What is Electrolytic Capacitor Symbol?
What is Electrolytic Capacitor Symbol?
Electrolytic capacitors are capacitors types known as a polarized capacitor that has an anode or positive plate created with the use of metal that makes an insulating oxide layer through an anodization process.
The oxide layer works as the dielectric of the capacitor. Solid, liquid, or gel electrolytes cover the surface of the oxide layer working as a cathode or negative plate of the capacitor.
They have thin dielectric oxide and larger anode surfaces, which make these capacitors capacitance-voltage multiple unit volume thatn ceramic or film capacitors and come with larger capacitance values. In this post, we will have a look at Electrolytic Capacitor Symbol & Working.
Introduction of Electrolytic Capacitor Symbol
The electrolytic capacitor is a capacitor that uses electrolytes to get larger capacitance than other capacitor types.
The electrolyte is liquid or gel and comes with a high concentration of ions. All electrolyte capacitors are polarized, which means that the voltage on the positive terminal is higher than the voltage on the negative terminal
it also comes with larger leakage current, equivalent series resistance, and limited working life.
It can be a wet electrolyte or solid polymer. It is made with the use of tantalum or aluminum.
Supercapacitors are special types of electrolyte capacitors called double-layer electrolytic capacitors and have a capacitance values of 1µF to 47mF.
Aluminum capacitors are used in power supply, and computer motherboards. As they have a polar nature can also used in DC circuits.
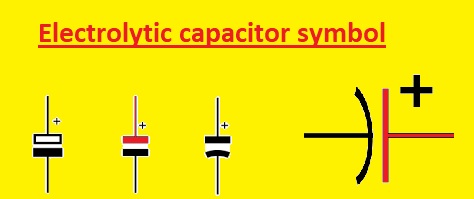
Electrolytic Capacitor Symbol
- Polarized capacitor electrolytic capacitor comes with a plus sign + which is an anode symbol and curved line denoting the negative plate and a straight line denoting the positive plate.
Working Principle of Electrolytic Capacitors
The electrolytic capacitor is made asymmetrically and comes with polarized components. This structure provdies high voltage and one side gets more power than the other.
It has a metallic or aluminum anode with an oxidizing cover layer that works as a dielectric and it is a positive electrode of the capacitor. it gets input voltage.
The cathode which comes with aluminum foil and liquid electrolyte, works as the negative electrode. This liquid is made with use of water and sodium borate or boric acid.
Some sugars are used to avoid evaporation. Aluminum oxide is used for the polarity of electrolytic capacitors. It is positioned through an electric field. If DC is given to an electrolytic capacitor must use accurate polarity.
Connect positive terminal with positive lead and negative with negative lead.
Types of Electrolytic Capacitors
- There are three main types of electrolyte capacitors listed here
- aluminum electrolytic capacitors
- tantalum electrolytic capacitors
- niobium electrolytic capacitors

Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor
- These capacitors come with aluminum anode, aluminum oxide dielectric layer, and conductive electrolyte.
- They are low-cost and provide high power.
- It can be divided into no solid aluminum and sold aluminum capacitors. Non-solid capacitors come with liquid or gel electrolytes, and the solid capacitor has solid polymer electrolytes.
Tantalum Electrolytic Capacitor
- Tantalum electrolyte capacitor comes with a tantalum anode, tantalum oxide dielectric, and conductive electrolyte.
- It offers stable capacitance values for different values of temperature and frequency.
- Tantalum capacitors have two types solid tantalum electrolytic capacitors, made with solid electrolytes, and hybrid tantalum electrolytic capacitors, made with tantalum with other capacitor materials.
Niobium Electrolytic Capacitor
- The niobium electrolyte capacitors also called columbium capacitors are electrolyte capacitors that has a positive anode and are made with passivated niobium metal or niobium monoxide, where the insulating niobium pentoxide layer works as a dielectric.
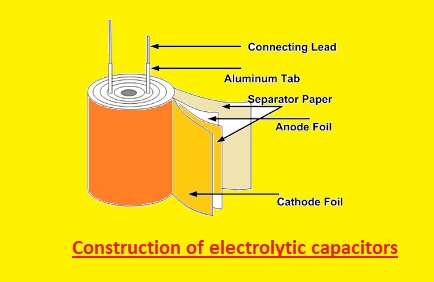
Construction of Electrolytic Capacitors
- ALuminum electrolyte capacitor is made with the use of two aluminum foils and a paper spacer configured on the electrolyte.
- One aluminum foil is covered with an oxide layer and foils work as an anode and uncoated work as a cathode
- During normal working conditions anode must be at positive than the cathode, so the cathode has a minus sign.
- Anode electrolyte-soaked paper and cathode are stacked.
- The stack is rolled and configured on the cylindrical casing and connected with the use of pins.
- Two geometries are as follows, axial and radial. Axial capacitor comes with a single pine on every side of the cylinder and radial structure has both pins on the same side of the cylinder.
Tantalum Electrolytic Capacitor Construction
- This capacitor is made with the use of tantalum metal working anode, that covers the oxide working as a dielectric, and conductive cathode. Tantalum works as thin dielectric layers.
Applications and Uses of Electrolytic Capacitors
- it used in resonant circuits.
- it is used in fading LED circuits.
- Filter circuits such as high or low-pass filter uses this module
- It removes noises from the circuit
- it is used for smoothing ripples in converters.
Which is better ceramic or electrolytic capacitor
Ceramic Capacitors:
Advantages:
- It has a small size strucrue, high capacitance value in a small design, low ESR value and ESL, and has different voltae ratings and can work for different temperature values.
Disadvantages:
- Its capacitance can be less stable with temperature changes, affected through DC bias voltage, causing microphonic noise and limited capacitance than electrolytic capacitors.
Electrolytic Capacitors:
Advantages:
- It also has a high capacitance value, is best for uses that need larger capacitance, and has features to handle high voltae ratings, the compact size relative to capacitance, best to use for energy storage and filtering.
Disadvantages:
- It has sensitive poles, less life than other capacitors, and voltage and temperature limitations as well and also has reliability problems
The ceramic capacitors are used since it has a small size, less ESR, and high-frequency value and are best for using decoupling, bypassing, and filtering.
Electrolytic capacitors is best for high capacitance value, and energy storage, and are used in power supply, audio devices, and industrial control systems.
How to Read Capacitance Value?
- First of all, read 2 digits in picoFarads such as 47 will be read as pF
- Read 3-digit numbers as base capacitance value in picoFarad and multiplier. The first 2 digits will be the base capacitor value in pF. The 3rd digit is a multiplier used on the base number for finding the actual value of the capacitor.
- Use the 3rd digit of zero through five to put the resultant number of Os behind the base value. 3rd digit 8 is multiply the base value with 0.01. 3rd digit of 9 is multiple base to 0.1. Such as 472 will show a 4700uF capacitor and 479 will show a 4.7 pF capacitor.
- Some small capacitor has codes like 1n0. Digits are values before and after decimal points and character explains dimensions such as 1.0 nF (nano-Farad)
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electrolytic Capacitors?
- Here are some advantages and disadvantages of electrolytic capacitors are explained.
Advantages:
- It has a high value of capacitance.
- It comes with a compact size.
- It is cost-effective than other high-capacitance capacitor types.
- It has different voltage values.
Disadvantages:
- Its polarity is sensitive, needing accurate polarity connection.
- Its working life is less thatn other capacitors and it needed inspection and replacement after some time.
- Its voltage is given and the temperature working not increasing then certain value.
- It has reliability problems like electrolyte drying, high ESR or leakage.
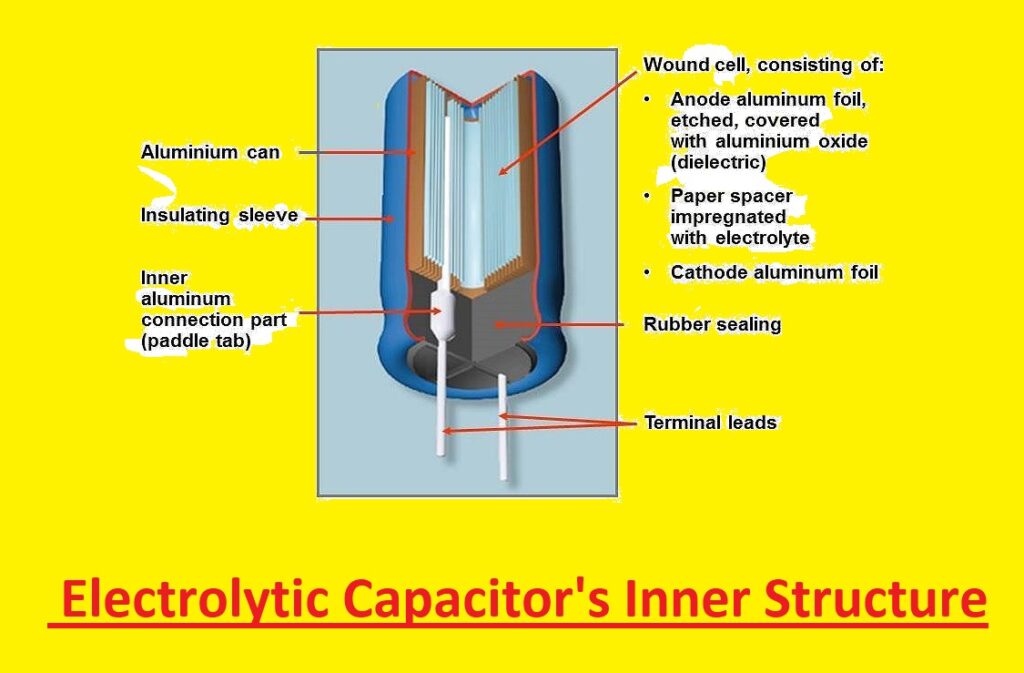
Electrolytic Capacitor’s Inner Structure
Here you can see inner structure of the electrolytic capacitor. Mostly electrolytic capacitors are polarized capacitors that are made with two thin layers of metal foil and a paper spacer filled with electrolyte. The dielectric oxide layer works as a dielectric medium and electrical insulation between anode and cathode foil
The supercapacitors are unique electrolytic capacitors known as double-layer capacitors. its power range is hundreds of Farads to thousands of farads. The diverse features of oxide structure affect electrolytic capacitors according to features.
Electrolytic capacitors have stable life featues, capacitors with low leakage current values, and e-caps have a rated voltage of about 100 volts all use amorphous oxide anode foils. Capacitors with high voltage like photoflash capacitors use crystalline oxide anode foils.
Why Choose Electrolytic Capacitors
The electrolytic capacitor can handle high-frequency circuits that normal ceramic capacitors can do due to high capacitance values. With that, they do a better job than supercapacitors in handling ripple currents. They are made to low volume which saves a high area of boards with less cost.
How to Read an Electrolytic Capacitor
For SMD electrolytic capacitors there are two main marking types. The first one defines the value in mF and operating voltage. Such as with the use of this method the 4.7 μF capacitor having an operating voltage of 25 volts will have a marking 4.7 25V. For another marking system, the letter is follows with 3 numbers. The first two numbers are picofarads and 3rd number is absolute zero. Such a 4.7 μF capacitor with a voltage value of 25 vols can have a marking E476. It is equal to 47000000 pF = 47000 nF = 47 μF.
Difference between Ceramic Capacitors & Electrolytic Capacitors
- Electrolytic capacitor comes with less stability than ceramic capacitors and their capacity can be different for high voltage and temperature changes. Ceramic capacitors have high frequency, and high voltage conditions with capacity remaining stable.
- The electrolytic capacitors are used for low-frequency decoupling and are part of low-frequency filters. While ceramic capacitor comes with featues to handle high-frequency noise.
- The structure of an electrolytic capacitor is like a cola can and the ceramic capacitor is a disc-shaped component and has a size about the coin or even smaller.
- Electrolyte capacitors are polarized and ceramic capacitors are non-polarized and do not need forward-biased voltage.
Styles of aluminum and tantalum electrolytic capacitors
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors make the bulk of electrolytic capacitors used for electronics due to larger diversity of size and less cost manufacturing. Tantalum electrolytic capacitor is used in the SMD version and has higher specific capacitance than an aluminum electrolytic capacitor and is used in devices having limited space or flat designs like laptops. They are also used in military devices, mostly in axial style, hermetically sealed. Niobium electrolytic chip capacitors are a new development in the market and are used as a replacement for tantalum electrolytic chip capacitors
How do you identify an electrolytic capacitor?
Read Also:
- On AC Capacitor Wiring Colors – 2024 Complete Guide
- What is the Difference Between: Ceramic vs Electrolytic vs Tantalum Capacitors
- What is a Capacitor Polarity – Construction, Its Types, Function & Applications
- What is the Role of Capacitor in a Ceiling Fan?
- Difference Between Capacitor and Inductor
- Introduction to Capacitor
- What is Synchronous Condenser (Capacitor)
FAQs
-
Can electrolytic capacitors be used in AC circuits?
- Electrolytic capacitors are used in circuits with positive pins with positive lead of supply and then negative point. Normally used where DC or pulsating DC voltage exists. Some special types of non-polarized electrolytic capacitors are used in ac circuits
-
How do we know the correct polarity of an electrolytic capacitor?
- These capacitors look like small tin cans that are polarized. The negative pin of the cap has a minus mark and color strip. The positive pin is a longer size.
-
Can electrolytic capacitors be used in high-temperature conditions?
- Mostly current capacitors like aluminum electrolyte or film capacitors are limited to the work temperature value of
- 125ºC – 150ºC or lower. For getting a high-temperature rating, ceramic and tantalum capacitors are used.
-
How can I extend the operating life of electrolytic capacitors?
- Capacitor working life increases by a factor of two for each +10°C reduction in temperature. With that working life reduces through the factor of 2 for +10°C increase in temperature.
-
Write the maximum capacitance value of an electrolytic capacitor.
- Electrolytic capacitor capacitance is about 1µF to 47mF. double-layer capacitor or a supercapacitor, has capacitance that can be thousands of farads.
-
What is the function of electrolytic capacitor?
It is used for the reduction of voltage fluctuations in different filtering devices. it is used in output and input smoothing filters when the DC signal is weak with the AC component. They are used for noise filtering or decoupling in power suppliesWhat is the difference between a capacitor and an electrolytic capacitor?
Electrolytic capacitors are best for larger capacitance values for larger ranges, that need stable conditions. Ceramic capacitors are good for smaller capacitance values that are used in variable conditions.What is the formula of a capacitor?
The capacitance of a capacitor is the ratio of the highest charge Q stored in capacitors to the voltage given about plates. Capacitance is the highest amount for a charge per voltage stored in the device= C = Q V . C = Q VIs electrolytic capacitor AC or DC?
Electrolytic capacitors are used in circuits that have the end marked positive always at positive potential rather than negative end. So they are normally used where DC or pulsating DC voltage exists. Special types of non-polarized electrolytic capacitors are used in AC circuits.
What is an example of an electrolytic capacitor?
A practical example is the use of an electrolytic capacitor as a filter in audio amplifiers, whose main work is to reduce mains hum. The mains hum is 50Hz or 60Hz electrical noise induced from the mains supply that can be audible if amplified.