage reading in number form without use of a pointer.
Conclusion
With their precision, usability, and different features, digital voltmeters have completely changed the method electrical measurements are done. it is commonly used in electronics, electrical engineering, automobile, and power generation and provides a higher value of improvements than analog voltmeters. Digital voltmeters are used as important tools in different fields because of their ability to deliver accurate voltage readings and user-friendly interfaces.
FAQs
Q1: Are digital voltmeters more accurate than analog voltmeters?
Yes, because digital voltmeters have more latest features and can provide exact numerical values they are typically more accurate than analog voltmeters.
Q2: Can we use a digital voltmeter to measure current and resistance?
Some digital voltmeters also provide current and resistance-measuring capabilities.
Q3: What is the advantage of using a digital multimeter instead of a standalone digital voltmeter?
Voltage, resistance, current, and other measuring operations are all measured in a single digital multimeter.
Q4: Can digital voltmeters measure both AC and DC voltages?
You can measure both AC and DC voltages with digital voltmeters,
Q5: Are digital voltmeters suitable for high-frequency voltage measurements?
Over their designated frequency range, digital voltmeters are not best for high-frequency voltage measurements. Accurate high-frequency measurements are made with oscilloscopes.
Explore Our Latest Articles: