 Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at the Full form of MCB in Electrical its construction, applications, and uses. The full form of MCB is a Miniature Circuit Breaker, any type of circuit breaker is a switch that operates automatically in case of excessive current flow through the circuit due to overloading or short circuit. The operation of the breaker is similar to the fuse to break the circuit as some non-favorable conditions occur in the circuit like over current flow when the fault is removed it again restores the circuit’s normal condition.
Hello, fellows, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at the Full form of MCB in Electrical its construction, applications, and uses. The full form of MCB is a Miniature Circuit Breaker, any type of circuit breaker is a switch that operates automatically in case of excessive current flow through the circuit due to overloading or short circuit. The operation of the breaker is similar to the fuse to break the circuit as some non-favorable conditions occur in the circuit like over current flow when the fault is removed it again restores the circuit’s normal condition.
There are numerous sizes and designs of breaker exit in the market according to circuit requirements. Small-size circuit breakers are used to provide protection in such circuits where less value current is used and if any circuit breakers are assembled in a large array or board then this assembly called switchgear is used to protect large circuits. Switchgear are installed at the grid stations to protect incoming and outgoing feeders. There are numerous types of circuit breakers according to current ratings and applications. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at a miniature circuit breaker and its related parameters. So let’s get started with the Full Form of MCB in Electrical.
Full Form of MCB in Electrical
- The word MCB stands for miniature circuit breaker like other circuit breakers this breaker also trips the circuit as a large amount of current flows due to short circuit or overloading conditions.
- In older small circuits that take less current used fuse to provide protection but nowadays fuse has been replaced with the miniature circuit breaker in these less current consuming circuits.
- The use of a miniature circuit breaker is more beneficial than the fuse as it restores current normal current flow as the fault is removed.
- But in the case of fuse it the normal operation of the circuit takes time until the wire of fuse with the new wire.
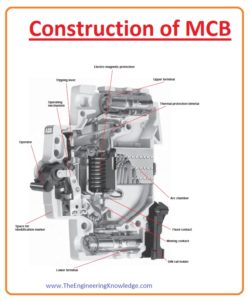
Construction of MCB
- These are some parts of the miniature circuit breaker that were used to design the MCB. Let’s discuss them with the detail.
External Casing:
- The exterior casing of MCB is constructed with any insulating material or plastic. It provides interior elements protection and assembles them at their respective places.
Contacts:
- There are numerous contacts are available in the form of pairs and one pair is immovable and the others are not fixed.
Knob:
- The knob is used to on and off the circuit breaker operation.
Mechanical Latch:
- During on position force is applied on the spring and compressed it in this condition to hold contacts in a normal position, latching is used in the miniature circuit breaker.
Bimetallic strip:
- During overloading conditions, the current flowing is larger than the rated value of current than these bimetallic strips used to provide protection.
Solenoid:
- A solenoid is a coil used to provide protection in the short circuit occurrence by releasing the mechanical latches.
- The solenoid operates only when the current flowing is three times the rated current of a breaker.
- Solenoid only operates in the case of a short circuit, not for overloading.
Arc Chutes:
- These chutes are used to quench the arc.
Operation of MCB
- There are main 4 functions performed by the miniature circuit breaker.
Switching
- The MCB can be on and off manually which makes it most effective during repairing the breaker.
- The exterior latching structure controls the immovable contacts as the knob press for on of the breaker.
- When the knob is pressed on the breaker then the pressure given by the operator’s finger latch becomes free and opens the contacts of the breaker.
Overcurrent Protection
- Due to overloading a large number of current flows through the breaker, and this current heated the bimetallic strip.
- Due to this heating shape of the bimetallic strip changes which presses the latch and the contacts of the breaker get off and the current stops flowing.
Short Circuit Protection
- Due to the short circuit, an abrupt increment in current generates magnetomotive force so strong that it operates the latches and off the contacts of a breaker.
Arc Quenching
- Due to overloading conditions, the arc is created among the non-movable and movable contacts of breakers.
The design of contacts is such that they move the arc towards the arc quenchers or chutes that will remove the arc in the breaker.
Working Principle of MCB
- When the excessive current flows through the circuit due to overloading and short circuit the bimetallic strip of the breaker gets heated and its shape changes.
- The shape variation of the bimetallic strip displaces the latching arrangements.
- The moveable contacts of the miniature circuit breaker are attached to the latching point any variation in the latching position also causes the movable contacts to open the circuit.
Types of MCB
- The types of circuit breakers are discussed here in detail.
Type B MCB
- The operating speed of a miniature circuit breaker is 3 to 5 times the value of the rated current.
- The type of breaker is used in such circuits where resistive or inductive loads are used.
- Due to this, these are normally used in homes.
Types C MCB
- The operation speed of this breaker is 5 to 10 times the value of its current rating.
- These breakers are normally used in highly inductive loads such as motors.
- In these loads switching surges are large and these MCBs is the best option for these circuits.
- These breakers are so installed in industries for inductive loads like induction motors.
Type D MCB
- The operation speed of these breakers is 10 to 25 times the value of the rated current.
- They are preferred for high inductive loads the use of these loads produces large numbers of surges after a small-time interval of frequently.
- These breakers are used in X-ray machines, UPS, larger motors, etc.
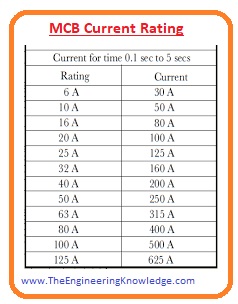
Rating of MCB
- The current rating is the value of the current over which the breaker gets tripped. The rating of MCB is fixed and its operating range is between one ampere to one hundred amperes.
Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, RCCB
MCB
- Miniature circuit breaker provides protection to the circuit from the high value of current caused by overloading, short circuit, and improper design.
- It is the best replacement of fuse as after fault detection fust must be replaced but it removal of the fault starts operation again.
- So MCB is cost-effective while the fuse is used only for a single time.
- This breaker is also available in different types of pole arrangements such as one, two, three-pole, and 4 poles with the neutral pole as well if required in any circuitry.
Features of MCB
- These are some features of miniature circuit breakers.
- Its current rating is a hundred amperes.
- It operates thermally.
- Usually, its tripping is not controllable.
MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker)
- A molded case circuit breaker is used to provide protection to any circuitry from the short circuit and overload current.
- It can use to handle the current of sixty-three amperes to three thousand amperes. This breaker can break the circuitry in case of fault manually and automatically.
- It also replaces the fuse as it can use again after removal of fault but the fuse can not be used again.
- As fuse to be purchased again but the breaker just reset for operation and it makes it cost-effective over the fuse.
Features of MCCB
- These are some features of MCCB.
- Its current rating is up to one thousand amperes.
- Its tripping current can be adjusted while in MCB not adjusted.
- It operates thermally.
ELCB (Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker)
- To protect electrical circuits from electric leakage the earth leakage circuit breaker is used as it can be guessed from its name.
- If someone intentionally touches the live wire and gets an electric shock, this breaker breaks the circuit in a time of 0.1 seconds and protects from serious damage.
- It is used in grid stations where high voltages are controlled and minor leakage current can be detected with the breaker and control electric shock due to current leakage.
Features of ELCB
- These are some features of ELCB described here with detail.
- For the interlinking of neutral, earth, and phase wire ELCB is used.
- Current leakage in any circuitry defines the operation of ELCB.
RCCB
- The RCCB stands for residual current circuit breaker used to provide protection to the circuit having less voltage flow.
- It has a switch to break the circuit when a fault occurs. It also provides protection to the person from getting an electric shock.
- Mostly this circuit is preferred for these circuits where a sudden electric fault occurs and electrical shock.
- To operation a practical understanding of the operation of this circuit, let’s assume that a person touches unintentionally a live wire he gets shocked suddenly but if the circuit contains this breaker as he touches the wire breaker breaks the circuit suddenly.
Features of RCCB
- These are some features of RCCB.
- Neutral and phase wire also can be attached to the residual current circuit breaker.
- In the presence of a ground fault, it breaks the circuit.
- To protect from electrical shock, these breakers are mostly preferred.
Differences between MCBs and MCCB
| Features | MCB | MCCB |
| Full Form | Miniature Circuit Breaker | Moulded Case Circuit Breaker |
| Tripping Circuit | Fixed | not fixed |
| Definition | A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) electrical device made for the protection of the circuit from damage by overload or short circuit. It interrupts current flow. | The MCCB is used for the protection of circuit from overcurrent and short circuits. it is covered in the molded casing for safety purposes |
| Poles | single, two, and three | single, two, three, four types |
| Uses | For domestic uses such as home wiring | commercial and industrial use |
| Rating current | 100 amps | 10-200 amps |
| Remote on/off | Not | Yes |
Differences between an RCD and MCB
| Features | RCD | MCB |
| Full Form | Residual Circuit Device | Miniature Circuit Breaker |
| Usage | personal safety purposes | Offers safety to instruments and controls the effect of overcurrent and overheating. |
| Definition | A Residual Current Device (RCD) fastly disconnects the circuit when finds any imbalance in current, avoiding electrical shocks and fire. | A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is used for controlling overloading. It automatically trips the current flow. |
| Working | its works based on differences in current passing from live and neutral wire producing magnetic field | It senses current passing through the circuit. If the current passing through the breaker is higher than any certain value it trips. |
| Tripping value | 30mA | 10, 16 or 32A |
Read also
- What to Do if Your Circuit Breaker Won’t Reset
- How Many Outlets on a 15 Amp Circuit Breaker?
- Difference Between Isolator and Circuit Breaker
- Difference Between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
- What is circuit breaker | Working Principle & Why Is It Important?
- What Is A Shunt Trip Breaker & How Does It Work? Detailed Guide
- Run a Short Circuit Analysis in ETAP
Faqs
- MCB is Miniature Circuit Breakers, and MCCB is Molded Case Circuit Breaker.
- MCB breaker works on measuring the incoming current of the circuit and its rise and ELCB works on current balancing principles, which menas it measures the total incoming current and outgoing current. The difference in them is that residual current that leaks to the earth.
So that is the detailed post about the full form of MCB in Electrical if you have any questions about MCB ask in the comments. See you in another interesting post. Have a good day. Thanks, for reading.










Wow that was odd. I just wrote an extremely long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say wonderful blog!
Thank you for sharing your knowledge.This article is very helpful to me, let me know how to choose the electronic components products I want, so I always trust this icsift store, You can buy this resistor from your electronic component supplier.