 Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will learn What is a Potentiometer. The potentiometer is an electronic component used for measuring and controlling of resistance of the circuit. In this, post we will learn different parameters about potentiometers such as construction, types, uses, working principles, and applications. So let’s get started What is a potentiometer?
Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will learn What is a Potentiometer. The potentiometer is an electronic component used for measuring and controlling of resistance of the circuit. In this, post we will learn different parameters about potentiometers such as construction, types, uses, working principles, and applications. So let’s get started What is a potentiometer?
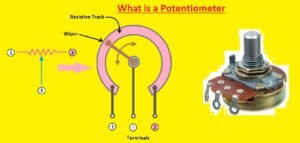
What is a Potentiometer?
- The potentiometer is 3 terminal resistor comes with sliding or rotating contact that make adjustable voltage divider.
- If two terminals use one end and wiper it works as a variable resistor or rheostat.
- The measuring instruments are known as voltage dividers used for measuring electrical potential, the component is the implementation of the same working.
- A potentiometer is used to control electrical devices like volume controls on audio instruments. It is also used in speed control of fans.
- It operated through processes used as position transducers, such as in the joystick.
- Potentiometers are rarely used for directly control power as power dissipated in a potentiometer will be comparable with power in a controlled load

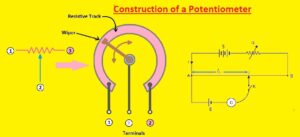
Construction of a Potentiometer
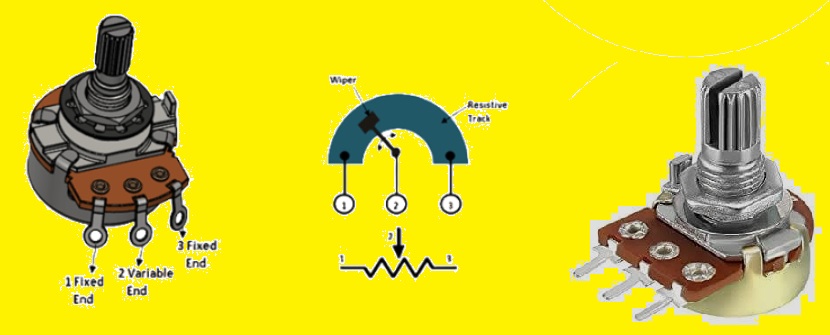
- The potentiometer is made with the use of a resistive material strips normally of carbon mixture. With has a wiper that can be set and placed on a strip.
- Each side strip is connected with a pin. The central pin is connected to the wiper.
- The wiper touches the strip at any point between the two ends. The position of the wiper defines the resistance between the wiper and the side pins. We can move the point where the wiper connects to the carbon strip through the turning shaft of the potentiometer.
- If we move the wiper to the left side, the resistance between the central pin and left pin reduces. And resistance between the central pin and right pin rises.
- If mobe wiper to the right side and reverse process will occur. When we buy a potentiometer, we have to set a value. Such as 100k. It is value that we will get if measure resistance between two endpoints. it is the highest resistance value we can get from a potentiometer.
Types of Potentiometers
main types of potentiometers are that are rotary, linear, multi-turn, and digital.
Linear Potentiometer
- This type of potentiomer has a resistive element in a straight line offering linear changes in resistance. it is used in volume controls, faders, and linear position sensors. This potentiometer is similar but the difference is that instead of rotary motion the sliding contact gets moved on the resistor linearly.
- The two ends of the straight resistor are connected with the source voltage. The sliding contact can slide on the resistor through a track connected with a resistor. The terminal connected with sliding is connected to one point of the output circuit and one with terminals of resistors is connected to the other end of the output circuit.
- This potentiometer is used for measuring voltage about the circuit branch, to measure the inner resistance of the battery cell for comparison battery cell with the standard cell. It is used in the equalizer of music and sound mixing systems.
Rotary Potentiometer
- It has a resistive element in a circular shape that offers circular changes in resistance. it is mostly used in switches, knobs, and rotary position sensors. Rotary potentiometer used for getting adjustable supply voltage to electronic circuits and electrical circuits. The volume controller of the radio transistor is a common example of a rotary potentiometer where rotary knob controls supply to the amplifier.
- This potentiometer comes with 2 terminal contacts between which uniform resistance is positioned in semi semi-circular pattern. The device also comes with a middle terminal that is connected to resistance through sliding contact connected with the rotary knob.
- Through a rotating knob, we can move sliding contact on semi-circular resistance. The voltage is taken between resistance end contact and sliding contact.
- The potentiometer is also called POT. POT is used in substation battery charges for adjusting the charging voltage of the battery. There are many uses of rotary potentiometers where smooth voltage control is needed.
Multi-turn Potentiometer
- The multi-turn pots were made with wipers that operated on a spiral or helical form or through the use of worm gear. Normally these pot comes with many rotations such as 5, 10, or 20 for high precision.
- These posts are used in trim pots on PCB boards that need high accuracy and resolution.
- Comonly used multi-turn potentiometer is potentiometer is Bourns.
Digital Potentiometer
- it is an electronic component that controls the functions of a mechanical potentiometer. It comes with a set of resistive elements and switches which used to regulate in digital form.
- It is used in audio and video instruments and industrial control systems
- The digital potentiometer is 3 terminal instruments, two fixed-end terminals, and one wiper terminal that is used for changing output voltage.
- Digital potentiometer comes with different uses such as celebrating systems, adjusting offset voltage, tuning filters, controlling screen brightness, and controlling sound volume
- The mechanical potentiometer has many disadvantages that make it not useful for uses where accuracy is needed.
- Size, wiper contamination mechanical wear, and resistance drift humidity are some disadvantages of a mechanical potentiometer. To minimize these disadvantages digital potentiometer is the best to house as it has high accuracy.

Advantages of Digital Potentiometers
- It offers reliable operation
- it has high accuracy
- It is small in size, multiple potentiometers can be configured on one chip.
- it has very little resistance drift
- It does not have a moving part
- it has less effect on environmental conditions such as vibrations, humidity, shocks, and wiper contamination.
- Its tolerance is ±1%
- Its dissipation power is low about tens of milliwatts
Disadvantages of Digital Potentiometers
- It is not best for high-temperature conditions and high power uses.
- Due to the parasitic capacitance of electronic switches, there are bandwidth factors that are in digital potentiometers. That is the highest signal frequency that can cross-resistance terminals that less thatn 3 dB attenuation in the wiper. The transfer equation is like to low-pass filter.
- The nonlinearity in wiper resistance added harmonic distortion to the output signal. The total harmonic distortion or THD defines the degrees to which the signal is degraded after crossing the resistance
Potentiometer Driver Cell
Potentiometers measure voltage by comparing measuring voltage with voltage about the resistance of the potentiometer. For the operation of a potentiometer, there should be a voltage source connected to the potentiometer circuit. This cell offers a voltage source to drive a potentiometer called a driver cell.
The driver cell provides current through the resistance of the potentiometer. The multiple of current and resistance of the potentiometer offer full-scale voltage of the device. By adjusting this voltage we can vary the sensitivity of the potentiometer.
It is normally done by adjusting the current through resistance. The current passing through resistance if regulated by the rheostat connected in series with the driver cell. So it is known that the voltage of the driver cell should be higher thatn the voltage measured.
How to Select a Potentiometer?
- The selection of an accurate potentiometer for certain use and installation conditions is important.
- Factors that must be considered is installation point, required size, and connection type.
- Not all features affect the device’s electrical parameters, but still, be carefully considered to make sure that the pot can easily be accessed and set when required.
- Another parameter that must be noted is the type of adjustment process. With mechanical models, it can be selected between slid or rotary knobs. In some applications use of a certain type or design can increase usability.
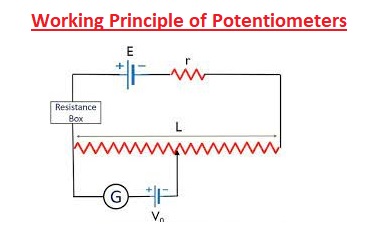
Working Principle of Potentiometers
- There are 3 main components of potentiometers, a resistive element, a wiper, and 3 terminals. Two of the terminals are for resistive strips and wipers.
- Innerly the two outermost connections terminals are connected with a resistive element. it is normally wire-wound and created with carbon, conductive plastic or cermet.
- The wiper contacts the Ohmic component through terminals. The wiper is sliding contact and if it moves with the track, the current flowing through the circuit varies.With contacts ohmic component through terminals. The wiper is sliding contact and if it moves over the track current flowing through the circuit varies. For mechanical trimmer potentiometers, this gets with the use of the rotary switch, slide, or screw.
- The divided voltage is produced at 3rd connection point. Such as if 16 volts are given and the potentiometer is adjusted to positive contact, 3rd contact provides complete voltage.
- But the potentiometer is set between positive and negative lines, 3rd connection has 8 volts, half of the voltage potential.
- if the potentiometer is configured with a negative connection terminal, the output potential is zero.
- It is noted that these features are applied to potentiometers with a linear taper and not to all types.
Applications of Potentiometer
audio Control:
- Rotary potentiometer and linear potentiometer are used for controlling volume and other audio-related signals of audio devices. Such as speakers, radio, Mobile devices,
Motion Control:
- In used for the creation closed closed-loop control in circuits. Potentiometers are used as position feedback devices that are known as servomechanism.
Television:
- In TV it is used to regulate image quality such as brightness, color, contrast, etc. It also used to regulate TV audio
Transducers:
- Potentiometer provide a high output signal so ti used as a replacement of the transducer.
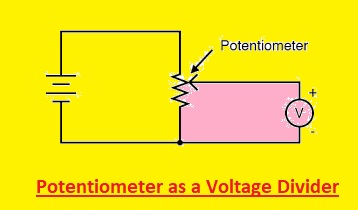
Potentiometer as a Voltage Divider
- A potentiometer is commonly used as a voltage divider. For using a potentiometer as a voltage divider, all 3 pins are connected.
- Any one pin of external pins is connected with GND, the other with Vcc and the central pin is voltage output.
- If a potentiometer is used as a voltage divider, the wiper position defines the output voltage.
- The given below circuit shows the potentiometer used as voltage divider.
- Normally voltae divider is used to convert larger voltage into small values.
- The output voltae can be measured with the use of this formula based on Ohm law
- Vout= Vcc x R2/ R1+R2
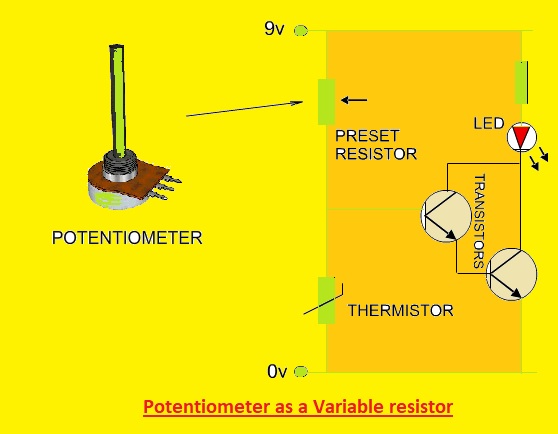
Potentiometers as a Variable Resistor
- Potentiometer comes with a resistive length that can be changed through the use of a knob or slider that changes the resistance between 2 terminals.
- The resistance of the potentiometer can be changed to any value through the knob. It is best to use of projects that need variable resistance, such as volume controls or tone controls for audio equipment.
Potentiometer vs Voltmeter
Difference Between Potentiometer & Voltmeter
Potentiometer
- The potentiometer has 2 terminals used for measuring unknown EMF of source through comparing with known EMF
- Potentiometer also called Pot or Potmeter
- it main use is to measure the unknown resistance of EMF source
- For working it needed a source whose emF known
- When EMF finds potentiometer does not draw curent from device source of known EMF.
- During measuring unknown EMF resistance of the potentiometer is infinity.
- It is highly accurate and sensitive to the voltmeter.
- It uses a null-deflection type instrument.
- Its common uses are to measure the EMF of cell, the internal resistance of the cell, etc
Voltmeter
- A voltmeter is 2 terminal device used to measure the potential difference or voltage between any two terminals in the circuit.
- it is known as the voltage meter
- it measures the voltage between two points.
- It not needed any voltae source to measure voltage.
- it draws current from the source while measuring voltage.
- It has high resistance but not infinity
- its accuracy is less than potentiometer
- it is a less sensitive device and uses a deflection type instrument.
- It gives the direct value of voltage thatn potentiometer.
- It is used to measure the voltage at two points of the circuit
Read Also:
FAQs
-
Write the Difference Between a Potentiometer and a Rheostat.
- The potentiometer comes with an adjustable range and is used for circuit control. It is connected to the panel for adjustment. The variable resistor comes with a small variable range and work circuit parameter compensation.
- Potentiometer used to control voltage on gate terminal. Rheostat work is revered, it controls current through load. These devices are used where only single input and many outputs are used
Read Also https://www.theengineeringknowledge.com/difference-between-potentiometer-and-rheostat/
-
Potentiometers Used in High-Power Applications.
- It is used to adjust the level of analog signals such as volume control audio equipment, and control input for electronic circuits.
-
Write the Working Principle of a Potentiometer.
- The working is based on a factor that the potential of any part of the wire is directly proportional to the length of the wire, which has a uniform cross-sectional area and constant curent passing through it.
-
How to Select the Right Type of Potentiometer for My Application?
- There are many types based on different models, it is good to use those that match the requirements of applications. Such as if there is a need device to work according to application.Such as if needed device to work with high resistance of 1000 ohms not use a device that can work for 100 Ohms
-
Write the Main Types of Potentiometers Used in Electronic Circuits.
- Linear Potentiometer. …
- Rotary Potentiometer. …
- String Potentiometer. …
- Logarithmic Potentiometer. …
- Rheostat Potentiometer. …
- Slide Potentiometer. …
- Trimmer Potentiometer.
-
What is a potentiometer used for?
- The potentiometer works as a variable resistor. it also works as a voltage divider that can used for both adjusting voltage output of circuit and measuring potential.
-
What is a potentiometer a device used to?
- The potentiometer is used for measuring electrical potential. It is one type of uniform high-resistance wire connected with insulating support, marked with a linear measuring scale