Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at the Full form of OLED its construction, applications, and uses. The full form of OLED is an organic light-emitting diode first OLED was manufactured in 1987 by the Ching W.Tang who belonged to Hong Knog and Steven Van Slyke (was American Chemist) during working at Eastman Kodak (is in American company manufactured camera). After that in 1999 Sanyo (Electronic company of Japan) and Kodak make partner with each other to create OLEDs. In September 1999 they manufactured 2.4 inches OLED first time created by any company in the world.
Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at the Full form of OLED its construction, applications, and uses. The full form of OLED is an organic light-emitting diode first OLED was manufactured in 1987 by the Ching W.Tang who belonged to Hong Knog and Steven Van Slyke (was American Chemist) during working at Eastman Kodak (is in American company manufactured camera). After that in 1999 Sanyo (Electronic company of Japan) and Kodak make partner with each other to create OLEDs. In September 1999 they manufactured 2.4 inches OLED first time created by any company in the world.
This 2.4 inches OLED had active matrix and complete colored display. After almost three years in September 2002, they introduced fifteen inches HD-TV haveing white OLED with color filters. The creation of small-molecule organic light-emitting diodes was initiated in 1997 by Pioneer Corporation, (Japanese company)than in 2001 TDK also start making small size OLEDs and the same year 2001 Samsung NEC make mobiles displays using OLEDs after one year in 2002 Samsung became the largest manufacturer of an OLED display. In today’s post we will have a detailed look at working, manufacturing, applications, and uses. So let’s get started with Full Form of OLED.
Full Form of OLED
- The word OLED stands for organic light-emitting diode also called an organic electroluminescent diode.
- This device comprises an electroluminescent layer manufactured with the organic layer that releases photons of light when current passes through OLED.
- The layer of organic material is placed among the 2 electrons one electrode is transparent.
- The screens of TVs, PC monitors, mobile screens, and other electronic devices screens are manufactured with the organic LED for digital displays.
- The OLEDs are categorized into 2 groups first one that uses small size molecules and a second one that used polymers.
- If we add movable ions in the organic LED than it becomes an electrochemical cell that provides different features than normal OLED.
- There are 2 techniques to control the OLED first one is a passive matrix and the second is the active matrix.
- In passive matric control technique, every row (pixels) in the display is controlled in a sequence while in active matrix each pixel is controlled separately with the use of thin-film transistor and provides a large resolution.
- Due to the emission of visible light in Organic LEDs, there is no need of background light.
- Due to this, these devices are less thicker than the LCD less weight and can display a deep back level.
- In darkroom or less lightroom organic led provide high contrast ratio than the liquid crystal display irrespective of cathode fluorescent lamp used as a background light source.
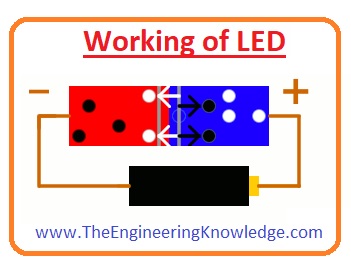
Working of LED
- Before a discussion of the practical working of OLED first, we discuss the working of LED that will help you to understand of OLED.
- For the LED working two different materials of semiconductors, one has a large number of free electrons and the other has large numbers of holes.
- The material has electrons called N-type while others have holes called P types semiconductor. Both these N types and P Types semiconductors are different from each other.
- After that attach these 2 semiconductor materials with each other and you can see no movement between electrons and holes.
- Now apply input supply at the terminals of both pieces and you will see current starts to flow this current is flow due to a combination of electrons and holes with each other.
- Due to a combination of electrons and holes ions are created that make a barrier to move the electrons and holes.
- When electrons move from one place to other they emit energy in the shape of light, light-emitting diode (LED) work on this phenomena.
- The energy emitting and movement of electrons from one energy level is explained in the article what is atom with the detailed.
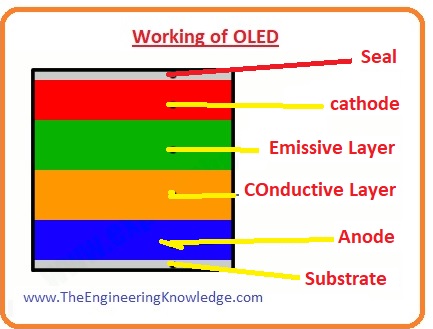
Working of OLED
- The working of an organic light-emitting diode is alike to the general diode and light-emitting diode, but the difference is that instead of n-type and p-type semiconductors that comprise of the organic materials for production of electrons and holes.
- There are 6 different layers in an organic light-emitting diode. The upper layer and the lowermost layer are manufactured with the glass or plastic to provide protection from the outer environment.
- Among the upper and lower layer, there are 2 terminals positive and negative, positive called anode and negative called anode.
- Further 2 layers are exits created with the organic material one is near to the cathode used to emit light and second after come to the anode called a conductive layer.
How OLED Emit Light?
- For the emission of light, we just connect the negative terminal of a battery with the anode and positive terminal with the cathode.
- When current flows through the input supply electrons move towards the cathode and anode loses the electrons and makes the holes.
- Now the condition is like the n-type material at the cathode and like the P-type, the condition is the same at the anode.
- The holes move towards the emissive layer from the conductive layer and combine with the negative electrons and neutralize each other and energy with the light of photon is released.
- This process happens numerous times in one second and continuous light emitted through the Organic light.
- For the production of colored light place colored filter after a glass or bottom layer.
Difference between LCD and OLED
- These are some differences between the LCD and OLED.
|
OLED |
LCD |
| Its full form is Organic light-emitting diode | Its full form is liquid crystal display |
| It uses organic materials like carbon to manufacture screens. | It screen made with the liquid crystal. |
| It’s every pixel that produces light radiations. | In this device background light such as lamp is used to provide light. |
| To show different colors its pixels blink and then off independently. | While in LCD pixels are not on and off independently, they use light at the backend and pixels panels to block white light and make different colors. |
| Its brightness is large | Its brightness is low. |
| when the brightness of colors on the screen is less it consumes less power. | It uses large amount of energy. |
| When the color is white it consumes high energy. | It uses a small amount of power. |
| Usage of organic material decreases operating life. | Its working life is high. |
| It is costly | It is less expensive |
Different Types of Old OLED
- In this given below pictures, you can see the older types of organic LEDs and their features.
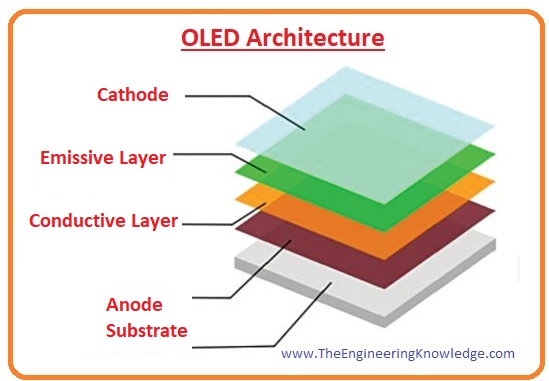
OLED Architecture
- The structure of the organic light-emitting diode comprises these parts.
Substrate:
- It is also known as the base of organic light-emitting diode that constructed with a glass of foil substance.
Anode:
- The other name of the anode is the emitter. When input supply is connected with it releases electrons.
Organic Layer:
- The layer over the anode is known as an organic layer, it comprises polymer as conductive and creates with the hydrogen.
Conductive Layer:
- This layer is for the movement of holes from anode to cathode and constructed with the organic material.
Emissive Layer:
- It used to transfer of electrons from cathode to anode and constructed with the material difference to the material used for the conductive layer.
Cathode
- It is the upper layer of organic LED and at this layer, electrons generate when the supply voltage is provided.
Advantages of OLED
- These are some advantages of OLED.
Less Price in Future
- The organic light-emitting diode can be printed on any substrate by using inkjet printer that
- Hypothetically make OLED less expensive than the liquid crystal display.
- But the manufacturing of Organic light-emitting diode is currently expensive than the liquid crystal display.
- But by using roll to roll vapor deposition technique can make OLEDs in less price and large numbers of pieces in a minute.
- But for creation of OLED having many layers, this technique makes some problems
Less weight and flexible plastic substrates
- OLED displays can be manufactured on the substrate created with flexible plastic.
- If a substrate is of the polyethylene terephthalate it will decrease the manufacturing price.
High-Quality Picture
- Due to the direct emission of light, the organic light-emitting diode provides a high value of contrast ratio and a large angle of view than the liquid crystal display.
Response time
- The response time of the organic light-emitting diode is high than the liquid crystal display.
- The response time of liquid crystal display can be one millisecond by using different techniques.
- Almost the one thousand time response time of organic light-emitting diode is larger than the liquid crystal display.
Disadvantages of OLED
- With the different benefits, it also has some disadvantages.
Lifespan
- The main issue of organic light-emitting diode faces is the less operation life of organic material used.
- The research in 2008 was done to monitor the performance of OLED that found that after continuous working for one thousand Hrs. there was a twelve percent decrease in the blue, seven percent decrement in red and an eight percent decrease in the green luminance.
- It is less than the lifetime of liquid crystal display and light-emitting diode, their brightness decreases become half after 25,000 to 40,000 operating hours.
- Due to the absorption of oxygen in the OLED structure decreases the operating life organic material as oxygen reacts with that material.
- A report created by the united states department of energy says that the operating life of OLED decreases with the increment of brightness, according to that report operating life at twenty-five percent brightness was forty thousand and ten-thousand hours at hundred percent brightness.
Color balance
- The organic substance used in OLED manufacturing to generate blue color light degrade within very little time as compared to the materials used for other color lights.
- In simple words, the output of blue color decreases as compared to others.
- This difference in the output of colors will vary the color balancing of the display screen.
- For balancing a more sophisticated control circuitry is needed and users of OLED should also have the knowledge to operate OLED and control circuitry.
Water Damaging
- The absorbance of water from the external environment can disturb the assembly of OLED. So its structure is such that water cannot pass from it.
Power Usage
- The power consumption for the organic led for the display of an image that is black is forty percent of the power used by the liquid crystal display.
- But to show an image with the white background like any document or web page it consumes more than three hundred percent power.
- So it will very easily decrease the battery of devices in which a white background is shown.
Applications of OLED
- These some important applications of OLED.
Mobile phones
- There are numerous smartphones are using OLED screens introduced in the year of 2016, such as Samsung A8+, Glonee S11S, and M7 Plus, iPhone X.
OLED TV
- Almost nowadays mostly televisions are using Organic LED screens and replaced the older LEDs display. Currently, every television making company working on the OLED to construct the screens.
- Toshiba X97, Bild9, Bild 5, Panasonic EZ950 all have screens of OLED.
Digital cameras
- Nowadays the used of organic LED displays are using in the screens of cameras. The first camera used organic LED display was manufactured in 2003 and the name is Kodak LS633.
- Currently, Canon PowerShot G1 X Mark III, DL24-85, HX80, etc using OLED display.
. Wearable Devices
- The devices like smartwatches are using OLED in screen manufacturing.
So friends that is the detailed post on the full form of OLED I have written each and everything related to OLED. If you have any queries about this post ask in comments. See you in next post have a good day.