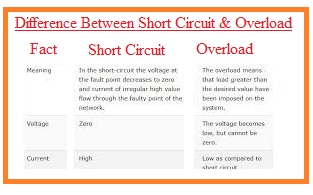
Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Short Circuit & Overload. The basic difference between a short circuit and overload occurs due to the existence of fault between lines or line-to-earth fault while overload occurs when a large amount of current is used by any device from the power supply. The overloaded condition is related to the circuitry or instrument. Any circuitry is overloaded when it uses more current than the rated value. The overloading occurs due to the damaging of instruments or fault occurs in the circuits.
Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Short Circuit & Overload. The basic difference between a short circuit and overload occurs due to the existence of fault between lines or line-to-earth fault while overload occurs when a large amount of current is used by any device from the power supply. The overloaded condition is related to the circuitry or instrument. Any circuitry is overloaded when it uses more current than the rated value. The overloading occurs due to the damaging of instruments or fault occurs in the circuits.
While short circuit occurs when metallic wires touched each other due to damaging insulation. When a short circuit occurs resistance of the instrument decreases or becomes zero due to the large current is flowing in the circuitry. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at both the short circuit and overload and compare them to find their difference. So let’s get started with Difference Between Short Circuit & Overload.
Difference Between Short Circuit & Overload
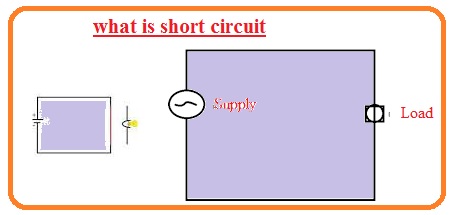
What is Short Circuit
- It is a type of circuit through which the current passes with less or zero value of resistance.
- it damages the circuitry when a current of high value passes.
- The inverse circuitry of a short circuit called an open circuit has infinity resistance
- the practical example of a short circuit is linking the positive and negative points of the battery have less resistance
- If a short circuit occurs for points having less resistance high current will passes
- If it is a battery terminal high current from the battery damage the internal structure and the battery becomes dead.
- In the case of a motor high current can damage the windings of the motor
- unlike normal circuitry short circuit can cause a very high-value current in some seconds.
- To avoid a short circuit there must be a use of fuse and breaker in the circuitry.
What is Over Load
- the current used by load rises the value of current getting from the supply overloading occurs.
- For motor overloading conditions define the high value of inertia at the shaft that the motor can operate.
- The high value of current flows in this condition than the rated current of the device
- Breker and fuse used to stop this process
Causes of Short Circuit
Different things, such as deteriorated insulation, flawed wiring, weak connections, or even external components like dampness or vermin, can cause short circuits. To avoid possible risks like electrical fires, it’s important to recognize and treat these issues right once.
Effects of Short Circuit
A short circuit might have negative outputs. Inadequate current flow through the circuit can results in device damage or electrical fires in the worst-case scenarios, also overheating and component or wire melting. Due to this, short circuits provide a serious safety concern and need to be handled right away.
Causes of Overload
The inappropriate distribution of electrical loads is frequently one of the reasons for overload. Overloading a circuit can occurs when there are many plugs in one place or when high-power appliances are configured with extension cables. Also, old or malfunctioning circuit breakers may be unable to recognize overloads and provide protection.
Related post:125 Amp Wire Size and Breaker Guide
What Size Wire Do I Need for a 60 Amp Sub Panel?
60 Amp Wire Size – Which AWG is Best for 60 Amp Breaker
Effects of Overload
When a circuit is overloaded, the wires and other components may get overheated, which may cause damage or even a fire. Circuit breakers or fuses may trip or blow as a result of overloads, cutting off the power and preventing further damage to the circuit. However, if the excess continues, it may have more serious repercussions.
Short Circuit vs Overload
| Short Circuit | Overload |
|---|---|
| Occurs when there is a direct connection between the live and neutral wires, bypassing the load. | Occurs when the current drawn by the load exceeds the maximum current rating of the circuit. |
| This causes a sudden increase in current flow, leading to a rapid rise in temperature. | This results in a prolonged high current flow, resulting in the circuit overheating over time. |
| It can lead to a blown fuse, tripped circuit breaker, or damage to electrical components. | Can cause the circuit breaker to trip or the fuse to blow, protecting the circuit from damage. |
| Typically occurs due to a fault in the wiring, like damaged insulation or a loose connection. | Often caused by connecting too many devices to a single circuit or using devices that draw excessive power. |
| Can be detected by a significant drop in voltage, a loud bang or spark, and the immediate loss of power. | This can cause the circuit to operate at reduced voltage, leading to dimming lights or overheating appliances. |
| Requires immediate attention to identify and rectify the wiring fault. | Requires redistributing the load or upgrading the circuit to handle the increased current. |
| Can be dangerous as it poses a risk of electric shock, fire, or damage to electrical equipment. | This can result in overheating and potential fire hazards if not addressed promptly. |
Tips for Preventing Short Circuits and Overloads
- Regularly inspect and maintain your electrical wiring and connections to identify any signs of wear or damage.
- Avoid overloading circuits by distributing electrical loads evenly and using separate circuits for high-power appliances.
- Install circuit breakers or fuses with appropriate ratings to protect against overloads and short circuits.
- Use high-quality wiring and components to minimize the risk of short circuits.
- Seek professional help from licensed electricians for complex electrical installations or repairs.
Common Misconceptions about Short Circuits and Overloads
- Misconception: Short circuits and overloads are the same thing. Clarification: While both involve excessive current flow, they have distinct causes and effects.
- Misconception: Short circuits only occur in old or faulty wiring. Clarification: Short circuits can occur due to various factors, including damaged insulation or loose connections.
- Misconception: Overloads only happen when too many devices are connected to a circuit. Clarification: Overloads can also occur if high-power appliances draw more current than the circuit can handle.
- Misconception: Circuit breakers and fuses are interchangeable. Clarification: Circuit breakers are reusable and automatically reset, while fuses need to be replaced after blowing.
- Misconception: Addressing short circuits and overloads is unnecessary unless a problem arises. Clarification: Proactively identifying and resolving these issues is crucial for safety and preventing equipment damage.
That is a detailed post about the difference between short circuits and overload if you have any queries ask in the comments. Thanks for reading. Have a good day.