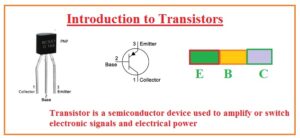
 Hello, friends welcome to another interesting post in this post we will have a detailed look at the introduction to a transistor. There are different electronic devices are commonly used in industries and different engineering projects that used different types of electronic components such as diode, LEDs, and capacitors. Like this electronic component, there is a most commonly used transistor that comprises of terminals it is used in different electronic devices as switches and amplifiers.
Hello, friends welcome to another interesting post in this post we will have a detailed look at the introduction to a transistor. There are different electronic devices are commonly used in industries and different engineering projects that used different types of electronic components such as diode, LEDs, and capacitors. Like this electronic component, there is a most commonly used transistor that comprises of terminals it is used in different electronic devices as switches and amplifiers.
As for the creation of different projects you must have contact an electronic project assembler or manufacturer. There are numerous projects assembled and suppliers are working in this world but the most commonly accessible and reliable is PCBWAY. It is a china based PCB supplier that provides also different features and services to electronic and electrical engineering projects you must contact it for the project assembly. they also provide PCB with a reasonable price and also have some discounts for the creation of PCB and projects. They provide 10 PCS with one to two layers in just five dollars. In thirty dollars 1 to 20 Pcs. You must visit that supplier for the creation of your project. So let’s get started with an introduction to transistors.
Introduction to Transistors
- The transistor belongs to the semiconductor family it is an electronic device that is used in different types of amplification switching circuits as well as the application of power.
- It is constructed by a semiconductor substance and has 3 pinouts that are used to make exterior linking with other circuit parts.
- The voltage gave at one pair of the pinouts of this module regulates the value of current at another group of its pinouts.
- Nowadays these modules are available in the market in single modules also exist in the form of integrated circuits that are used in an embedded system.
- The transistor is constructed by silicon and germanium with and other types of semiconductor substances are used for the creation of the transistor.
- If the transistor is a type of field-effect transistor it has only one category of charge carrier and in the case of BJT it comprises of 2 categories of charge carriers.
- If do a comparison between the transistor and the vacuum tube then we come to know that the size of the transistor is less than the tube and uses less power than the tube.
- But some special category of the tube has some advantages over the voltage in case of a large value of functioning frequencies.
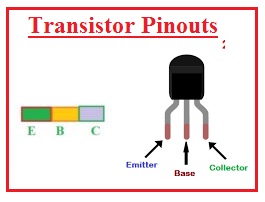
Transistor Pinouts
- There are three main pinouts of this electronic component.
- Emitter it is the first pinout from this pin output.
- Base it is the central part of the transistor where normally supply is connected and operates as control of the valve.
- Collector, It is the larger part of the transistor than the other two and has a larger number of carriers
What is BJT
- The BJT or bipolar junction transistor is a category of transistor that consists of 2 types of charge carriers like holes and electrons.
- While in another transistor like FET three is a single type of condition is used due to one type of charge to current flow.
- It is used in different types of switching and amplifier circuits where a small value of current is given at its one point and other parts of circuits large current is controlled
- There are 2 main types of junction in BJT first one N and the other is P. In the P region, there are positive charges or hole is the majority carriers and N region has electrons or negative charge carriers as the majority.
- The junctions are created through the combination change in the doping substance used.
- These transistors are generally used in different electronic devices like computers, laptops, and some other electronic devices due to their simple and reliable operation.
- They are employed in digital switching and amplifier operations.
- There is a certain type of BJT that used to control large value of voltages as a radio frequency amplifier
Transistor Mode of Operation
- There are normally 4 types of operation mode exit in the transistor that are explained here.
Forward Mode
- In this mode of operation, there is forward biased condition for the base and emitter and a reverse-biased biased for the base-collector.
- There is a large value of current gain that exists in the transistor in common emitter arrangements.
- The value of ICE is equal to the base current and has a larger value than base changes
Reverse Mode
- In this mode, the connection for forwarding biased mode are reversed to make it reverse mode.
- In this mode emitter and collector, parts are switches
- As the design of BJT is such that it has a large value of current gain in forward mode while in reverse mode its value decreases two to three times.
Saturation Mode
- In this mode there both junctions is in forwarding forwarding-biased state in the case of saturation mode there is large current flows from the emitter to the collector. This mode operates as on an off configuration of the switch
Cutoff
- In this mode of operation the reverse-biased state than the saturation state. In this mode very few current passes.
Transistor as Switch
- The switch used in digital electronics to control the function of the circuit is created through the use of a transistor.
- In the below figure the circuit configuration for the transistor as the switch can see which indicates that with the increment in the base voltage there is an increment in the emitter and collector current since the base is operating as control that controls the applied voltage.
- The voltage about the collector loss since the resistance value between the collector and emitter decreases.
- If there is just 0 resistance among the collector and emitter then the value of IC can be regulated through the use of resistance offered by the load.
- This mode of operation is saturation the current is passing from the collector to the emitter.
- In saturation, state switch is on
Transistor Applications
- The main applications of these modules are explained here.
- It used as a switch
- It used as an amplifier
- It used as a current control device in the form of BJT
- Used as a voltage control device in the form of FET
Field effect transistors or FET
- The FET is a transistor type that controls the flow of current through the use of an electric field. There are two types of FET JFET and MOSFET.
- It has three pinout sources, gates, and drains. It controls the current movement through the voltage applied at the gate that controls the conduction between the drain and source-like base and controls the current flow between the emitter and collector.
- FET is also called a unipolar transistor because it has a single-carrier operation. It means conduction in these transistors is done through electrons or holes not both like BJT transistors. These transistors provide a high value of impedance for less value of frequency.
- MOSFET type of FET is commonly used in electronics
MOSFET Transistor
- Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor or MOSFET is a type of FET transistor that is created through controlled oxidation of silicon.
- It has an insulated gate that controls the conduction of this transistor. The conduction of transistor can be regulated through use of applied volts in different applications like switching and amplifier circuits
- MISFET is the same as MOSFET and IGFET are also same.
- The basic advantage of using MOSFET in electronic circuits is that it needs very little input current to control load current the BJT transistor.
- It has two modes of operation enhancement mode and depletion mode. For enhancement mode voltage given to gate terminal increases the conductivity of the module and for depletion mode voltage given at the gate decreases the conductivity
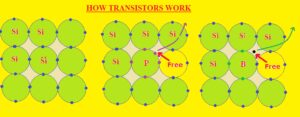
HOW TRANSISTORS WORK
- Silicon is a semiconductor material that lies in the fourth group of the periodic table and has four electrons in a valance shell.
- Doping is a process through which impurities like boron or phosphorus are added to enhance the semiconductor features.
- The below diagram figure denoted as indicates pure silicone material and dots in this figure denote electrons. Figure denoted as b shows that silicon has doped phosphorous material.
- The phosphorus is pentavalent is an impurity that belongs to the fifth group of the periodic table and has five electronics in the outer shell.
- Four electrons of silicon are bonded to four electrons of phosphorus and one electron remains free. It makes N type of semiconductor material. If supply is provided to material electrons flows that cause current
- Figure denoted as d doped with boron that is from the trivalent impurity and third group of the periodic table.
- Three electrons of boron make the bond with three silicon and one remains un bond and the hole is created. This material is called a P-type semiconductor that has trivalent impurity and hole
- The transistor is a combination of N and P materials. It has two combinations NPN and PNP.
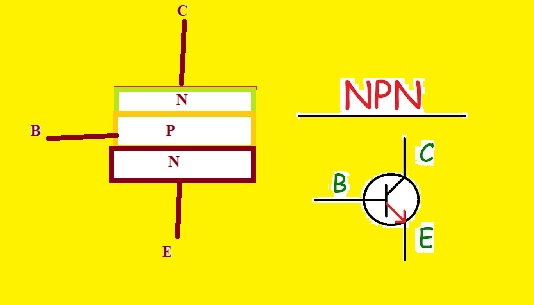
What is NPN Transistor
- In the below figure, you can see the NPN transistor’s internal structure
- In the below figure, you can see the upper N region. The upper N end is the collector P region is the base and the lower N region is the emitter
- The PN junction between two N region is small and current easily passes that region electrons goes to the P region and are positioned in the Holes of the P region
Advantages of Transistor
- It used as a single IC
- It helps to create highly efficient circuits
- It provides the high-speed switching
- It uses less power
- Operating life is longer
- It uses fewer input volts
- Less expensive and small size
Transistor Limitations
- It can be damaged through electrostatic discharge
- It lack high electron movement
- It also disturbs by cosmic rays and radiation
Is a transistor AC or DC?
- The transistor uses dc volts to operate so it is dc component not AC
Why it is called a transistor?
- A Transistor word is a combination of transfer and resistance. Because it transfers resistance from one point to another of the device. So it is called a transistor. it has a high value of input resistance and a low value of resistance t output.
What are the 2 main types of transistors?
- FET and BJT are two main types of transistor
What is the unit of the transistor?
- The transistor works as a switch and amplifier. Standard units of transistor of electrical measurement are Ampere (A), Volt (V), and Ohm (Ω),
Which region of the transistor is lightly doped?
- The base is lightly doped thatn emitter since the base has high current flow
What is the normal biasing of the diodes of the transistor?
- The emitter-base junction is forward-biased and the collector base is reverse-biased
How many depletion regions does a transistor have?
- There are two depletion regions in the transistor
Read also:
- Introduction to A1015 PNP Transistor
- Difference between Vacuum Tube and Transistor
- Introduction to C945 Transistor
- Siren Circuit using 2N2907 Transistor
- Introduction to BC847 Transistor
- What is PNP Transistor: How It Works and Its Applications
- Introduction to BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor), Pinout, Working, Characteristic & Applications
Faqs
- Transistors are commonly used in electronics. Its common uses are switches, amplifiers, oscillators, modulators, detectors, BJT, FET, HBT, avalanche transistor, etc.
- The transistor is created with 3 components base, collectors, and emitter. These 3 components are transistor pins emitter is the first pin and affects the output of the transistor.
- The transistor is like an electron valve. The base pins like handles that adjust to allow more current or fewer electrons to flow in the emitter to the collectors
- Transistors is semiconductor devices used for amplification or switching signals. Transistor are divided in three types bipolar transistors (bipolar junction transistors: BJTs), field-effect transistors (FETs), and insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs).
That is all about the transistor i tried to cover each parameter related to the transistor. If you have any further queries ask in the comments. Thanks for reading have a nice day





Superb blog! Do you have any hints for aspiring writers?
I’m planning to start my own site soon but I’m a little lost on everything.
Would you suggest starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many options out there that I’m completely overwhelmed ..
Any recommendations? Appreciate it!
Oh my goodness! Amazing article dude! Many thanks, However I am having difficulties with your
RSS. I don’t know why I cannot join it. Is there anybody else having identical
RSS issues? Anyone that knows the solution will
you kindly respond? Thanx!!