Hi, friends welcome to the new post. In this post, we will learn What is a Cold Solder Joint and How Can You Prevent it? Soldering is a technique commonly used in electronics and electrical work. It helps to make connections between different components. In some conditions, soldering process can casues fault connections that are known as solder joints. In this post, we will cover different parameters of cold solder joints, and their causes, and see how to solve this issue. So let get started with What is a Cold Solder Joint
Introduction Cold Solder Joint
Soldering is the process that links two metal surfaces with solder, metallic alloy comes with less melting point. It creates a conductive and mechanical connection between components at the PCB board or in electrical wiring. If this process is not made accurately can make cold solder joints.
What is a Cold Solder Joint?
Definition and Explanation
A cold solder joint resulted faulty solder connection which did not accurately connect different components with each other. Cold solder joints, are weak brittle, and can be damaged creating strong and continuous connections. it can result in different issues in electronic devices such as degradation of signal, intermittent connections, and damaging the devices
Causes of Cold Solder Joints
There are differnt causes of cold solder joints that are explained here
- Insufficient heat: If soldering irons do not have accurate heat solder does not melt completely resulting in the import connection
- Improper solder: Less solder or not properly applied casues weak joints.
- Contaminated surfaces: Ther is difficult to create proper solder due to Dirty or oxidized metal surfaces
- Poor soldering technique: If there is an improper technique used for soldering that results the different issues
Importance of Quality Soldering
Impact of Cold Solder Joints
Cold solder joints resulted in faulty electrical connections and devices become malfunctioning. In circuits, these fault connections can affect signal flow and affect the operation of devices. With that, these joins casues short circuits, so overheating, electrical fires, and affecting components
Safety Concerns
In safety-related applications, such as medical devices or automotive electronics, casues cold solder joints can exist. Malfunctioning due to error solder connections can affect the health of patients or also lead to accidents on the road. So, a high-quality soldering process is required
How to Identify Cold Solder Joints
Visual Inspection
A visual inspection can find cold solder joints.
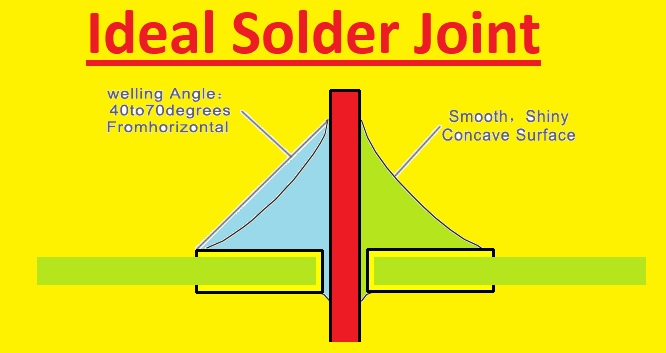
- Dull or grainy appearance: Cold solder joints normally do not come with the smooth, shiny, surface of accurately configured solder joints
- Incomplete coverage: if the solder does not accurately flow and converted cold solder joins exist
- Cracks or fractures: Brittle solder connections resulted in cracks or fractures,
Tips for Preventing Cold Solder Joints
Use Proper Soldering Techniques
- Heat both the component and the pad: Confirm that both component pins and pad are heated accurately before applying solder
- sufficient time for heat transfer: Give some time to melt the solder and flow smoothly to make a strong connection
- Avoid excessive movement: Try to avoid high motion during the soldering process that reduces cold joins
Ensure Clean and Dry Surfaces
- Clean the surfaces: To have good soldering there must be removal of greases, dirt, or oxidation
- Use flux: Use flux to connection points to reduce oxides and increase solder flow and wetting.
Adequate Heating and Cooling
- Use an appropriate soldering iron: Choose a soldering iron that comes with effective power to get the required temperature quickly
- proper cooling: Do not touch the connection the solder becomes sold and completely cooled
Choose the Right Soldering Iron and Solder:
- appropriate soldering iron tip: Use a tip according to a component that has to be soldered for heat transfer
- high-quality solder: High-quality solder comes with the right composition and the flux core ensures accurate flow and bonding.
Cold Solder Joint Symptoms
- Poor electrical conductivity. Cold solder joints come with high resistance and solder joints. It can casues problems with current flow and result in overheating
- Loose connections. There can be loose connections that result the bad mechanical strength. Due to that joins can affected by the vibration and as a result, compone cannot be removed easily
- Cracks and breaks. Joins can be brittle and prone to cracking and breaking. causes the joint damage completely, so the circuit is affected
Effects of Cold Solder Joint
- High electrical resistance: There can be high resistance due to these joints in the component and soldering. That casues overheating, less operation, and damage to the device
- Mechanical weakness: it can cause cracks or breaks than accurately soldered joints.
- Poor heat dissipation: Heat cannot flow easily from these devices accurately and gets overheated
- Interference with radio waves: It interferes with the radio waves. Can affect electronic devices that use radio waves, televisions radios, and cell phones.

How To Repair and Fix Cold Solder Joints
- Cold solder joints found. They are nonuniform and roug, or discolored. They can be loose
- Remove the component from the circuit board.it is done by correctly praying it off with a small screwdriver or by using a solder sucker.
- Clean the solder pads. With a clean cloth or paper towel for the elimination of dirt, and oxidation
- flux to the solder pads. Flux helps solder to flow and minimize the oxidation effect
- Heat the solder pads with a soldering iron. Soldering iron does not come with a temperature to melt solder as a result vaporizes the flux.
- Add solder to the solder pads. Solders should flow easily and smoothly on the solder pads.
- Hold the component in place while the solder cools. it will prevent components from moving and breaking the solder joint.
- Reassemble the circuit board. When cold solder joints are repaired board is tested to confirm that it is working properly.
Here are some steps to help prevent cold solder joints in the future:
- Use the correct soldering iron.
- The proper amount of solder must applied
- Soldered surface must be soldered
- Apply flux to the surfaces to be soldered.
- Put components in place while soldering.
- Allow the solder to cool completely before removing the components.
Type of Cold Solder Joints
- Disturbed joints: This type of joint exists when the component is moved over molted solder configured correctly. They are featured by a concavely shaped and tilted pin in the solder. They saw rough and a bit frosty.
- Overheated joints: They are made if the soldering wire is not melted or if the application of heat. it resulted in overheating of flux on board
- Insufficient wetting: it casues on pin or board. That is a symbol of the non-heating of solder smoothly on board and pinout. Imporepr wetting of pins defines that burned pin then board. it is also caused by to application of too little wetting material.
Conclusion
Cold solder joints cause different issues in electronic devices. Such as improper connections degradation of signal and safety measures. Understanding the reason for finding symbols. and according to accurate rules of soldering methods we can aovids cold solder joints.
FAQS
How do you prevent cold solder?
- Cold solder joins occur when solder is applied and not melted completely. The best solution to avoid them is that make sure the soldering iron is accurately preheated with effective power to get the required soldering temperature
What is a cold joint when soldering?
The cold solder joins casues when solder is not accurately melted during the soldering process making inaccurate joints. That is known as a rough or lumpy surface and also a crack created with the passage of time on joints
- What is cold solder called?
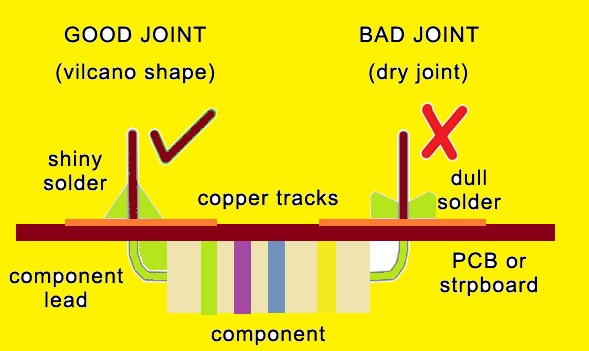
A cold solder joint is also called an old solder or a “dry joint.”
- How do you prevent dry solder joints?
- Surfaces must be clean
- Make sure that the component’s pin and board pads do not have dirt, greases, or oxidation
- What is a dry joint and how can it be avoided?
A dry solder joint is a soldering fault that is caused if solder not accurately wet or configured with compones leads and board pads. As a result, a weak connection occurs.
Differnt factors such as oxidized surface, improper soldering, ineffective heat or use of low quality solder casues dry joints