 Hi, reader welcomes to the new post. In this tutorial, we will discuss the Cross-Field Theory of Single-Phase Induction Motors. The induction motor belongs to the ac family of motors. There are two main types of induction motors single-phase and three-phase induction motors. single motor called single phase motor since it operates on single-phase and a three-phase induction motor operates on 3 phases.
Hi, reader welcomes to the new post. In this tutorial, we will discuss the Cross-Field Theory of Single-Phase Induction Motors. The induction motor belongs to the ac family of motors. There are two main types of induction motors single-phase and three-phase induction motors. single motor called single phase motor since it operates on single-phase and a three-phase induction motor operates on 3 phases.
In this post, we will cover details about the cross-field theory of single-phase induction motors and its related parameters. So let’s get started with cross field theory
Cross-Field Theory of Single-Phase Induction Motors
- Cross field theory of single-phase induction motor is explained here
- The cross-field theory of single phase induction motor helps to view the induction motor from a different point of view.
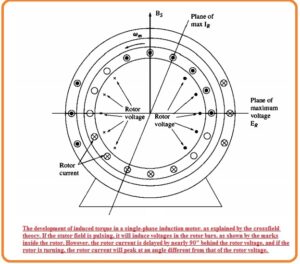
- This theory is related to the voltage and current which are static stator fields that can be produced in the windings of the rotor when the rotor is rotating.
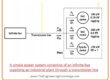
- Let us assume that a single-phase induction motor has a rotor that is taken to speed through the use of any exterior technique.
- This type of motor can see here.
- Voltage is produced in the rotors through the peak voltage existing in the windings moving directly through the windings existing in the stator.
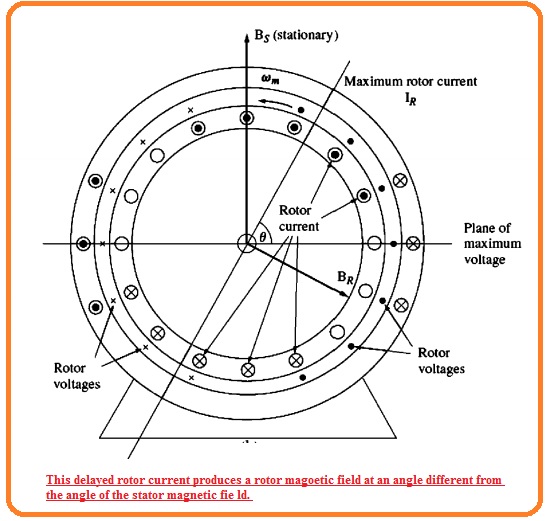
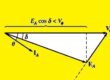
- This rotor voltage generates a current in the rotor but the sine of the high value of reactance of the rotor, the current lags the voltage through the angle of ninety degrees.
- The rotor rotating speed is almost equal to the synchronous speed so ninety ninety-degree lagging factor in current generates the ninety degrees angular shift among the plane of peak rotor voltage and the plane of peak current.
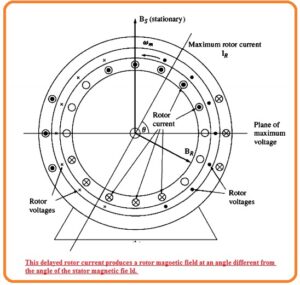
- In the below figure you can see the resultant rotor field.
- The rotor field is less than the stator field, since the loss of the rotor but there is a difference of ninety degrees angle in space and time as well.
- If these 2 fields are added for different time intervals so we can see that the net field in the motor is revolving in the anticlockwise direction.
- Through the rotating field existing in the motor induction motor will create the total torque in the direction of movement and that torque will retain the rotor moving.
- If the rotor of the motor is moving in a clockwise direction the net torque will have a clockwise direction and will again retain the motor moving.
What is cross-field theory in induction motors?
- The details for cross-field theory is how the rotor produces torque. On the basis of cross-field theory, stator flux can be divided into two components that are at 90 degrees to each other. One works along the stator winding axis and the other works as perpendicular to it.
What is the operation principle of cross field machine?
- Stator winding is excited with a single-phase ac supply. this supply generates alternating flux that works along the axis of the stator winding. Due to flux, emf is produced in rotor conductors in a result of transformer action.
What is the theory behind induction motor?
- The induction motor is an AC motor in which the current in the rotor generates torque through electromagnetic induction from the magnetic field of the stator winding.
- In an induction motor, there is no need for electrical connections to the rotor
What is the revolving field theory of induction motors?
- The revolving field theory of single phase induction motor is resolved flux crossing air gap in two components rotating in reverse directions but with constant magnitude.
What is the definition of crossed field?
- Two fields are at 90 degrees to each other
What is cross field effect?
- Crossfiled effect is sensitivity to a field that is orthogonal to the sensing direction of the sensor. This effect is nonlinear and common to magnetic sensors having ferromagnetic material.
Why is cross field named so?
- Both electrical field E and magnetic fields can generate force on charged particles. If two fields are at 90 degrees to each other then they arecrossed fields.
What is the basic theory of induction motor?
- The motor that works on principle of electromagnetic induction is called the induction motor. Electromagnetic induction process in which emf induces over electrical conductors when it connected in rotating magnetic field
Why is single-phase not self-starting?
- If a single-phase AC supply is provided to the stator winding of a single-phase motor, it generates flux, that alternates over on a single axis. it is not synchronously rating flux, so not generate rotation. So single-phase induction motor is not self-starting.
Which is the cross field device?
- Cross-field devices like magnetrons and crossed field amplifiers, use electrons in magnetic and electrical fields to generate EM emissions and can be used in different applications.
Which law is used in induction motor?
- According to Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, the relative speed between stator RMF and rotor RMF causes induced EMF in the rotor conductor. Rotor conductors are short circuits and rotor current is generated due to induced emf.
Read also:
- What is Circle Diagram of Induction Motor – Definition, Construction & Its Parts
- Different Types of Induction Motor and Features
- Difference between Induction Motor and Induction Generator
- Difference Between Single Phase and Three Phase Induction Motor
- Single Phase Induction Motor Starting Methods
- Induction Motor DC test for Stator Resistance and Locked Rotor Test