 Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Forward & Reverse Biasing. The basic comparison between forward and reverse biasing is that in forward biasing configuration positive end of the battery is attached to the P region of the semiconductor substance and the N region with the negative end of the battery. In the reverse biased condition, the P region is attached to the negative end of a battery and the N region to the positive end of the battery. Biasing is a technique through which a power supply is provided to the semiconductor instruments.
Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Forward & Reverse Biasing. The basic comparison between forward and reverse biasing is that in forward biasing configuration positive end of the battery is attached to the P region of the semiconductor substance and the N region with the negative end of the battery. In the reverse biased condition, the P region is attached to the negative end of a battery and the N region to the positive end of the battery. Biasing is a technique through which a power supply is provided to the semiconductor instruments.
The applied potential has 2 categories forward and reverse bias. In forward-biased conditions, the potential barrier of the diode decreases and allows the flow of current. But in the reverse-biased state due to potential difference potential barrier increases due to charges not crossing the junction and the current not flowing. In reverse biasing there is a huge amount of resistance is offered that does not allow to flow of current. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at both forward and reverse biasing with the detailed and compare them to find their differences. So let’s get started with the Difference Between Forward & Reverse Biasing.
Difference Between Forward & Reverse Biasing
Forward Biasing
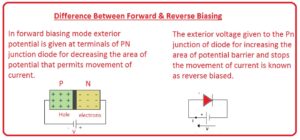
- In forward biasing mode exterior potential is given at terminals of PN junction diode for decreasing the area of potential that permits movement of current.
- In this mode configuration of connection is the negative end of the battery is attached with the negative or N side of the device and the positive end of the power supply with the P region of the device.
- The area of the depletion region is less than the reverse-biased condition.
- The value of resistance offered in the configuration is less.
- In forward biasing the area of potential barrier decreases.
- The value of voltage given is larger at the anode than at the cathode.
- In forwarding biased conditions, current flows through the device.
- The value of the current depends on the applied voltage.
- In forward biased state device operates like a conductor.
Reverse Biasing
- The exterior voltage given to the Pn junction of the diode for increasing the area of the potential barrier and stopping the movement of current is known as reverse bias.
- In reverse-biased mode, the negative end of the battery is attached to the positive or P end of the device, and the positive point of the battery with the anode or N region of the device.
- In this configuration area of potential barrier increases.
- The current does not flow in reverse-biased mode due to high resistance.
- The magnitude of the current is zero.
- In this mode voltage at the cathode is larger than the anode.
- For reverse biased conditions small value of reverse current flows.
- The area of the depletion region is larger than the forward-biased condition.
- In this configuration movement of current high resistance is offered.
- The device operates like an insulator in the reverse-biased state.
Read also:
- What is a Rectifier Diode? Symbol & Uses, Applications
- Introduction to FR102 Diode Pinout, Datasheet, Applications, Uses Features
- Introduction to 1N5401 Diode
- Introduction to 1N5408 Power Diode
- Difference Between Diode vs Transistor
- Difference Between PN Junction & Zener Diode
- Introduction to 1N5408 Power Diode
FAQs
- Forward biasing is when current flows in a forward direction due to voltage provided in the forward direction. For Forward bias, The type anode of the semiconductor is connected with the positive end and the N-type pin is connected with the negative point of the battery
- The base-emitter junction is forward-biased, so VBE≈0.7 V (silicon). The base-collector junction is reverse-biased, so VCB is larger. Conventional current passes in the collector and base and out of the emitter
- Reverse bias defines the use of external voltage about the semiconductor diode so positive terminals of the battery is connected to the N side and negative terminals are connected with the p-side of the diode.
- The main benefit of bias in the diode are decrease in current flow. The main benefit of reverse bias is that it reduces current flow in semiconductor devices. It can be best for managing and controlling the functions of electronic devices.
- Current flows in the reverse direction when the diode is reverse biased called reverse current. Reverse current is smaller than forward current.
- Forward bias reduces diode resistance and reverse bias increases diode resistance. Current passes easily in forward bias and reverse bias does not allow current to flow in the diode
- NPN transistor where collector potential is higher than emitter potential and base potential is 0.7 volts higher than emitter potential. The base-emitter junction is forward-biased while the base-collector is reverse-biased.
- The process of providing external voltage to a PN junction semiconductor diode is called biasing. External voltage to PN junction diode is provided through forward biasing or reverse biasing. If the p-n junction diode is forward-biased, it helps the electric current flow.
- No external voltae is provided to the PN junction diode.
- Zener diode is used as voltage references and shunt regulators for regulating voltage in small circuits. If connected in parallel with a variable voltage source so it is reverse biased, the zener diode conducts when the voltage reaches the diode’s reverse breakdown voltage.
- The reverse bias comes with an anode voltage that is less thatn the cathode voltage, while the forward bias comes with an anode voltage larger than the cathode voltage.
- Reverse bias comes with marginal forward current and forward bias has a larger forward curent
That is a detailed post about the difference between forward biasing and reverse biasing if you have any further queries ask in the comments. Thanks for reading. Have a good day.