Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will learn What are the Steps Flexible PCB Manufacturing Process. Flexible Printed Circuit Boards are common and famous due to their flexible, reliable function. They come with benefits than rigid PCBs, like good use fo space, reliable structure, and flexible nature. In this post, we will learn different factors for the flexible PCB manufacturing process. So let’s get started with the Flexible PCB Manufacturing Process
Introduction to Flex PCB
Flexible PCBs, known as flex circuits or flex boards, are used to the connection bend and twists having a good function. It has a thin, flexible substrate made with polyimide or polyester that converts the structure of complication and fits in tight areas. Flex circuit manufacturing has many steps involved such as ensuring the manufacturing of high-quality, reliable boards.
Understanding Flexible PCBs
These boards come with three layers substrate, conductive traces, and protective cover layers. The substrate operates as a base and has flexible traces made with copper and make connections with electrical connections. The protective layer protects traces and increases their reliability
Benefits of Flexible PCBs
. The flexible nature of these boards is for the integration of compact and less-weight layouts decreases with over-assembly. it does not use connectors and features to remove wiring helps the simple assembly, and reduces time and expenses for production. But the flexibility of these circuits reduces mechncal damages due to vibration and increases the reliability of the design
Designing a Flexible PCB
Steps in the Flexible Printed Circuit Manufacturing Process
Step 1: Material Selection
First of all material is selected for board creation. The material was selected based on stability for heat, dielectric features, and costs. Polyimide and polyester are used since they have high resistance for temperature, flexibility,, and electrical insulation. Conductive traces created of copper
Step 2: Circuit Design
When the material is selected design is made. Here schematic of the circuit is made that explains all compone and routing traces. Circuit design provides good electrical features and signal quality
Step 3: PCB Layout
Circuit design is transformed into a practical layout. That comes with components on a flexible substrate and routing traces to make connections.
Step 4: PCB Printing
Now the board is printed. Here transfer of circuits in the circuit design on a flexible substrate using methods such as inkjet printing, screen printing, or photolithography. it needed the correct circuit pattern
Step 5: Component Mounting
When circuit desing is completed components are mounted. SMT is used normally to connect components of flexible board. The compone are properly connected with the use of a soldered-on substrate while avoiding solder joint and other functions
Step 6: Soldering
Now, the flexible boards face a soldering process for proper connections. Solder paste is used for exposed pads, and the board faces a reflow process. Heat-melted soldering paste makes a strong connection of the components and the traces.
Step 7: Testing and Quality Control
Different tests are performed on board to ensure quality and reliability. Automated optical inspection and electrical testing are done to detect any manufacturing faults, like short circuits or open circuits.
Step 8: Final Assembly
After clearing the tests barod is ready for final assembly. With the more required components attached on barod
Flex PCB Manufacturing Process & Advantages – JLCPCB
JLCPCB has started the flexible PCBs, which come with easy PCB assembly, and is now offering c $25 for five pieces. JLCPCB has also provided $54 signup vouchers for new users at https://jlcpcb.com/
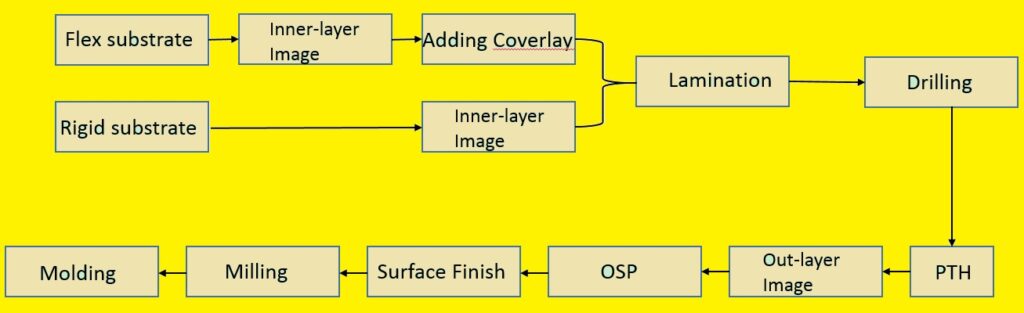
JLCPCB Flex PCB Manufacturing Proces
Flex Circuit Design:
Design of the board is made with the use of CAD, flexible boards are designed in a professional way.
Material selection:
Proero substrate materials are selected for the board. PET layer and Poyimide are commonly used by JLCPCB. They have high resistance temperature, and a flexible nature. Conductive paths are made on these materials. Since they are highly conductive and flexible, copper used for layer creation
Adhesive materials such as epoxy, acrylic, or silicone, are used to connect layers of flexible boards
Coverlay material: The conductive material on the Flex PCB is protected with the use of polyester and polyimide and this process is called coverlay
Solder mask material:
In the soldering process, materials are used for the protection of a conductive layer called a solder mask, Epoxy or other photo-imageable materials are frequently used to make solder masks. Components connected to boards are also protected from environmental conditions by this mask application.
Material preparation:
The surface of the substrate material is then cleaned and etched to provide a smooth, clean surface for the printing of the circuit.
Circuit printing:
The main step in the creation of these boards is photolithography. With the use of photoresist and etching, the circuit pattern is transferred from a planned layout to the substrate material in this technique. Photoresist material is applied to surfaces after the preparation of the material. UV light casues photoresist, light-sensitive substances to become hard. Then photomask alignment is made that places photomask on the substrate and glowing UV light is applied to expose the photoresist material in the desired pattern.
Circuit layout printed on a substrate having photomask. To ensure the accurate configuration of the circuit layout on the substrate, the photomask must be aligned.
UV Exposure
Etching
here extra photoresist material is removed from the substrate with the use of a solvent which dissolves photoresist after the circuit has more substrate material, just printed circuit design on the substrate.
Component placement:
Soldering:
Reflow or wave soldering process uses cor component connection on board
Testing:
Differnt tests are performed to check teh faults of the baord and make sure that all components are connected accurately
Flex PCB Testing
In the production of Flex PCBs, the following testing techniques are frequently used:
Electrical testing: In this test, electrical connections are checked of Flex PCBs. Voltage is provided to the circuit and current flow in the board. Differnt parameters like resistance, capacitance, and impedance, are measured in addition to any circuit breaks or short exits
Visual inspection: Cracs scratch and delamination, or alignment issues are checked during the visual inspection magnify glass used for this purpose
Functional testing: Un this test baord proper working ns required functions checked.
X-ray inspection: Soder joints existing on the boards are checked with the use of X-ray inspection
Advantages of Flex PCBs
Flexibility
These boards are flexible in nature and easily bend, and twist, without affecting the connection. So best for applications where flexibility is needed
Space Saving
Rigid circuit boards are not made to be configured in smaller locations but flexible boards are easily configured
Durability
Extreme heat and vibrations 2 conditions that help to make boards operate for a longer duration. So best for use in automotive, military, and aerospace sectors.
, JLCPCB provides new users with up to $54 in registered discounts. To purchase premium flex PCBs, register and upload your Gerber files here: https://jlcpcb.com/