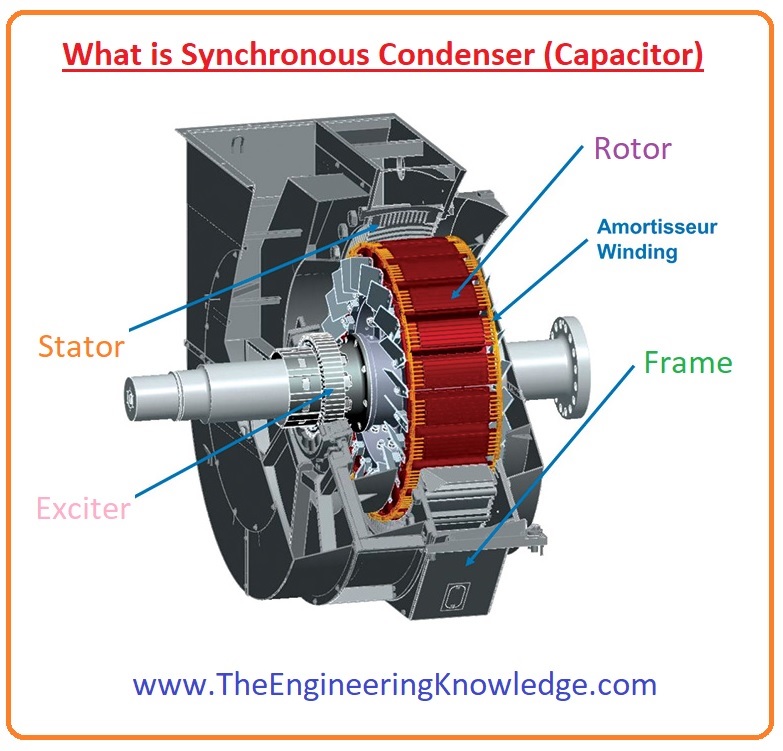
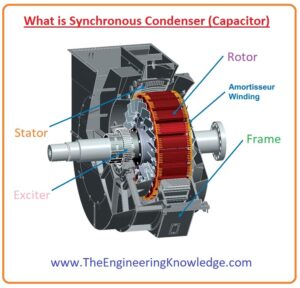
 Hello friends, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we are gonna have a look at What is Synchronous Condenser (Capacitor) and its importance in different electrical machines. In electrical system synchronous condenser is synchronous motor that gets excitation from DC source, there is no load connected with its shaft but it moves without any load. It also recognized as a synchronous compensator and synchronous capacitor. This motor is not used for mechanical power creation means electrical energy into mechanical transformation but for the stability of power at grid station. It stable the P.F and voltage of system for this purpose its field is regulated by voltage regulator to get or transmit reactive power according to system requirements. The fitting (installation) of this motor is similar to other electric machines.
Hello friends, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we are gonna have a look at What is Synchronous Condenser (Capacitor) and its importance in different electrical machines. In electrical system synchronous condenser is synchronous motor that gets excitation from DC source, there is no load connected with its shaft but it moves without any load. It also recognized as a synchronous compensator and synchronous capacitor. This motor is not used for mechanical power creation means electrical energy into mechanical transformation but for the stability of power at grid station. It stable the P.F and voltage of system for this purpose its field is regulated by voltage regulator to get or transmit reactive power according to system requirements. The fitting (installation) of this motor is similar to other electric machines.
The increment of field current of this motor increases the reactive power to the system. Its main benefit is the simplicity with which the quantity of correction can be regulated. Due to some short circuits in machines effect the stability of a system that is maintained by the K.E of a rotor of a synchronous motor. These devices are mostly used in such a system where higher voltage DC conversion occurs and reactive power is maintained by these condensers. In today’s post, we will have a look at its working, circuits, applications and some other parameters. So let’s get started with What is Synchronous Condenser (Capacitor).
What is Synchronous Condenser (Capacitor)
- A synchronous condenser is the replacement of capacitor banks for P.F. improvement in an electrical system.
- Its main benefit over capacitor banks is that its reactive power can be varied according to system requirements on a regular basis.
- When the voltage of system decreases then reactive power provided by the capacitor banks also decreases but in case of synchronous condenser it is the reverse, reactive power increases when voltage decrease.
- Due to this effect, these condensers are used with synchronous motor for power factor improvements while if capacitor banks are connected with the motor they increase losses in the motor.
- The power ratings of this condenser connected with the system is between twenty MVAR to two-hundred MVAR and used hydrogen as a cooling agent.
- Normally ninety-one percent of hydrogen is exiting in these condensers but for saving operation it should be seventy percent.
- If we rotate a simple loop in a magnetic field then it will produce ac voltage.
- When linked to a circuitry current flowing depend on how the voltage on the structure (system) is dissimilar from this open-circuitry voltage.
- One point you should keep in mind that the torque in either motor or generator relies on active power (P), not on the reactive power (Q).
- With the increment in the load connected with synchronous motor, the value of stator current Ia also increases irrespective of the field current.
- With the increment in load on shaft of motor in P.F becomes unity in both over-excited and under-excited motors.
- This variation in the P.F is higher than the variation in armature current Ia with the increment in load.
- The angle of Ia changes with the variation in IF. The armature current’s value is high for less field excitation and less for high excitation.
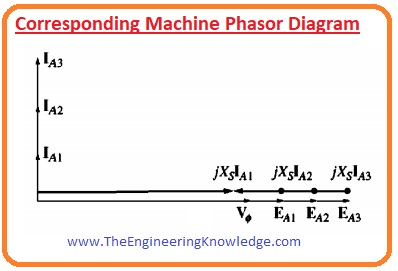
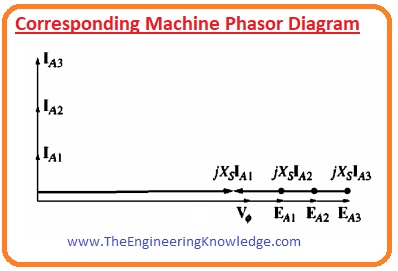
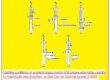
Synchronous Capacitor or Synchronous condenser Phasor Diagram
- A synchronous motor bought to run a load can be functioned overexcited to deliver reactive power Q for an electrical system.
- In previous years these motors were only used for P.F improvements of the system not to run a load
- The phasor diagrams of synchronous motor working in over-excited conditions without any load shown below.
- As there is no load connected with motor so power (EAsinand Iacosø) drawn from motor is 0.
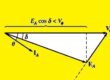
- As KVL equation for synchronous motor is given as.
Vø =EA + jXsIA
- The terms jXsIA is pointed towards left in phasor diagram and armature current Ia and ninety-degree
- if we compare Ia and Vø than we can see that it is like a capacitor.
- An overexcited synchronous motor without any load behaves like a huge capacitor to an electrical network.
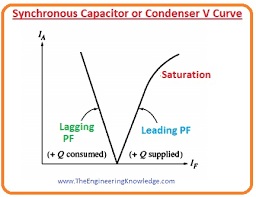
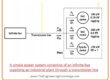
Synchronous Capacitor or Condenser V Curve
- The V curve of a synchronous condenser is drawn in a given figure.
- As the active power provided to motor is 0, at unity P.F that means armature current is zero.
- As the IF is augmented over this point, the line current upsurges in a linear manner until get saturation.
- The given figure shows the result of increment in IF on phasor diagram.
- Nowadays, conservative static capacitors are cheaper to purchase and use than a synchronous condenser.
- Nevertheless, some synchronous condensers can still use in older industries.
Synchronous Condenser Applications
- These are some important applications of a synchronous condenser.
- As synchronous motor in over-excitation states has leading PF. This feature enhances its use in different industries for power factor improvements.
- Induction motors transformer behave like inductive loads and operate at lagging P.F. when induction motors are connected with light output (load) then the motor consumes the larger value of Q that decreases the P.F. Due to this increases in reactive power increases the losses in the system.
- So synchronous motors are joined with the induction motors to deliver reactive power to an induction motor. That increases the P.F of the system and current drawn from the motor.
- The synchronous capacitor has the ability to deliver continuous P.F improvements with the capability to generates up to one-fifty percent extra vars.
Capacitor bank Vs Synchronous Capacitor
- Through 1950 the working of a synchronous capacitor is very popular in industries.
- They remain replacement of capacitors for P.F improvements as due to harmonic in system capacitor gets overheated and disastrous catastrophes.
- Synchronous capacitors are also maintained voltage. Capacitor banks generate a reactive power in such a way that it is directly proportional to the square of terminal voltages.
- So if the voltage of the system connected with the capacitor bank decreases, the capacitor’s reactive power also decreases, and if system’s voltage increases then also capacitor’s reactive increases that create problems.
- While in the case of a synchronous capacitor it not happen, these condensers generate a less reactive power in case of high voltage and high reactive power in case of less voltage that remains the system stable.
- A synchronous capacitor is also known as Dynamic Power Factor Correction These motors are very suitable for such a system where modern controllers are used for regulation of power factors like PLC.
- A synchronous capacitor is also used to regulate the voltage at distant transmission lines, especially that are connected with inductive load.
- I also have written some related articles you can also read them are listed here.
- Introduction to Synchronous Motor
- Synchronous Motor Torque-Speed Characteristic Curve
- Synchronous Motor Starting Method
- What is Synchronous Condenser (Capacitor)
- Synchronous Motor Power Correction.
- Types of Synchronous Motor
- Effect of Field Current Changes on a Synchronous Motor.
Friends it is the detailed post on synchronous condenser I have mentioned each and everything related to this post with the detailed. If you have any query about this article can ask in the comments. See you in the next tutorial Synchronous Motor Starting Methods.
.