Hi, guys welcome to the new post. In this post, we will have a look at what is a Capacitor Polarity. Capacitors are the main component of electrical devices and circuits. For capacitors to properly connect and work there must be knowledge of their polarity. The construction, types, uses, and applications of capacitors will be explained here. So let’s get started with What is a Capacitor Polarity
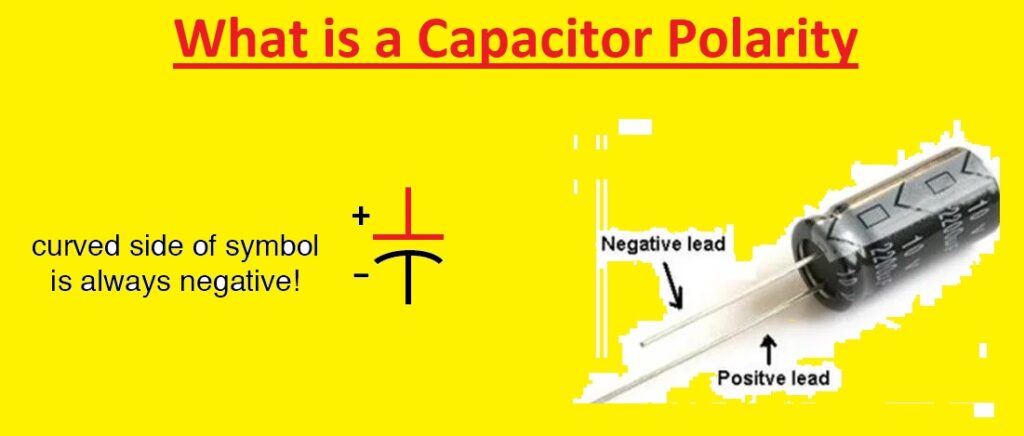
What is Capacitor Polarity
- Capacitor polarity defines the positive and negative terminals of a capacitor. it is important since the capacitor can connected with the circuit in accurate polarity. if the capacitor is attached in incorrect polarity, can damaged.
- There are 2 main types of capacitors polarized and non-polarized. A polarized capacitor comes with positive and negative pins and is connected with the circuit in proper polarity. Nonpolarized capacitors do not have positive or negative pins and can be attached in any polarity.
- Tantalum and electrolytic capacitors are two main types of polarised capacitors. Comonly used type of polarised capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor. it is made with a metal foil which is covered with a layer of oxide, that operates as dielectric material. As the oxide layer is thin, there is a high capacitance per unit volume. Power supply and different projects that need a larger capacitance use electrolytic capacitors.
How to Identify Capacitor Polarity
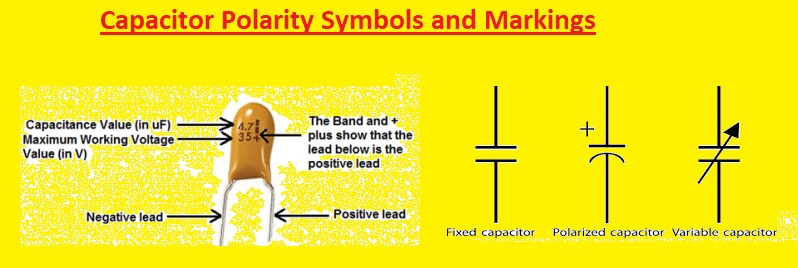
- Check the positive (+) or negative (-) sign on the capacitor. it is a simple method to find the polarity of a capacitor positive symbol with a solid line and a negative sign with a dashed line
- Find longer lead on the capacitor. The longer lead is postie and the smaller negative of the cathode.
- color coding scheme. red stripe on a capacitor shows that the positive lead is the red stripe.
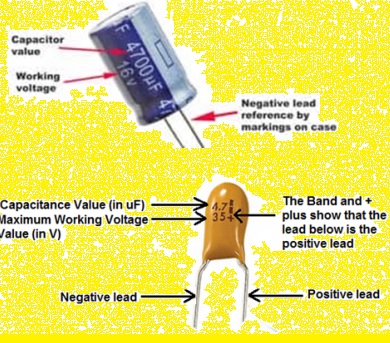
- Check the datasheet: The datasheet of the capacitor must have data for the polarity of the capacitor. It can come with markings used for indication of polarity, also other details for capacitor
Types of Non-Polarity Capacitors
- Ceramic capacitors: it is a non-polarized capacitor. Made with ceramic materials, like porcelain mica, or polyester. They have different capacitance values, from some picofarads to a few microfarads. It is a reliable and effective capacitor type that has good operation. its small size is best for high-frequency circuits, and stability for high temperatures helps to make sure they well work for these conditions.
- Silver mica capacitors: it is part of a ceramic capacitor that is designed from a silver-mica dielectric. It is used for applications where capacitance has low values high stability, and fewer losses. Its main use is power RF circuits. It is also used in high-frequency tuned circuits, such as filters and oscillators.
- Polystyrene capacitors: it is made of polystyrene dielectric. it is used as a replacement for ceramic and mica capacitors in audio circuits. But this capacitor is not restricted to use in audio applications, it is best for circuits that are needed through a hole high tolerance tolerance capacitor.
- Polypropylene capacitors: Their main features are high capacitance, less dielectric absorption, and different temperature values. it is used in high-frequency high power uses like induction heating, pulsed power energy discharge, and ac capacitors for electrical distribution. The ac voltage rating of this capacitor is 400 kV.
Non-Polarized Capacitors and Polarized Capacitors Comparison
- A polar capacitor comes with electrolytes as a dielectric material that helps to get high capacitance. Dielectric in structure is used to show capacitance value. It also defines the voltage level that a capacitor can handle. non-polar capacitor uses a metal oxide layer for dielectric material. Polyester is used as a dielectric.
- The operation of electrical components defines the circuit’s accuracy. it can be found that the power supply uses a metallic oxide dielectric capacitor for the filter. So best to use a polar capacitor of more thatn 1MF. So best to use for coupling and decoupling circuits. While a non-polar capacitor has a polarity of less thatn one microfarad. Its working makes it best for frequency selection, resonance, and current limiter.
- Both have different dielectrics but come with the same capacitances. It does not matter if they come with the same volumes. SO polar units can have a higher capacitance than nonpolar ones.
- The shape of the capacitor is also based on polarity. The main factor is point discharge. For electrolyte polar capacitors will have a circular shape. Getting square is difficult. Based on the use of the circuit capacitor can be rectangular, tubular, sheet, or circular.
- The polar capacitor has high capacitance and others are not good for high-frequency uses. THough some can handle high frequency, like tantalum capacitors. While non-polar capacitor has good frequency features and small size. They are less cost and not good for larger capacity operations.
Construction of Capacitors
Capacitors have two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. Different types of dielectric materials are used like ceramic, tantalum, or electrolytic materials. The conductive plates are made with metal, store and discourage charges when voltage is provided to the device
Types of Capacitors
There are differnt types of capacitors some are explained here
Electrolytic Capacitors
Polarised electrolytic capacitors have high values of capacitance and polarized nature. They are used in power supplies, audio amplifiers, and devices that need high-capacitance
Ceramic Capacitors
Non-polarized ceramic capacitors have different sizes and capacitance values. They are used in electrical circuits for bypassing, filtering, and decoupling purposes.
Tantalum Capacitors
They also have high capacitance in a small package and are also polarised. They are used in devices with constrained storage, such as laptops and mobile phones.
Film Capacitors
They have good stability and are non-polarized. They are frequently used in conditions where high voltage and temperature tolerance are necessary.
Capacitor Polarity and its Importance
Polarity is the main parameter of capacitors with an electrolytic or tantalum construction. its use is reverse voltage or connecting them incorrectly can cause electrolyte leakage, explosion, or damage to components. polarity markings must be known on these capacitors and attached appropriately to the circuit.
Capacitor Functions
Energy Storage
The capacitor releases charges when connected to in circuit that is stored in its plate. They can control voltage levels in the circuit or serve as temporary power sources.
Filtering and Smoothing
To provide a steady power supply, capacitors are used to filter out noise and ripple voltage.
Timing and Oscillation
In circuits like oscillators and timers, capacitors and resistors are connected to control the timing and frequency of oscillations.
Applications of Polarized and Non-polarized Capacitors
Polarized Capacitors Uses
- Polarized capacitor for example electrolyte capacitors is used in power supply decoupling circuits for smoothing voltage ripples and minimizing the noise in power sources.
- It is also used in amplifier circuits, engineers use a polarized capacitor for blocking dc signals and allowing ac signals.
- it is also used in timing circuits, such as oscillator circuits, for regulation frequency and timing circuits.
- The polarized capacitor is used in coupling and bypassing circuits, helping to make the same connections with two different circuits that block undesired frequencies.
Non-Polarized Capacitors Uses
- The non-polarized capacitor like ceramic has constant and reliable capacitance for a different frequency. it makes them best for high-frequency uses.
- These capacitor has featues to reduce undesired frequency and increase signal quality. These components provide an easy method for optimization audio or video signals for less interference.
- it is best for the creation of radio frequency circuits like antenna matching systems that need fine tuning to get the required frequency value.
- Non-polarized capacitors work for timing circuits such as oscillator networks, influencing the frequency and time of their operation.
Capacitor Polarity Symbols and Markings
Capacitors having polarity mostly have symbols or markings that show the correct orientation. Common symbols have “+” and “-” signs, arrows, or shaded regions. check and define these markings to ensure correct installation.
What Happens After Reversing the Polarity of a Capacitor?
If the polarity is reversed, the capacitor can be damaged or short-circuit.
Some electrolyte capacitors are made with features to handle reverse voltage in certain limits according to limitations
Do all Capacitors have Polarity?
Not all capacitors have polarity. Two terminals, one positive and one negative, are on polarised capacitors. Anode and cathode are the names of the positive and negative terminals. When connecting a polarised capacitor to a circuit, confirm its polarity because doing so might harm the capacitor.
The positive and negative terminals do not exist in non-polarized capacitors. Any direction can be used to connect them to a circuit. Materials used to make non-polarized capacitors are ceramics, that are mica, porcelain, and polyester. They are utilized in many different applications, including timing circuits, oscillators, and filters.
What is the capacitor’s positive side?
On an electrolytic capacitor positive pin called an anode is larger than the negative pin is anode. The anode is connected to high voltage and the cathode at negative or low voltage
Polarity of the Electrolytic Capacitor
Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors
- This capacitor comes with an aluminum structure that works as a valve. When positive voltage through electrolytic fluid metallic oxide layer is created. That oxide layer is an insulator that works as a dielectric.
- Polarization exists on the oxide layer avoid flow of electric charge. Aluminum electrolytic capacitor comes with manganese dioxide as a cathode, and aluminum as an anode.
Niobium and Tantalum Capacitors
- It is best to use for surface mount devices such as medical military and space devices. With tantalum as an anode, oxidation is an easy process like an aluminum electrolytic capacitor. tantalum comes with high conductivity, for wire contact. Also, the oxide is made on the surface, so there is more area for charging storage.
- Niibium capacitor operated with oxidizing material in wire for creating insulator. Insulators work as dielectrics having high permittivity as compared to tantalum-based capacitors.
What Happens After Reversing the Polarity of a Capacitor?
The polarity of the capacitor indicates that the polar capacitor needed to be in the forward forward-biased state. Anode connected with high voltage and check polarity before connection. If there is a wrong connection make or reverse polarity dielectric will damage. The result is a short circuit, making the capacitor overheating and causing electrolyte fluid leaks.
Which side of capacitor is positive?
Does AC capacitor have polarity?
Why are capacitors nonpolarized?
How to test a capacitor?
How do you check if a capacitor is bad without a multimeter?
Conclusion:
Electronic circuit design, and operation, and based on capacitor polarity. Engineers, and students, working with electronic devices must have capacitor polarity. power of capacitors and build effective and reliable electronic systems by choosing the accurate capacitor, paying attention to the proper polarity, and adhering to best practices.
Read Also:
- On AC Capacitor Wiring Colors – 2024 Complete Guide
- What is the Difference Between: Ceramic vs Electrolytic vs Tantalum Capacitors
- What is the Role of Capacitor in a Ceiling Fan?
- What is the difference between crystal, resonator and oscillator?
- Difference Between Capacitor and Inductor
- Different Types of Capacitors and Uses
FAQs
Q1: Can non-polarized capacitors be connected in reverse?
A1: Non-polarized capacitors can be used in any direction without causing any problems because they don’t have a fixed polarity.
Q2: What happens if you connect a polarized capacitor in reverse?
A2: An electrolyte leak, component damage, or possibly an explosion can be caused by connecting a polarised capacitor in reverse.
Q3: Are there any capacitors that don’t have polarity markings?
A3: Non-polarized capacitors do not need special markings because can be connected in either direction, whereas polarised capacitors often have distinct polarity marks.
Q4: How can I determine the polarity of a capacitor without markings?
A4: A multimeter is the best option to use for finding the polarity of a capacitor. Adjust the multimeter to the continuity or diode test mode, and positive probe to the positive terminal of the capacitor, and the negative probe to the negative terminal
Q5: Can capacitor polarity affect circuit performance?
A5: improper capacitor polarity can cause circuit issues, decreased operation, or failure of the device or system.