Hello, readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will discuss What is the Difference Between Ceramic vs Electrolytic vs Tantalum Capacitors. Capacitors are two terminals electrical devices that store enegy in the form of electric charge. It has two electrical conductors that are separated by some distance. The space between conductors is filled with Vacuum or insulation material used called dielectric. There are differnt types of capacitors used in electronics such as tantalum, electrolytic capacitor, and ceramic. Every capacitor comes with different features and parameters. In this post, we will discuss different capacitors and find their differences. Let’s get started with Ceramic vs Electrolytic vs Tantalum Capacitors
Introduction to Capacitors
Before discussing the types of capacitors first learn the capacitors working. A capacitor stores energy by gathering the electric charges on two closely configured plated separated insulators. Capacitor also called condenser, and also condenser microphone
How Does Capacitor Work
The capacitor is a two-plate conductive device that has insulation between two plates and current changes the capacitor and voltage generated across plates. The capacitor holds voltage due to insulation between two plates.
Capacitor change dissipates when the current supply is disconnected. A voltage capacitor can hold and define the charging and discharging time of a capacitor. Conductive plates of some types of capacitors are polarized, which means one plate is positive and the second is a negative charge. Polarity helps the capacitor to make connections with circuits. If plates are properly connected it makes the capacitor faulty.
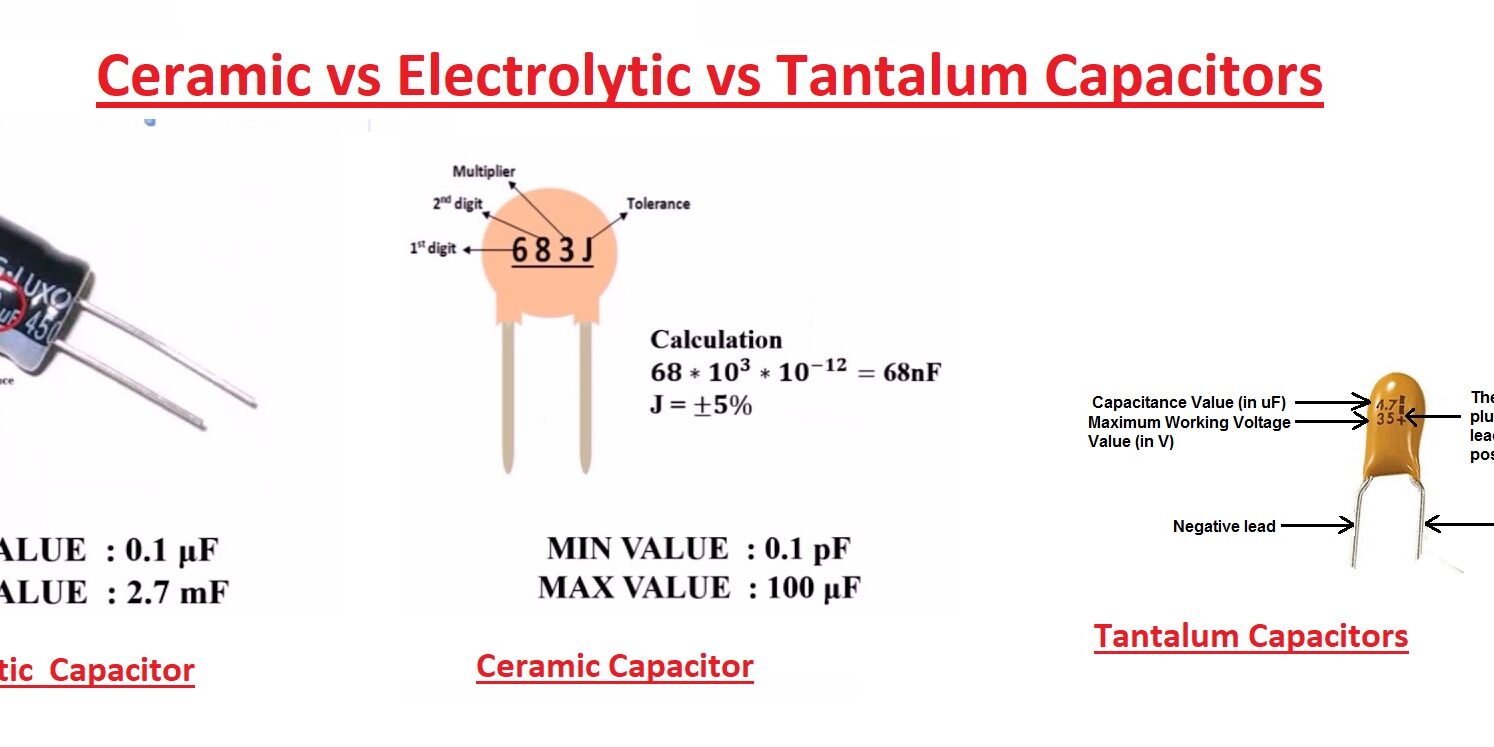
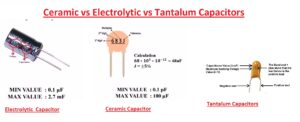
What are Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitor is commonly used capacitors in electrical devices since they are reliable and less costly to make. Ceramic capacitors come with ceramic or porcelain discs that come in non-polarized make and are used in many applications. Ceramic material comes with good dielectric since it has less conductivity and best supports the electrostatic fields. Ceramic materials are inorganic and non-metal also are nitrite or crystalline oxide. Common examples are carbon and silicon
Ceramic Capacitor’s technical features
| Characteristic | Class 1 | Class 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitance stability | High | Good |
| Losses | Low | Higher |
| Tolerance | ±1% | ±15-20% |
| Size | Small | Larger |
| Voltage rating | Low to High | High |
| Power rating | Low | High |
| Applications | Sensitive applications, high-frequency circuits | Less sensitive applications, power circuits |
What are Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors are polarized types of capacitors that come with the anode or positive plates of metal that make an oxide layer with the anodizing process. The oxide layer created works as a dielectric capacitor. Normally this oxide layer is rapped in liquid, solid, or gel electrolyte.
This capacitor has a thin oxide layer and anode surface. So these capacitor comes with higher capacitance voltage multiple per unit volume than ceramic and film capacitors.
The main types of electrolytic capacitors are aluminum electrolytic capacitors, tantalum electrolytic capacitors, and niobium electrolytic capacitors.
These capacitors are non-symmetrical and work with high voltage on the anode. This voltage value is higher thatn the cathode. So their covering has mentioned polarity.
Difference Between Tantalum and Electrolytic Capacitor
A Tantalum capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor that works as a passive component in circuits. An electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor that has an anode of metal that makes an oxide layer as a result of the anodizing process.
The main difference between electrolytic and tantalum capacitors is that tantalum capacitor uses a sintered pellet of high-purity tantalum powder with tantalum pentoxide used as a dielectric component and electrolytic capacitor comes with the anode of meta tha makes odixe layers.
Electrolytic Capacitors Features
Capacitance and Tolerance:
The electrolyte and anode of this capacitor affect capacitance. Capacitance is based on frequency and temperature. Capacitors with non-solid electrolytes have a larger sense of frequency and temperature than capacitors with solid electrolytes.
Unit of capacitance is microfarad. The capacitance value is defined by the manufacturer that called nominal or rated capacitance. The percentage of rated value is called capacity tolerance.
Capacitance Drift:
Capacitance comes with a larger tolerance of 20 percent. But it drifts from nominal value with time. The aluminum electrolyte capacitor has a nominal capacitance of 47 uF and will have a capacitance between 37.6µF to 56.4µF.
Tantalum capacitors also come with high tolerance, like less maximum operating voltage. But not used as the best replacement of aluminum capacitors.
What is Tantalum Capacitors
A Tantalum capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor tha works as a passive component of electronic circuits. it has a pellet of porous tantalum metal used as a capacitor anode. It is covered with an insulating oxide layer, tha can make dielectric. it is covered with a solid electrolyte that is the anode.
Tantalum capacitor is thin and has a high permittivity dielectric layer. its capacitance per volume is high value and less weight helps differentiate from another capacitor. Tantalum is a chemical element that comes with atomic number 73 and Ta symbol. It is a rare material and its color is blue-grey.
it has high corrosion resistance. it is a minor component in alloys since it is part of the refractory metal group. The working of the tantalum capacitor oxide layer works as a barrier about the tantalum anode then positive voltage is connected. The thickness of the oxide layer created is proportional to the voltage connected. The oxide layer that was created works as a dielectric of the capacitor.
This capacitor is used in hold circuits for getting long working as an alternative to an aluminum electrolytic capacitor. It is used in computer motherboards.
Tantalum Capacitors Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Dielectric | aluminum oxide |
| Voltage | 4 to 400V |
| Capacitance | 47 to 10000µF |
| Advantage | Different values of breakdown voltages and capacitances |
| Disadvantages | Electrolyte leakage affects working Large package size |
| Lifespan | 100,000 hours. |
Comparison of Ceramic, Electrolytic, and Tantalum Capacitors
Here is a comparison of the different characteristics of ceramic, electrolytic, and tantalum capacitors:
| Characteristic | Ceramic Capacitor | Electrolytic Capacitor | Tantalum Capacitor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacitance Range | Picofarads to microfarads | Microfarads to farads | Microfarads to farads |
| Voltage Rating | Low to medium | High | Higher |
| Size | Small and compact | Large-size | Compact and less size than electrolytic capacitors |
| ESR | Low | Medium | Low |
| Frequency Response | Best for high-frequency applications | Medium | Used for high-frequency projects |
| Cost | Low | Moderate | Relatively larger cost |
| Applications | Consumer electronics, automotive, telecommunications | Power supply, audio devices, industrial electronics | Mobile devices, medical devices, aerospace systems |
Factors to Consider When Choosing Capacitors
The capacitance, voltage rating, leakage current rating, and temperature, are the main factors for the size of the capacitor and for use in the circuit different factors such as equivalent series resistance, frequency, reverse voltage rating, operating losses, operating lifespan, and the mean time before failure (MTBF).
All these are factors for the selection of capacitors to use in different projects and devices
Ceramic vs Electrolytic capacitors
The basic difference between these capacitors is that ceramic material separates two conductive plates in a ceramic capacitor. While electrolyte and metal oxide separated two conductive plates in an electrolytic capacitor.
Dielectric is ceramic materials in ceramic capacitors while electrolytic capacitor has a thin oxide layer as dielectric. Ceramic capacitors are non-polarized and electrolytic capacitors are polarized.
| Features | Electrolytic Capacitor | Ceramic Capacitor |
| Polarization | polarized capacitor. | Non-polarized |
| Anode terminal | anode terminal is higher than the cathode. | Both equal. |
| Range | 0.1 μF to 4700 μF | 10 pF to 0.1 μF |
| Temperature Stability | Poor | Good |
| Tolerance | High | Low |
| Life | Shorter | Longer |
Tantalum Capacitors vs Ceramic:
- For capacitors logarithmic reduction in capacitance with time is called the aging process. Ceramic capacitors have aging factors and tantalum does not. Tantalum capacitors do not come with a wear-out mechanism.
- Tantalum capacitors are polarized that means can be connected with DC supply in accurate polarity. Ceramic capacitors are non-polar so can be used with AC sources.
- There is less change in capacitance in tantalum capacitors for temperatue and non-linear behavior for ceramic
- For voltage connected tantalum capacitor has consistent stable voltage while ceramic does not. As a result high voltage permittivity of dielectric shrinks in ceramic capacitors and causes variation in capacitance. The variation in capacitance of ceramic capacitors is linear and easily accounted for.
Are ceramic capacitors better than electrolytic ones?
Which type of capacitor is best?
Are tantalum capacitors better than ceramic?
FAQs
What are electrolytic capacitors?
An electrolytic capacitor is a type of capacitor that uses an oxide film made of aluminum, tantalum or oxidizable metal as a dielectric. Due to its larger capacitance, it used extensively in power supply circuits
What is the difference between ceramic electrolytic and tantalum capacitors?
A Tantalum capacitor is polarized, which means needed a certain value of the voltage at positive terminals, like an electrolyte capacitor. Ceramic capacitors are non-polarized and they can run with AC voltage.
Are tantalum capacitors better than electrolytic?
High-end motherboards mostly use solid capacitors created with aluminum, tantalum, or polymer. Solid capacitors reduce the chance of leakage or explosions resulting of electrolytes expanding due to overheating.
Are ceramic capacitors better than electrolytic capacitors?
For high-frequency operations ceramic capacitors are best to use
What is the advantage of a tantalum capacitor over a ceramic capacitor?
Tantalum capacitors (TC) face less change in capacitance features due to circuit DC voltage and/or temperature variations, reducing the need to verify the effective capacitance – unlike ceramic capacitors (MLCC).
What are the disadvantages of tantalum capacitors?
unfavorable failure mode can cause thermal runaways, fires, and small explosions, but this can be avoided with the use of external failsafe devices like current limiters or thermal fuses.
Can we replace the ceramic capacitor with tantalum?
multi-faceted and tantalums will not best to replace ceramics in all cases. Ceramics and tantalum share common case sizes for SMD components, so they can be replacements for each other in certain situations
Can I replace electrolytic with tantalum?
Not replace aluminum electrolyte capacitors with ceramic or tantalum capacitors.
What is a tantalum capacitor used for?
Solid tantalum capacitors are famous for their small size, high capacitance, and stability at high temperatures, so best for use in portable electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, and digital cameras.
Which is better tantalum or ceramic bypass capacitor?
Tantalum capacitors come with high capacitance and high stability, and MLCC comes with low inductance and ESR. So use according to applications.