 Hi, friends welcome to the new post. In this post, we will have a detailed look at Transistor Symbols. Transistors are the main component of electric devices that are used as amplifiers and switching components in circuits. The knowledge of transistor symbols is necessary for new users of transistors to have a details understanding of the circuits. In this post, we will cover the details of transistors, working, definition, and other parameters. So lets gets started with So let’s get started with Transistor Symbols.
Hi, friends welcome to the new post. In this post, we will have a detailed look at Transistor Symbols. Transistors are the main component of electric devices that are used as amplifiers and switching components in circuits. The knowledge of transistor symbols is necessary for new users of transistors to have a details understanding of the circuits. In this post, we will cover the details of transistors, working, definition, and other parameters. So lets gets started with So let’s get started with Transistor Symbols.
What is a transistor?
- The transistor is a semiconductor component that is used as an amplifier and switch in differnt projects.
- It comes with three terminal emitters, a base, and collectors. The voltage given to the transistor base pin defines the value of the current flowing through the transistor. Bae terminal works as a control like the tap.
- Bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs) are two main types of transistors. Each type of transistor with certain symbolic representation that is helpful in finding the type of transistor used in teh project circuit
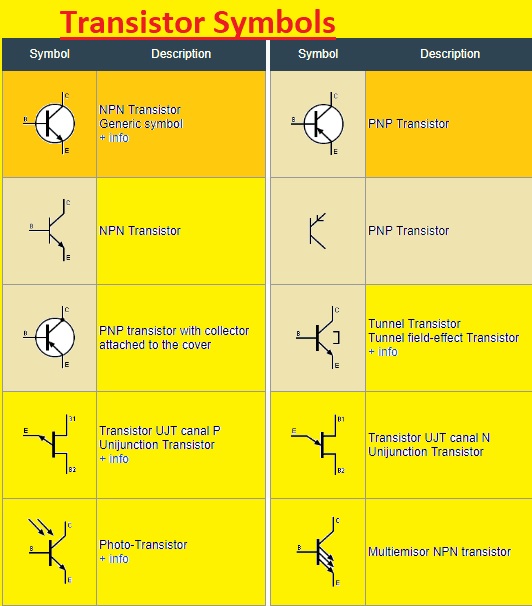
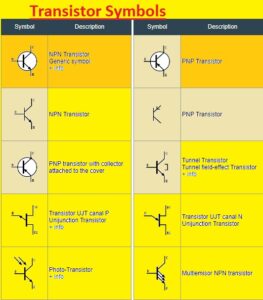
Transistor Symbols
- Every transistor comes with a certain symbol that helps to define the transistor features BJT and FET symbols make them different from each other here some symbols are listed
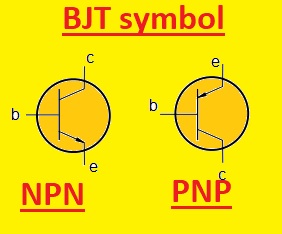
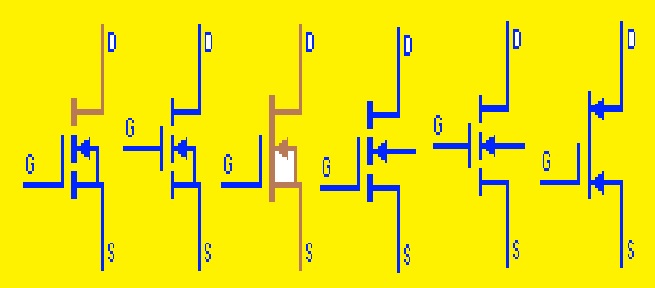
Bipolar junction transistor (BJT) symbol
- The emitter, base, and collector pins of transition that are added in the symbol of BJT. The line having a direction to the emitter is used to show the collectors and the arrow in towards the outer direction is used to show the emitter. The connecting emitter and collector is the base
- The main types of BJT are NPN and PNP transistors. The voltage needed for the transistor is defined on the basis of the polarity of the transistor also the current direction
Related Topics
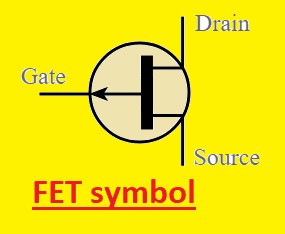
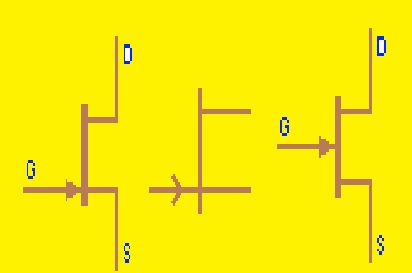
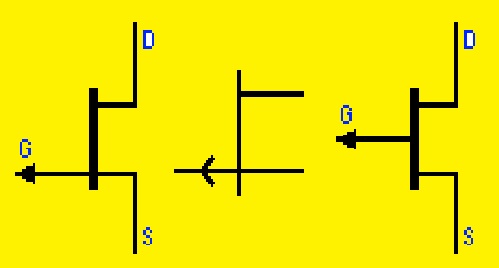
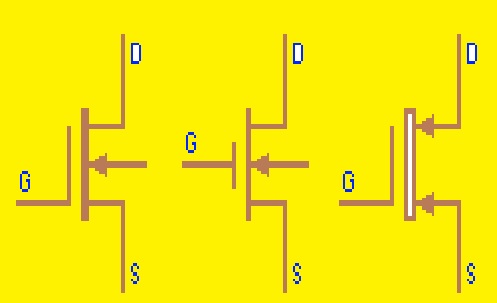
A field-effect transistor (FET) symbol
- The gate, source, and drain are the main pins of FET that are added in its symbol. The joining of the source pin and drain parallel to the channel denotes the gate. The drain is shown with an arrow that is moving outward from the channel and the source is shown with an arrow directed in the reverse direction
- The main types of FET are N- N-channel and P-channel. The types of FET define the voltage value required for biasing and the direction of the current
Terminals of Transistor Symbols
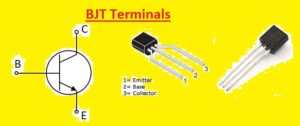
BJT terminals
- The emitter, base, and collector main pinout of BJT transistor. The power supply is positively connected with the collector and negatively with the emitter.
- The base works to control and regulate the flow of current in the transistor control circuit is configured with a base terminal that controls the current flow in the transistor
FET terminals
- Source, Gate, and Drain pinout of FET. The drain is attached to the positive battery and the source to the negative of the battery. The gate works as a control base in BJT controls the current in teh transistor and is connected to the control circuitry
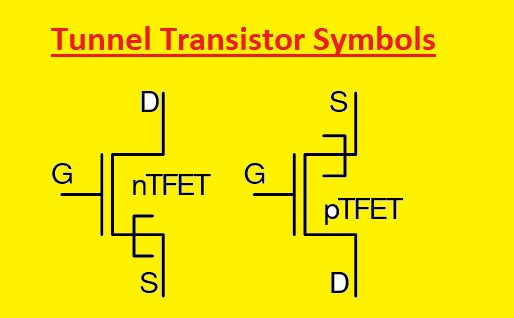
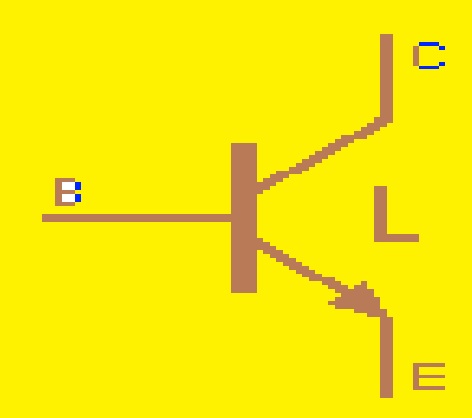
Tunnel Transistor Symbols
- The emitter and collector are two main parts of of tunnel transistor symbol. The base of the transistor is denoted as the direction for the emitter and other parts are used to show the transistor collector.
- This transistor does not have an accurately defined base part like another transistor. But the narrow part of semiconductor material that takes part in electron tunneling makes a separation between the collector and emitter..
- The symbol for a tunnel transistor can be seen here
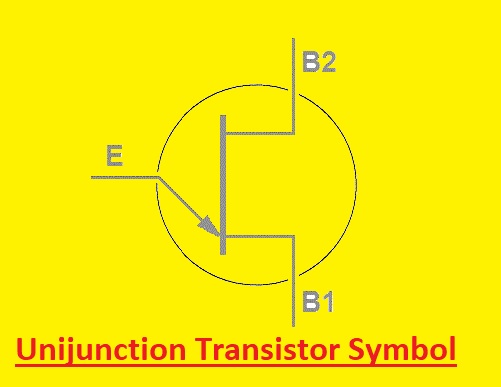
Unijunction Transistor Symbol
The emitter, base 1, and base 2 are the three main pinouts of the UJT symbol. Base 2 or B2 is shown with a line that joins base 1 and the emitter through a diagonal line that is connected with base1
The UJT symbol is here
It is good to note that the UJT symbol can vary based on teh type of transistor and manufacturer. To ensure sure accurate working of the transistor it is suggested to use the datasheet of UJT
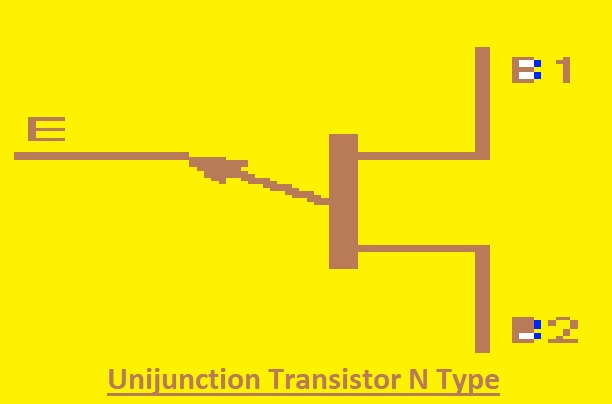
Unijunction Transistor N Type
A unijunction transistor is made with the use of light doped base having a highly doped emitter to make a single junction. It is called a double-base diode. The potential at emitter according to base control current in base. N-type UJT is created of light-doped P base and with a high-doped N-type emitter. They are used for triggering thyristors.
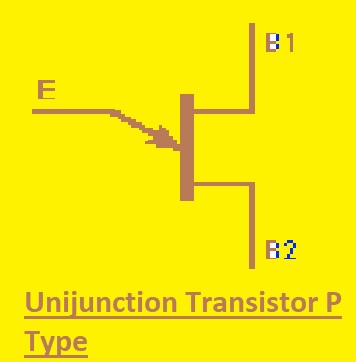
Unijunction Transistor P Type
It is made with a bar of light-doped N-type material having highly doped P-type close to base 2. Its working is like N-type UJT and voltage polarity is reversed.
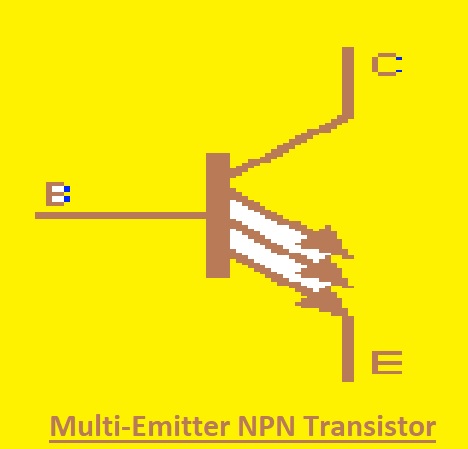
Multi-Emitter NPN Transistor
It is a special BJT that has many emitters. The emitters are independent of each other and the current through the emitter is based on voltage according to the base of the transistor. These transistors are used in TTl or NAND gates.
Schottkey NPN Transistor
It is made of a Schottky diode and transistor. The Schottky diode is connected between the base and the collector. It maintains the transistor from saturating through shunt high current. It helps in fast switching due to the time delay for removing stored charges in saturated mode.
JFET Transistor N channel
JFET or junction field effect transistor is a unipolar transistor since current flow is due to one carrier. JFET is voltage controlled, or current flow is regulated through voltage at the gate terminal. Voltage increases or reduces depletion region controlling current flow. The N-channel JFET comes with an N-type channel between the source and drain and the gate is created with P-type material.
JFET Transistor P channel
In a symbol of P channel JFET is denoted with an arrow pointing outwards. The P channel JFET is created with the use of P-type channel between the D and S pins and the gate is made with N material. P channel JFET switches off by maintaining a positive gate to source voltage.
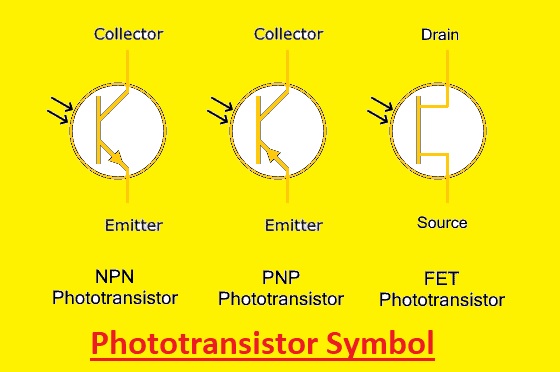
Phototransistor Symbol
- Its symbolical representation is like the conventional transistor and comes with arrows pointing towards the base. When light strikes the transistor it activates
The photo-transistor symbol is here
- On teh base of the manufacturer, the type of transistor direction of the arrow on the phototransistor can vary. So must check teh datasheet for a proper understanding of the transistor
Avalanche Transistor Symbol
The symbol of this transistor is like the regular transistor, but has a small arrow directed to teh collector. This arrow denotes the avalanche breakdown that exits in this transistor.
NPN Darlington Transistor Pair
it is a special transistor created with a connecting emitter of one BJT to the base of another BJT for increasing current gain and sensitivity. It can be created with an NPN or PNP transistor through the connection shown in the figure. The total gain of the Darlington transistor is multiple of gains individual BJT and the voltage loss is double at the base-emitter.
Sziklai Transistor Pair
This transistor is made with use of two NPN and PNP transistors in the Darlington pair structure. The main benefit of this design is that switch on with 0.7 volts and total gain is the same Darlington pair.
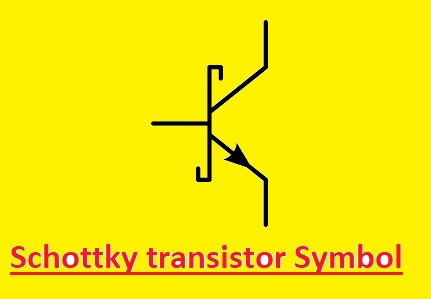
Schottky transistor Symbol
- A little arrow pointing to the collector is added in teh normal transistor symbol to make a Schottky transistor.
The Schottky transistor symbol is here
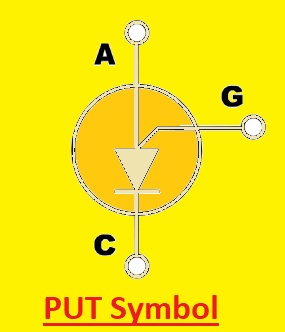
PUT Symbol
- The symbol of this transistor comes with two diodes facing each other having a gate terminal in the middle. The base of the transistor, gate terminal is shown through an arrow having directions from left to right. PUT is called UJT has four PN layer-like thyristors that operate like UJT if programmed with two outer resistors. It has anode, cathode, and gate terminal. Voltage at gate terminal switches PUT on and off when it crosses the cutoff level
The PUT symbol is drawn here
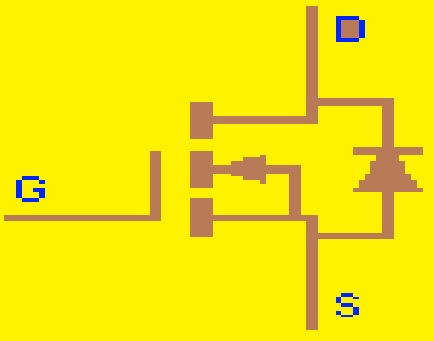
Depletion Type MOSFET
Metal oxide semiconductor FET is a field effect transistor whose gate is isolated from the current carrying channel so it is known as IGFET. It is voltage voltage-controlled curent device. The depletion MOSFET is normally ON at zero gate-source voltage. it switches off by applying positive or negative gate-source voltage for P or N channel MOSFET respectively.
Enhancement Type MOSFET
The E MOSFET does not normally conduct when gate-source voltage is zero. it turns ON by applying a positive gate-source voltage for N channel and a negative gate-source voltage for the P channel E MOSFET. The enhancement type is like a normal open switch and the deletion type is like a closed switch.
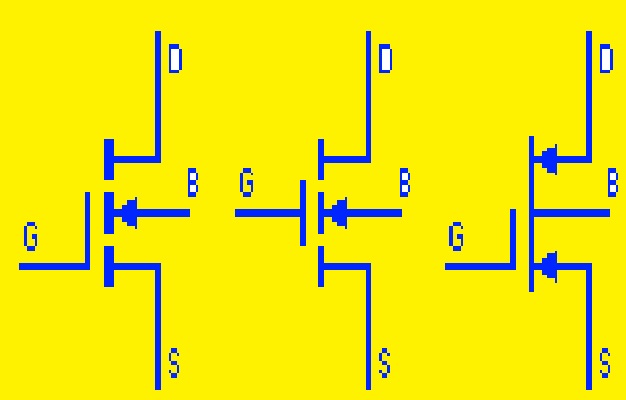
Enhancement Type MOSFET with Bulk
This type of enhancement MOSFET comes with 4 terminals. The extra terminal is called the Bulk or body terminal. it is not an input nor output pin but is used for grounding purposes. It is used internally connected with source pin that is released in symbol to show a schematic with less clunky wiring.
Logic Level FET Transistor
Logic-level FET transistors are made to be used with digital logic systems. They are used for switching heavy loads when provided with digital logic. Positive logic voltage normally is five volts and the gate source starts conduction at the highest current.
Operating Conditions of Transistor Symbols
- Biasing, amplification, and switching are the three different operating modes for transistors.
Biasing
- Set the dc voltage and curent values in a transistor circuit that process called biasing. Biasin is used to keep the circuit stable and ensure the transistor operates in a certain mode
Amplification
- With the use of a transistor as an amplifier, signal strength is increased. The simple input signal is proved to the transistor is amplification mode and the output is an amplified signal. The weak signal from a microphone or radio is amplified to a certain level that can operate a loudspeaker using this mode, which is used in audio amplifiers.
Switching
- it is a process that involves the application of a control signal to switch on and off the flow of current with the use of a transistor. IF working in switching mode transistor works as a switch and is on or off. In this mode power supply and digital logic circuits used
Transistor operating conditions
Here are the maximum rating and biasing conditions for 2N2222A are shown
| Parameter | Maximum Rating | Biasing Condition | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Collector-emitter voltage | 40 Volts | 12 Volts | |
| Collector current | 800 milliamperes | 100 milliamperes | |
| Emitter-base voltage | 7 Volts | 0.7 Volts | |
| Base current | 20 milliamperes | 5 milliamperes | |
| Power dissipation | 625 mWwatts | 200 millwattswatts |
Common Mistakes in Interpreting Transistor Symbols
- Defining the symbol of transistors can be difficult and new users face different errors. There is some confusion between the BJT emitter and collector which is a common error. Another error is that the current direction in FE is shown by the arrow shown in the symbol.
- it is good to define the structure of the transistor and features as circuit desing to have fewer errors
Advantages transistors
-
Advantage Explanation size and weight Transistors are small size devices and have less weight than vacuum tubes so they are the main part of small size devices Low power Transistors use less power as compared to vacuum tubes so they can operate for a longer duration Reliable it is a reliable component since can work for many years without any damage. Low cost They can be manufactured with less cost and also used in different devices due to less cost Versatile Nature it is used for different uses like amplifiers, switch circuits, and modulation due to its versatile nature
Disadvantages transistors
- They are affected by the high temperatures that can damage them
- it produced the noise and affected the working of devices where it used
- it can dissipate heat can cause thermal damage
- its manufacturing is complex and costly since needs the latest devices
Applications of Transistors
- it is used to amplify the weak signal to a strong signal so used in the microphone,
- It is used as a switch for on and off-circuit operation. so used to control the motor, lights system
- it makes the digital circuits like microprocessors and memory units
- it also made filters and oscillators that are analog circuits. It employed in industrial control systems
- it is part of motor controls and power electronic devices
To prevent errors that might harm your circuit, always study and comprehend circuit designs carefully. You should also double-check your understanding of transistor symbols.
Read Also:
- Difference between Vacuum Tube and Transistor
- Introduction to C945 Transistor
- Introduction to 2N2219 NPN Transistor
- 2N3702 Transistor Working & Application
- Introducing to BC556 Transistor: How It Works And Where You Can Use It
- What is PNP Transistor: How It Works and Its Applications
- Difference Between NPN vs PNP Transistor
Faqs
- What are the transistor symbols?
- The NPN transistor symbol has arrows from base to emitter. it means that current flows from collectors through the base in the emitter.
- What are 3 types of transistors?
- The transistor is divided into three types, BJT field effect, and IGBT transistor. The bipolar transistor is a transistor type that uses both electrons and holes for charge current.
- What are PNP and NPN transistors?
- BJT is divided into Npn and PNP transistors. The NPN transistor has two N-type semiconductors and one P-type. PNP has two P terminals and one thin N layer.
-
Why it is called a transistor?The transistor is a combination of transistor and resistance. It is due to tha transfer resistance from one point to another point of the device, or in other words resistance transfer. So it is called a transistor. It has high input resistance and low output resistance.What are the 2 main types of transistors?Two main transistor types are BJT and FETWhy are transistors used?Transistors are used as switches or gates for electronic signals, opening and closing gates many times per second. it makes sure the circuit is on if the curent passing and off if the current not flowing. The transistor is used in complicated switching circuits that have modern telecommunications systems.Why use PNP vs NPN?PNP transistor comes with low turn-on voltage, which makes it best to use for high-speed applications. NPN transistor has the benefits of high curent carrying features that make it best for low power uses.Why is MOSFET used?it is used in amplifier circuits and switching purposes. Its featues to change conductivity with voltage given can used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. MOSFET is now common as compare to BJT in digital and analog circuits