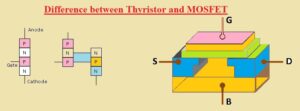
 Hello, readers welcome to the new tutorial. We will discuss Difference between thyristor and MOSFET. A thyristor is known as SCR which is a solid-state semiconductor component having 4 P and N layers and MOSFET is metallic-based FET and created through the oxidation process of the silicon part.
Hello, readers welcome to the new tutorial. We will discuss Difference between thyristor and MOSFET. A thyristor is known as SCR which is a solid-state semiconductor component having 4 P and N layers and MOSFET is metallic-based FET and created through the oxidation process of the silicon part.
Here we will discuss different parameters to find the differences between thyristor and MOSFET. So let get started
Difference between thyristor and MOSFET
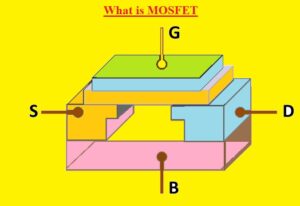
What is MOSFET
- A MOSFET is also known as a metal oxide silicon transistor or MOS is a category of IGFET or insulated gate FET that is made by thermal oxidation of a semiconductor material, usually silicon.
- The isolated gate voltage calculates the electrical conductivity of the transistor, this conductivity behavior changes with magnitude if the given voltage can be used in amplifiers and switching circuits.
- In 1959 MOSFET was first created by Egyptian engineer Mohamed M.Atalla and Dawon Kahng who was a Korean engineer.
- This electronic component is most commonly used in electronic circuits, and between 1960 and 2018, nearly (1.3 × 1022) MOSFETs were created.
- It is also very often used in digital, and analog circuits, and power devices.
- The main advantages of MOSFETs are that no input current is needed to regulate the load current as required with BJTs.
- A voltage applied to the gate of the E-MOSFET can increase the conductance from the off state.
- Whereas with a D-MOSFET, the gate voltage can reduce the conductance from the on the state.
- The switching speed of this module is high, its size is small, it consumes less power.
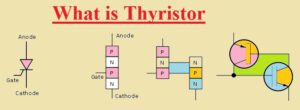
What is Thyristor
- This controlled electronics turn on the module, which needs a trigger pulse to operate.
- It has four layers of NPNP or PNPN.
- In some cases, it is an analog of SCR
- It works as a bistable switch when the gate has a current connection and operation continues when the voltage on the component is not reversed.
- It is used to control a high current value through 2 points that connect to a control point
- It exists in two categories of structural armament.
- In firestone, there are two terminals and the other one is three terminals.
- They have applications where high values of volts and current are involved.
- It is used for AC control and zero crossing control.
- Its operation is synchronous if it works in phase at the voltage indicated on its terminals.
- There are three guidance modes, it has reverse, forward, and forwards guidance mode
It has three intersections. - It has three anode-cathode terminals and a gate.
- Used in phase fire control units
- Its power-handling capability is better than that of a diode.
- It required a higher value of voltage to operate than a diode.
- It is more expensive than a diode.
- This is heavy equipment.
Thyristor vs MOSFET

- Larger volts needs for thyristors and also high current while MOSFET operates on medium level volts and high current
- Thyristor has less switching frequency than MOSFET
- Losses during operation for thyristors are less and MOSFET has high
- A thyristor is current controlled and MSOFE is volts controlled device
- MOSFET needed continuous supply to operate while the thyristor need one pulse
- Thyristor gets off through line communication and MOSFET through the gate
- For series circuits thyristor used for volts equal circuits for thyristor and MOSFET not used
- There is no 2nd breakdown for the thyristor and MOSFET has fewer chances for 2nd breakdown
- MOSFET is sensitive than the thyristor
That is all about the Difference between Thyristor and MOSFE all details has explained. If you have any query ask in the comments. Thanks for reading