 Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will have a detailed look at J-STD-001| J Standard Soldering Requirements. The commonly used standard is J-STD-001 which defines the specifications for soldering electronic assemblies. It provides the soldering process with a detailed framework, making sure the dependability and caliber of electronic devices. In this article, we will discuss J-STD-001 in detail. So let get started Introduction to J-STD-001
Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will have a detailed look at J-STD-001| J Standard Soldering Requirements. The commonly used standard is J-STD-001 which defines the specifications for soldering electronic assemblies. It provides the soldering process with a detailed framework, making sure the dependability and caliber of electronic devices. In this article, we will discuss J-STD-001 in detail. So let get started Introduction to J-STD-001
What is J-STD-001?
- The Joint Electron Devices Engineering Council (JEDEC) and the IPC Association Connecting Electronics Industries make the J-STD-001 standard. It defines the different parameters such as materials, procedures, and inspection standards, for soldering electronic projects. This standard first time was in 1992 since that there many changes have been made in it to use in the latest technologies

Importance of J-STD-001
- The stability and functionality of electronic devices are based on the soldering process used to make the products. Electrical failure made by improper solder junctions required costly preparation and replacement of devices. The overview given by the J-STD-001 for soldering ensures the high value of caliber and dependability of electronic assemblies.
- With that, this standard fulfills the needs of customers, authorities, and industry standards. Following the different rules can have good of electronic devices
J standards
- The Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association (JEITA) makes this standard a group of standards for electronic parts and devices. There are different parameters covered in these standards like lead-free technology, soldering, and environmental parameters. The J-standards is mostly used in Japan and also accepted all over the world
- To maintain the high standard for quality for electronic devices there are following new advancements in the engineering field. J standards are checked during the design, manufacturing, testing, and supply.
J standards Soldering
- Soldering materials, tools, and processes involved each follow the J standards. The standards provide the rules and guidelines for using soldering alloys, fluxes, and cleaning agents to ensure high-quality soldering joints. These standards also define the rules for finding and removing the faults due to soldering like cold joints and solder bridges, with criteria for soldering joints like wetting, fillet creation, and voiding. There are some parameters made of soldering tools, like for soldering irons and reflow ovens, to make proper solder junctions,
- To avoid contamination and ensure their efficiency, the rules are also for soldering materials handling and storage. So in results, these parameters are for the design, manufacture, and testing of electronic parts and machinery, especially when it comes to soldering.
Requirements of J-STD-001
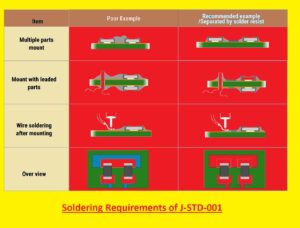
J-STD-001 explained the needs for different parameters of the soldering process that are listed here
Soldering Materials and Equipment
- The standard makes rules for solder alloys, cleaning solutions, fluxes, and different materials used for the soldering process. With that, it defines instruments of soldering like soldering irons, reflow ovens, and wave soldering machines.
Soldering Processes
- it is for different soldering operations like hand soldering, rework, and wave soldering, which are defined in J-STD-001. There is detailed instruction given for parts, applying the solder, and making sure the joints form properly.
Soldering Defects and their Prevention
- it is used for different soldering faults such as cold joins, solder bridges, and voids, and also gives rules to prevent these errors.
Solder Joint Acceptance Criteria
- are criteria for assessing solder junctions made by J-STD-001. it defines the rules for high degrees of voiding, wetting, and solder fillet size.
Training and Certification Requirements
- The person doing the soldering must have skills and expertise. So he must be according to the rules defined by JSTD
Soldering Materials and Equipment
Solder Alloys
- The features of solder alloy such as their composition, purity, and melting range, must the according to J-STD-001. The types of solder alloys good for different soldering techniques are also identified.
Fluxes
- Oxides and impurities were eliminated from the component surface and PCB boards with the use of fluxes.
- The need for fluxes like composition, types, and activity level, must be according to standard. It also defines how to apply and remove fluxes.
Cleaning agents
- Flux residues and pollutants are removed from the board with the use of cleaning chemicals. Features of cleaning agents like composition and compatibility with soldering supplies and machinery, must be according to defined standards
Soldering equipment
- Tools used for the soldering processes such as soldering irons, reflow ovens, and wave soldering machines according to STD-001.
Soldering Processes
- There are parameters for different soldering processes such as hand soldering, rework, and wave soldering, made by J-STD-001. Must follow to have an accurate soldering process
Hand soldering
- A soldering iron is used to melt and apply solder in a manual way in the hand soldering process. The features of handle soldering include an accurate soldering iron temperature, size of tip, and shape according to standards. With that, it defines how to ready components for the application of solder
Rework
- Repairing or changing a solder joint that faulty is not according to acceptance criteria is known as rework. The need for rework is according to standard with detailed guidelines for applying new solder and removing existing solder. There are standards defined for inspecting reworked solder junctions.
Wave soldering
- The board is passed over the wave of molten solder in mass soldering that called wave soldering. The features for wave soldering are proper wave height, temperature, and conveyor speed, according to the rules.
Soldering Defects and their Prevention
Read Also What is a Cold Solder Joint and How Can You Prevent it?
Cold joints
- Solder joints that are not made accurately due to improper heating or wetness are called cold joints. There are some standards for preventing cold junctions, like the use of proper soldering iron temperature and using required flux.
Solder bridges
- It is solder connections that resulted due to the short circuits since they connected the neighboring wires. The need for preventing bridges is defined by the rules like using the right quantity of solder and flux application
Voids
- These are spaces that affect solder joints and electrical features of the board to avoid these void follows rules to use of the proper quantity of solder and heat also
Solder Joint Acceptance Criteria
Solder fillet size
- The amount of solder gathered close or component pins is called solder fillet size. According to component size and lead configuration, specified by rules the smallest and largest solder fillet sizes are permitted.
Wetting
- Features of solder to flow and attach to the pad on board and component causes wetting. For this, there are rules defined by JSTD
Industry-Specific Application of J-STD-001
- An industry-specific standard known as J-STD-001 defines the rules and parameters for making high-quality electronic assemblies, with that also have parameters for soldering. It is mostly used in the electronics manufacturing process, and it is good for aerospace, defense, medical, and automotive industries that use electronic components in safety-critical applications.
In the aerospace and defense modules, these rules are used to ensure the safety of electronic assemblies used in aircraft, spacecraft, and military instruments. With that design and testing of soldering devices standard specifies accurate standards for the handling, storing, and use of soldering materials. it comes with different techniques for spotting and avoiding soldering errors like insufficient fillet creation, inadequate wetting, and voiding. - These standards are also used in the medical field in different instruments to have proper functioning. Since many devices can have detrimental effects on patient safety, they must work according to the rules. The standard provides details guidelines for handling and string soldering material and using the right soldering process.
- J-STD parameters are also used in the automobile sector and they provide guidelines for the design and testing of soldering equipment, as well as the use of soldering materials. It also contains techniques for spotting and avoiding soldering faults such as ineffective fillet creation, and voiding. The standard also has rules for handling and storage processes for soldering materials to avoid contamination, which causes failure of electronic components.
J-STD-001 vs. IPC-A-610
| J-STD-001 | IPC-A-610 |
|---|---|
| it defines rules for high-quality electronic assemblies, concentrating on soldering electronic components | it is for electronic assemblies to pass visual inspection before acceptance |
| focuses on the specifications for producing high-quality electronic assemblies | Make rules for the minimal standards for acceptable electronic assembly workmanship |
| Make rules for choosing and using soldering supplies and instruments | instructions for visually inspecting and rating electronic assemblies |
| methods for locating and avoiding soldering errors | visual examination, the standards for acceptable electronic assembly, also soldering |
| lists the satisfactory soldering junction parameters, such as wetting, fillet creation, and voiding. | standards for component installation, through-hole soldering, and surface mount soldering |
| Defines how soldering materials must be handled and stored | focuses on the need for managing and storing electronic assembly |
| soldering irons and reflow furnaces are designed and explained | installation and alignment of electronic components properly explained |
| specifications for avoiding electrostatic discharge (ESD) harm | for preventing ESD damage to electronic parts |
| gives details for inspecting and testing electronic circuits | gives instructions on how to mark and label devices. |
| Define requirements for the education and licensing of those working in electronic assembly | standards for a variety of coatings, such as encapsulants and conformal coatings |
Conclusion
The J-STD-001 standard, which is important for electronics manufacturing, defines the rules for soldering materials, tools, and products. The reliability and operation of electronic devices can be ensured by manufacturers by following standards
Although the standard looks somewhat complex it comes with details guidelines for soldering that reduce the chances of errors and ensure reliable results. Manufacturers can guarantee high quality and dependability of their electronic products by proper training and tools that fulfils J-STD-001.






