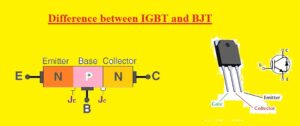
 Hello, readers welcome to the new post. We will discuss Difference between IGBT and BJT. These two are the main types of transistors used in different types of electronic devices and projects. These two devices have a PN junction in their configuration.
Hello, readers welcome to the new post. We will discuss Difference between IGBT and BJT. These two are the main types of transistors used in different types of electronic devices and projects. These two devices have a PN junction in their configuration.
Here we will cover different parameters of these two transistors and finds common differences existing between them. So let’s get started.
Difference between IGBT and BJT
What is BJT
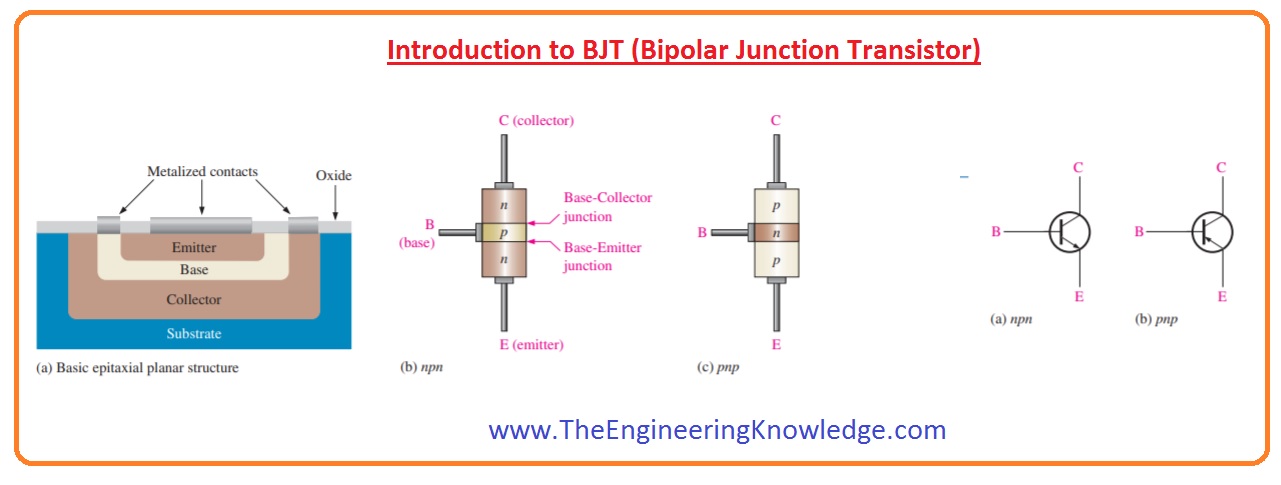
- The BJT stands for bipolar junction transistors and comes in three pins configuration Base emitter and collector.
- Its common uses are in switches and amplifier circuits.
- Its structure is that P-type material is placed among the two N materials to form the NPN configuration and for the PNP configuration there is N material is placed in the center.
- So according to this configuration, there are two main types of BJT PNP and NPN.
- There are two PN junctions are configured in the transistor.
- Its central parts are called the base and the other two are the emitter and collector. The collector is the larger part that has a larger number of charge carriers.
- There are two charge carriers that help to flow current in the BJT electrons and holes.
- The larger value current is collectors that is regulated through the base current IB and this feature helps to use for switches and amplifier circuits.
- BJT is known as the current controlled module
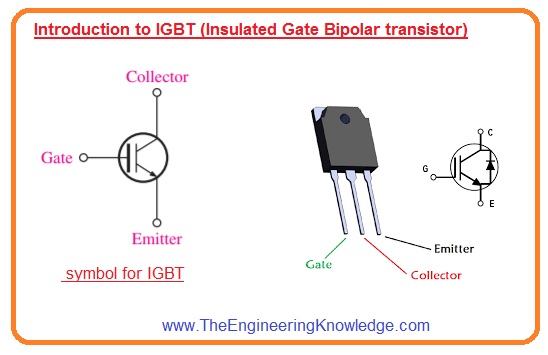
What is IGBT
- IGBT is also three terminal electronic components. Its pinout is emitter-collector and gate. It has a gate then base like BJT.
- It is used for high power control operations and also for high-speed switching. It was the first time was sued in the 1980s
- This transistor comes with dual features of MOSFET and BJT. It is controlled through the gate as MOSFET controlled and has current volts features of BJT.
- So it can be used for high current operations also high power circuits
Structure of IGBT
- Its inner circuit is a combination of 2 transistors and MOSFET and its output is a combination of PNP NPN and MOSFET transistors.
- This transistor confines the less value of saturation volts of the transistor to the high value of input impedance with switching speed of MOSET.
IGBT Types
- There 2 main types of IGBT on the basis of the N+buffer layer the category iof IGBT has n+buffer layers known as Punch through IGBT and others called non-punch through IGBT.
- On the basis of different features, this two IGBT are called symmetrical and nonsymmetrical IGBT.
- For symmetrical IGBT there are the same forward and reverse breakdown volts.
- While asymmetric IGBT have reverse breakdown volts less than the forward breakdown volts
- Symmetrical IGBT is used in AC circuits and asymmetrical IGBT is used for DC circuits
IGBT vs BJT

- The BJT stands for bipolar junction and IGBT insulated gate bipolar transistor
- IGBT is three pinouts used in amplifiers and switches and IGBT also has 3 pins used in power electronics
- Pins of BJT are emitter-base and collector and IGBT has EMitter collector and gate
- BJT used for current controlled operations nd IGBT for voltage control functions
- Base used as a control in BJT and Gate used as a control for IGBT
- The circuits for IGBT is simple and for BJT is complicated
- The switching speed of IGBT is high that BJT
- The switching speed of BJT is the order of 10 and IBJT has 0.5
- BJT uses high power and IGBT uses less for operation
- BJT has high losses for switching than IGBT
- BJT has a frequency for switching about twenty kHz and IBJT has one sixty kilohertz
- Impedance for BJT is less than IGBT
- Small save operating area for BJT than IGBT
- BJT handles less power than the IGBT
- BJT has negative and IGBT has positive temperature coeiffiecnt
That is all about the Difference between IGBT and BJT all details for the Difference between IGBT and BJT has covered than will helps to find the differences. thanks for reading