 Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will discuss What is Countersink Holes in Engineering. You may be familiar with the term “countersink holes” if you work in engineering. These types of holes are used to make smooth, surfaces between two pieces in different engineering projects. In this post, we will cover countersink holes in more detail including their varieties, uses, and construction. Let’s get started with What is Countersink Holes in Engineering?
Hello readers welcome to the new post. In this post, we will discuss What is Countersink Holes in Engineering. You may be familiar with the term “countersink holes” if you work in engineering. These types of holes are used to make smooth, surfaces between two pieces in different engineering projects. In this post, we will cover countersink holes in more detail including their varieties, uses, and construction. Let’s get started with What is Countersink Holes in Engineering?
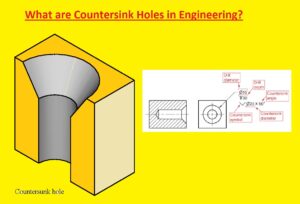
Definition of Countersink Holes
- The countersunk hole is a conical-shaped hole that is made at the surface of the material to help the screw to be easily configured on the surface.
- it is done to reduce the sharp edges that casues safety risks or affect the device’s operation.
What is a Countersink?
- A countersink is a cone-shaped hole that comes with a larger aperture at the top and a narrowed opening at the base which is curved out of materials made of metal or wood
- These helps are used to make a regular and smooth finish by helping bolts to easily be configured on materials of surfaces
- To make this hole is made at the top for fitting the screw and narrow at the lower end to help screw or bolt threads to firmly grasp the material.
- They used to get strong and secure fitting between two layers or components in engineering, metallurgy, and carpentry.

Waht is Countersink Callout
- An engineering drawing or design document that comes with details of a countersink hole to be made at a certain position on a part or assembly is called a countersink callout.
- The callout comes with details related to materials, size, and angle of countersink and other related data
- its main purpose is to make sure that countersinks are made according to requirements and follow rules
- The accurate callouts help to make strong and accurate fitting between two pieces and it makes sure the functionality of the device made
What is Countersink Angle
- The angle at which a cone-shaped hole, or countersink is made is called a countersink angle. A countersink angle is measured in degrees with values from 60 and 120 degrees. The size, types, and hardness of the screw or bolt to be used, the thickness and hardness of the material drilled, with the required look of the completed product, affected by the angle needed for a given countersink.
- Normally soft materials are bent at a larger angle while hard are less degrees. To maintain tight fitting between two layers and prevent damage or failure of the product, it is needed to use the proper angle for a countersink.
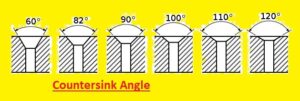
Standard Countersink Angle
- 90 degrees is the commonly used countersink angle, with 82 to 120 degrees are also used. The application and screw used define teh angle used for the countersink.
- Such as flat head screws normally needed a countersink angle of 82 degrees, and oval-head screws need a countersink angle of 100 degrees.
- For angle there must be materials and desing must be considered. To have accurate fitting and avoid any damage use the correct angle according to the need
Counterbore vs Countersink
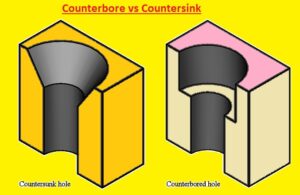
- Though counterbore and countersink holes are created in a material, they have different functions.
- A countersink is a cone-shaped hole made for a screw or bolt head to connect to the material’s surface, making a smooth and uniform finish. A countersink is used to have a bigger hole for the screw or bolt head while maintaining a tight grip on the material with the threads.
- counterbore is a cylinder shape hole drilled in material that enables the head of a bolt or screws to be below the surface of the material. A counterbore is provdies head of a screw or bolt with more room to configure without obstructing the assembly’s other components or surfaces. In applications such as metalworking, woodworking, and aerospace, counterbores are frequently used
Double-Sided PCB Board, Construction, Working, Types & Applications
Types of Countersink Holes
- There are 4 main types of countersink that are explained here
Flat Countersink Holes
- it is a conical-shaped opening and has lower part flattened features with flat countersink holes. If a screw or bolt head needed to pass in the surface these holes are used
C’sink Holes
- C-sink holes come with conical showed bottom and cylindrical show top part. It is used to make tapered seating surfaces for flat-headed screws or bolts.
Cone-shaped Countersink Holes
- A tapered opening makes a cone-shaped hole in a countersink hole. When a countersink hole has to be made at an angle, these holes are used.
Multi-step Countersink Holes
- Multiple levels of conical-shaped openings exist in multi-step countersunk holes. For screws or bolts with different head diameters, it is used.
Applications of Countersink Holes
There are different types of applications of countersinks that are explained here
Aerospace Industry
- In the aerospace industry, these holes are used in the manufacturing of aircraft components. These holes are used to connect the body of the aircraft with the frame and make a surface that decreases drag and enhances aerodynamics.
Automotive Industry
- They are also used in the automotive industry to make body panels and other parts of the vehicle’s frame strongly connected. These perforations are to make a flush surface, which enhances the vehicle’s look and lowers air resistance.
Construction Industry
- In the construction industry, they are used to connect metal components brackets, hinges, and fasteners to wooden structures. These types of holes are used to prevent protrusions that could damage the surface and to ensure a secure and tight fit.
Electronic Industry
- Countersink holes are also used in the electronic industry to connect circuit boards to a device’s housing. These holes are used d to make a flush surface, guaranteeing that the devices look tidy and clean.
How Countersink Holes Are Made?
Two methods used for the creation of counterholes
Manual Countersinking
- In manual countersinking, a hand tool like a countersink is used to drill holes at certain angles. After that, the bit is rotated until the necessary depth and width are obtained.
Automatic Countersinking
- Using a machine that is programmed to drill holes automatically is called automatic countersinking. The machine can be set to make holes of different sizes and angles using a countersink bit.
Advantages of Countersink Holes
- The main advantages are explained here
- Good aesthetics
- Minimize air resistance and drag
- Enhanced functionality
- Provides safety featues
Disadvantages of Countersink Holes
it has disadvantages explained here
- The changes of cracks and fractures if not done correctly
- Reduced strength due to the removal of material
- The need for specialized tools
Conclusion
Countersink holes are commonly used in different engineering applications to make flat, continuous surfaces between two parts. There are different countersink hole designs, and each is used in certain applications. There are benefits and drawbacks to both the manual and mechanical methods of making countersink holes.
Faqs
-
Write the purpose of countersink holes.
- Countersink holes are used to make a flush surface between two components, to have a strong fit.
-
How are countersink holes different from counterbore holes?
- While counterbore holes are cylindrical in shape, countersink holes are conical.
-
Write main types of materials can be countersunk.
- Wood, metal, plastic, and composites are among the materials that can be countersunk.
-
Are countersink holes necessary for all engineering applications?
- No, not all engineering applications call for countersunk holes. The application-specific needs determine how they should be used.
-
How to choose the right type of countersink hole for my application?
- The material being used, the size of the screw or bolt head, and the angle at which the hole must be drilled will all affect the best type of countersink hole to use. The size of the hole must be the same or larger than the of tool that is going to be used. The good rule is that the countersink is 50 percent larger than the internal hole.





