Hello, readers welcome to new post. Here we will discuss about What is Fuse. Fuse is a very commonly employed protective instrument in the electrical system. In commonly used in systems operating at low voltage levels. It is also used for a circuit that uses medium-level volts and for distribution lines of eleven kilovolts that use switch and contactors having fewer short circuit features.
Currently, there are different types of fuses are constructed having certain values for current and volt ratings, response time, and breaking capacity. Here we will cover the different features of fuse and applications. So let get started.
Rewireable Fuse
- This type of fuse when operating then can be replaced with a new wire after. WIre of fuse is placed in the asbestos tube to stop the splashing caused by the volatile metals.
- Its drawback is that offered incorrect protection due to the inaccurate ratings
- due to open environment arrangements, deterioration of components occurs.
Cartridge Fuse
- In this fuse silver component having a certain shape positioned in a barrel of insulating material has quartz
- The combination of insulators and quarts gives protection from the arc
- Fine rating values and features of fuse always give the circuit not used for the rewireable fuse.
- Arc and energy existing in the insulating tube due to fault stop damage.
- Its stability is largely due to sealed pack and less face environmental conditions
- It is normally used for high short circuit duty due to high-speed operation and can handle one lac ampers current
Fuse Operating characteristics
- The inverse characteristic of a fuse can be seen here. Inverse means that can bear the nominal current values indefinitely and with the current increment their withstanding time decrease caused to blow them
- The blowing time reduces with the current increment
Fuse British standard 88
- These standards restrict the increment in temperatures
- Fusing factor that is 1.4
- Also, restrict the breaking capacity
- These paramrets depend on one another and making them balance good quality fuse can be configured.
- If the fusing factor is fewer temperatures is large so close protection and possible of blowing are needed
Energy let through of Fuse
- The operating speed of the fuse is high and remove the fault current before it get the first peak
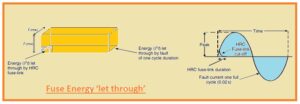
- If fuses remove the power in the first quarter of the cycle in result power will be I²t
- By making comparison circuit breakers can remove fault up to ten cycles and let-through power will summation of I2 in case of ten cycles
- The energy released at the fault is so close compared to let through the energy of the fuse.
Selection of Fuse on bases of Applications
- If current passing in the fuse remains til their baring time thine blow
- These features restrict the usage of fuses in circuitry that has an inrush current high.
- Since motors draw the inrush current six times larger than the full load current so fuse cannot be used in overload protection
- So fuse preferred for short circuit current then overload.
- Fuse used for short circuit protection and overload protection on the basis of some paramrets discussed below.
- For circuits where loads do not change over the normal value when switching is on and operating conditions
- Resistive circuits have these features so for these loads fuse can be used to get the overload protection
- Can also be used for short circuits
- Such circuits that has variation in the loads over the normal ratings such direct online motors crans rolling mills