 Hello, friends, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, I am going to explain What is Circuit Breaker. The first-time circuit breaker was invented by Tomas Edison (who was the inventor of the United States of America) in 1879. He used this circuit breaker in lighting circuitry to minimize short circuits and overloading. Before the invention of a circuit, breaker fuses were used in different circuits but in large power and grid systems, this fuse did not operate well and did not provide protection to huge circuitry. In the grid station where large no of generators of high ratings are linked where these circuit breakers are necessary to break the faulted component from the circuitry.
Hello, friends, I hope all of you are enjoying your life. In today’s tutorial, I am going to explain What is Circuit Breaker. The first-time circuit breaker was invented by Tomas Edison (who was the inventor of the United States of America) in 1879. He used this circuit breaker in lighting circuitry to minimize short circuits and overloading. Before the invention of a circuit, breaker fuses were used in different circuits but in large power and grid systems, this fuse did not operate well and did not provide protection to huge circuitry. In the grid station where large no of generators of high ratings are linked where these circuit breakers are necessary to break the faulted component from the circuitry.
Nowadays from every simple circuit to complex circuit from our house wiring to large buildings’ electrical wiring or generation system, distribution systems all use a circuit breaker to protect their load from short circuits or overloading conditions. There are many types of circuit breakers like a miniature circuit breakers, SF6, oil circuit breakers, air circuit breakers, and vacuum circuit breakers. In today’s post, we will have a look at circuit breaker construction, principles, applications, types, and some related parameters. So let’s get started with What is Circuit Breaker.
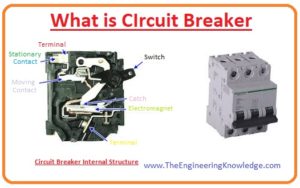
What is Circuit Breaker
- The circuit breaker is an electrical device that is used in a different circuit to provide protection from different faults like a short circuit, it breaks the circuit when a fault occurs.
- It operates both mechanically and the automatic way its construction is such that it automatically brakes circuits.
- During the construction of the breaker, it keeps in mind at which current value it will operate as nowadays such circuits are working in our power system that needs a high accuracy circuit breaker.
- In simple words, the main operation of a circuit breaker is to stop the flow of current when a fault occurs.
- Its advantage over a fuse is that after its operation of removal of a fault, it starts operation again while the fuse must be changed after fault detection.
- There are numerous ratings of circuit breakers available for small-size devices that used less current to larger circuits like switchgear panels that used high voltage.
- If we look at its operation then it is known as OCPD (over current protection dive).
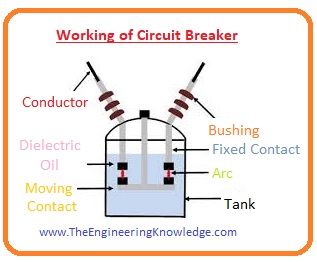
Working of Circuit Breaker
- The operation of the circuit breaker is simple it first of all senses the fault occurs in the circuit.
- In small circuits or less voltage rating breakers sensing of fault is done by the breaker itself then it breaks the circuit.
- Normally heating is produced by the large current of fault used for that detection purpose.
- While in large circuits or in grid stations for sensing fault protection relays are used that detect a fault and send a signal to the breaker then it breaks the circuit.
- For this large system, there is a need for a separate power source like a battery, but some circuit breakers get supply from current transformers.
- After sensing the fault occurring in a circuit the connections of breakers get separated, for these contacts separation mechanical energy provided by the spring or compressed air applies force on these contacts to open.
- The magnetic field of current produced by the fault is also used for the tripping of the breaker.
- In smaller circuit breakers there is a manually operated lever is installed to remove the load or again join the contacts that separated during a fault.
- While in larger circuit breakers motors are installed to provide energy to the spring that was used during tripping.
- The breaker’s contact has the ability to bear the heat produced during fault and can also bear the heat of the arc then generates during the breaking of the circuit.
- For that purpose, the materials used for the construction of breaker contacts are copper, silver, or some other material that can bear high temperatures like alloys of metals.
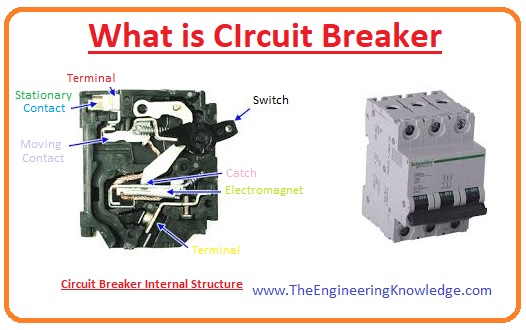
Circuit Breaker Working Principles
2 main contacts in a circuit breaker are Fixed contacts and Moving contacts
When the breaker is closed, that is a normal condition, contact touch each other and carry current.
In a closed breaker, current-carrying contacts are called electrodes that work with each other due to the pressure of the spring.
Switching and maintenance of the system is looked after by opening or closing the arms of a breaker. The breaker is opened through a pressure application to trigger.
if there is a faulty current passing through any component of a system, the trip coil breaker is energized and moves from each other open circuit.
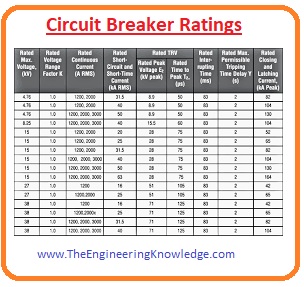
Circuit Breaker Ratings
- The circuit breakers are constructed with different ratings according to their applications and the circuits for which they will be installed.
- The ratings of MCB (miniature circuit breaker) are fixed if we want to vary its rating then there is a need to change the complete structure of the breaker.
- But larger rating breakers have the ability to change their operation rating let’s suppose we have a breaker of four hundred ratings it can also be set to operate at three hundred ampere current.
Circuit Breaker Tripping Principles
The circuit breaker comes with two different tripping principles for protecting the circuit.
Thermal protection that causes circuit interruption for overheating
The protection design through the electromagnet principle is due to short circuits.
if the breaker is in on state, current flows from lower terminals to the bimetallic strip to the electromagnetic coil, then moving contact, and stationary contact, and to the upper terminal.
Circuit Breaker Types
- Different types of circuit breakers are classified according to structure, tripping type, and voltage ratings.
Low voltage circuit Breaker
- Less voltage circuit breakers are normally used in our homes, offices, and some small industries. Some small rating circuit breakers are discussed here.
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker): the rating of this breaker is to one twenty-five amperes. The tripping current of this breaker is not adjustable.
- MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker): the rating of these breakers is sixteen hundred amperes. Its operation is thermal and non-thermal.
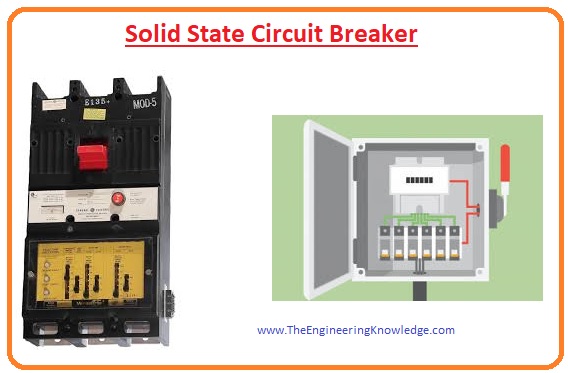
Solid-State Circuit Breaker
- This type of circuit breaker is a new invention in circuit breaker categories that changed from mechanical to electrical Another name of a solid-state circuit breaker is a digital circuit breaker.
- It provides many benefits over the other breakers like its operating time is fault-detecting, and its fault-detecting power is also high its operating life is also longer.
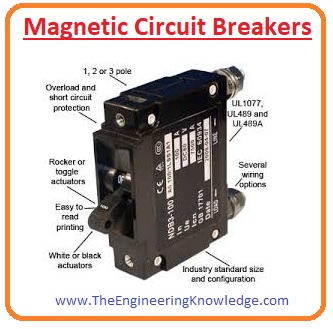
Magnetic circuit breakers
- This type of circuit breaker uses a solenoid for tripping purposes of disconnect connections the force used for disconnection depends on the amount of current.
- In some circuit breakers instead of solenoid electromagnetic force is used for tripping.
- The contacts of the breakers are fastened to each other through a latch. With the increment of a current due fault, the solenoid’s pull releases the latch, due to the connections of breakers getting off.
- The breakers are mostly used in the United States of America.
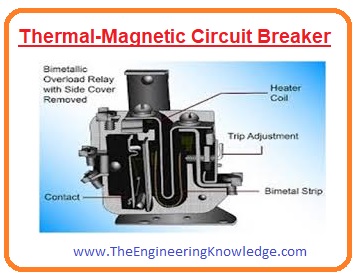
Thermal-Magnetic Circuit Breaker
- The thermal-magnetic circuit breaker is mostly used in DBs (distribution boards).
- In this circuit breaker, there are 2 types of elements used for the detection of faults.
- This ist element is an electromagnet that is used to detect the large surging current in the circuitry. Surging current is very dangerous for our home appliances like air conditioners, freezers, etc.
- The electromagnet operates very fast when surge current flows through the circuit and disconnects the circuit.
- The 2nd detection element in this circuit is the thermal bimetallic strip work for the less-level electric surges or for overloading conditions.
- When a fault occurs then current passes through this bimetallic strip due to current heating produced that bends the strip and removes it from the circuitry.
- Its popularity is due to that it responds very fast to a fault and starts its operation when a fault is removed.
SF6 Circuit Breakers
SF6 is a sulfur hexafluoride breaker where sulfur hexafluoride used as arc extinguishing
The sulfur hexafluoride gas attracts elections. Circuit contacts are opened, and gas flows through the chamber striking an arc.
The free electrons are absorbed through SF6 causing immobile negative ions. For arc extinguishing, the insulating strength of the medium must be high. Both contacts, fixed and removing contacts are put in an arc chamber with the gas.
Advantages of Air Circuit Breaker
- it reduces the fire hazard.
- Arcing products can removed.
- The contact gap is less as dielectric strenght increases.
- it is best for frequency uses since arcing time and arc energy are small.
- it can interrupt current.
Disadvantages of Air Circuit Breaker
- The features of arc extinguishers are not good
- it is sensitive to types of voltage.
- Compressor needed to maintain air circuit breaker.
- It is sensitive to the variation in voltages.
- The properties of arc extinguishers are inferior.
Read also:
- Difference Between a Single and Double Pole Breaker
- Where is the Doorbell Breaker Located? Easy Way to Findout
- What to Do if Your Circuit Breaker Won’t Reset
- Top Reasons Why Electric Outlet Stopped Working Breaker Not Tripped?
- 60 Amp Wire Size – Which AWG is Best for 60 Amp Breaker
- What Is A Shunt Trip Breaker & How Does It Work? Detailed Guide
Faqs
- The main breaker controls the current flow from two main wires to hoe bus bars. Tripping the main circuit breaker disrupts 240 volts of current before reaching the branch breaker. If the main breaker is tripped it will off the devices
- The breaker is an electrical switch made for the protection of the circuit from damage due to overcurrent, or short circuit. It is main function to interrupt current flow after protective relays detect fault.
- If current overflow exists in MCB, bimetallic strips get heated and deflect through bending. The deflection of the bimetallic strip releases the latch. The latch resulted in MCB to off by stopping the current flow in a circuit.
- A breaker is a switch made for an automatic open circuit to avoid damage to components, overheating and fire overload
- The circuit breaker is an automatically operated switch that detects issues and through interrupting continuity, has featues to discontinue electric flow.
What are the advantages of a circuit breaker?
- It is best to replace mechanically operating fuses.
- highly reliable.
- more functional.
- If the trip can easily fixed
- Discharge voltage on lines to earth after disconnection.
- it disconnects part of the system from live parts in case of no load condition.
- Switching during normal and abnormal conditions interrupts the fault currents.
- MCB comes with a fixed tripping circuit and MCCB has a moveable tripping circuit. Pole-in breakers define some switching and safety phases it has for maximizing protection. The MCB normally comes with 1, 2, or 3 piles, and MCCB has 4 poles.
What is another name for RCCB?
- RCCb full form is Residual Current Circuit Breaker. and called RCB or RCD.it is an electrical wiring devices that disconnect circuits when detects a current leaked to earth wire.
That is the detailed tutorial on the circuit breaker I have mentioned and everything related to a circuit breaker in this post. If you have any issues or queries related to circuit breakers ask in the comments. Thanks for reading. See you in the next tutorial.








I didn’t know that a circuit breaker protects a circuit whenever a fault happens. I don’t know a lot about electricity but I can imagine how important this is. It keeps the electric system from messing up and frying your whole home.
I like the helpful info you provide in your articles. I will bookmark your weblog and check again here frequently. I’m quite sure I will learn many new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
It’s nice that you mentioned how the main operation of a circuit breaker is to stop the flow of current when a fault occurs. I was looking at a list of industrial electrical parts earlier and I saw some circuit breakers in it. I heard circuit breakers are quite essential, which is why they are being used for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes.