Hello readers, welcome to the new post. Here we will discuss What is an SMT Line? SMT Manufacturing Line and Assembly Process. Surface Mount Technology is a surface mount technique used in electronic components and it is very commonly part of the electronic manufacturing industry. Then the conventional plug-in electronic components, SMT components are smaller in size, have less weight, and have lower power techniques. In the SMT line process the components are soldered on the surface of the board and an accurate position and connection of the component is made with the use of machine placement and other instruments. In this post, we cover the details of line components’ functions and assembly processes. So, let get started with What is an SMT Line.
What is SMT Line
Based on automation levels there are two types of SMT lines. The first one is automatic production lines and the second one is semi-automatic production lines. The groups of SMT lines based on size are.
- Large production lines
- Medium production lines
- Small production lines
The automatic SMT production line comes with the creation of line equipment that is completely automated. The complete process does not need manual handling.
Semi-SMT line is not completely automatic. So it can include Manual printing PCBs, manual loading of PCB,s and manual unloading of board.
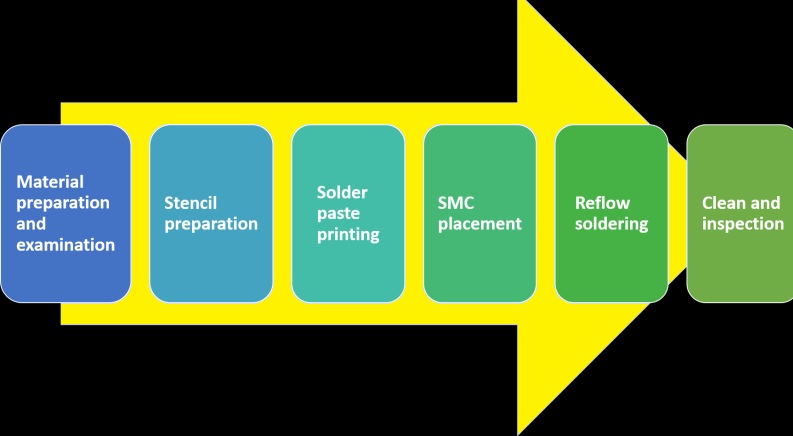
SMT line process
Empty board loading
- Check that thickness and size of the empty board are constant with process needs to avoid issues such as faulty connections.
- Ensure that the surface empty board is in good condition to avoid scratches on the surface. During the production of an empty board, minimize the electrostatic interference to avoid static curent from damaging components.
- The empty boards needed to be put in a dust-free and oil-free environment to avoid dust, and grease on the empty board.
- Different loading techniques used for empty boards such as thin board loading use special carrier racks to avoid bending and board deformation.
Solder paste printing
In this phase, solder paste is printed through a steel plate on the pads of the board where soldering has to be performed. The position and volume of solder paste affect soldering quality. These solder pastes melt during the SMT process, a high temperature of the reflow oven, and solder components to the board for the solidification process.
Solder paste inspection
The quality of solder paste printing affects the welding part, so make sure stable quality and more optical instruments will connected after solder paste printing check that it is good or not and has less tin, tin leakage, and extra tin. After inspection there is a board with bad solder paste printing, we can choose first it and wash off the solder paste on it and again apply solder paste or remove extra solder paste
SMD
High-speed patch properly connects electronic components SMT at a certain point of the board. This type of SMD passive components are inductors, resistors, and capacitors are called Small chips and have small sizes, and 2 terminals are soldered. So when putting small parts on PCB board, the accurate position needed is low. The high-speed placement machine comes with nozzle heads and speed is fast and differnt components can be connected in a single second. However, it is not best for larger parts with a certain weight to be processed through a high-speed placement machine. But it will slow the speed of small, fast components.
Pre-reflow AOI
The pre-reflow AOI is performed before the reflow soldering to enhance the quality of the patch before reflow. Another reason is that some boards directly solder shield to the board for the SMT process. When the shield is configured on board, not easy to check the patch and solder through API or visual inspection. For this pre-reflow AOI test is performed.
Reflow soldering
Solder paste is melted at high temperature and then cooled, electronic component SMT and board are strongly connected. The high and low temperatures affect the soldering quality of the board. According to features, a general reflow oven sets the preheating zone, heat absorption zone reflow zone, and cooling zone to get good soldering.
The extreme temperature limit in reflow not is higher thatn 250 centigrade. After the board passes through a reflow oven, the assembly of the board is completed, leaving soldered parts.
PCB cleaning
It works to remove the welding residues bad for the human body like flux on assembled boards. The instruments used in the washing machine and locations will not be fixed.
Post-reflow AOI
Post-reflow AOI is the standard configuration of the SMT line process but not each SMT production line comes with AOI machines. The main objective of post-reflow AOI is that some circuit boards with high density do not effectively carry open and short circuit test (ICT), so AOI is employed.
But as AOI is optical interpretation it comes with inherent blind spots. AOI did not check the quality of components like false soldering, BGA solderability, resistance value, inductance value, and capacitance value. So some advanced EMS manufacturers come with X-RAy which is used for products with high quality demands and highly reliable operation to detect the soldering pins quality.
Visual inspection
Irrespective of the post-flow AOI test , the common SMT line process also has an inspection for board assembly. The main casues of manual inspection are that PCBA is modified type, users needs components to use substitute materials, proper direction of components like diodes, triodes, aluminum capacitors, and switch is accurate and with that open circuit, faulty welding and parts are checked
Main elements of SMT line
- SMT loader: it stacks and loads board on the conveyor
- Stencil printing machine: it applies solder paste to a blank board.
- Pick and place machine: it properly puts surface-mounted components on board
- Oven: it bakes board with the use of heating profiles that are best for PCBA
- SMT unloader: It gets finished, board
Advantages of an SMT line
- It is a low-cost process due to the reduction of manual labor and less material waste.
- It has shortened production cycles that increase efficiency.
- It increases the board’s quality.
- It is best to use due to less manual work.
SMT Related Terms
SMT: In this method, components are placed and soldered on board pads. The use of SMT technology is known as SMT PCBA manufacturing.
PTH: Through-hole is board assembly method has comparison with SMT. The components with longer lead connected board through holes and soldered with copper hole walls.
PCB: The PCB baord is made by lamenting and drilling many layers of fiberglass epoxy, prepreg, and copper layers that are etched to circuit graphics and plating copper in holes.
SMD: A surface mount device, is an electronic component used in the SMT process. As compared to the PTH component for PTH assembly, SMD comes with a small weight and size of 1/10 PTH component of a similar function. It makes smt common due to the smaller size and fine circuits of electronic devices.
Read also:
- Introduction to SMT PCB Reflow Soldering Process
- SMT is better Than Through Hole
- How SMT Assembly Process and its types
- Difference between Through Hole and SMT
- Main Factors for Good SMT Manufacturing
- Advantages of SMT Technique
Faqs
- Why is SMT used?
- SMT helps component to connect on the board surface without drilling. Differnt electronic circuits use surface mount components as they are compact and can be connected on any side of the board. They are best used for applications having high routing density.
- What is the use of SMT?
- SMT can connect different electronic components, like resistors, diodes, capacitors, transistors, integrated circuits, and connectors.SMT is made to reduce manufacturing costs and make effective use of board area.
- What is an example of SMT?
- An example of SMT is connecting resistors on board. A resistor will have a small, surface-mounted device on board surface and then solder in position
- What are the three types of SMT?
-
- There are 3 main types of SMT:
- Wave soldering: Wave soldering is bulk soldering process used for the production of board. The circuit board is passes over a pan of molten solder where the pump generates an upwelling solder that is like a standing wave.
- Reflow soldering: reflow soldering comes with solder paste used to connect many components temporarily wit pads when complete assembly has controlled heat.
- Selective soldering: In this method components on boards are connected in a faster way then by hand. It is a commonly used technique in manufacturing applications..
- There are 3 main types of SMT:
- What are SMT components?
- CHIP, MELF, QFPs (Quad Flat Packages), SOICs (Small Outline Integrated Circuits) QFN (Quad Flat No Leads), and BGA (Ball Grid Array).
- What is SMT material?
- Common materials of SMT assembly are solder paste, adhesive, flux, cleaning agent, heat transfer medium etc. Solder pase in SMT assembly is important for solder material and adhesive to fix SMC on board
- What machines are in an SMT line?
- Pick and Place Machine.
- Solder Paste Mixer
- Oven.
- SMT Loader.
- Solder Paste Printing Machine
- SPI Machine
- Reflow Machine
- AOI.
- What type of PCB is SMT?
- SMT is for any type of PCB board but is mostly used for multilayer boards. These boards has many layers of copper that used for component mounting in different layers
- What is SMT and PCB?
- SMT used for mounting electronic components on board and PCB board is a substrate on which components are connected.
- How do you calculate the capacity of an SMT line?
- SMT capacity is measured based on the processing time, of board orders.
- What is cycle time in SMT?
- it is the time taken to make part or the time taken by the machine to complete cycle. Some machines made many parts in one cycle and other just one
- What is the formula for machine capacity?
- Machine hour capacity is the total amount of time the machine takes to make the product. This can be used for each singel product by taking the product of a number of available machines by the hours that employees can use them.
- Capacity = (Number of components per hour) x (Number of boards per hour)
- Machine hour capacity is the total amount of time the machine takes to make the product. This can be used for each singel product by taking the product of a number of available machines by the hours that employees can use them.
- How do you calculate unit capacity?
- it is the work of a machine done in unit time. It is measured in components per minute or boards per minute.
- What is 1 unit of capacity?
- 1 unit of capacity is the amount of work that a machine can do in 1 minute.
- What are the 4 units of capacity?
- The 4 units of capacity are:
- Components per minute
- Boards per minute
- Components per hour
- Boards per hour
- The 4 units of capacity are:
- How do you calculate the flow rate?
- Flow rate is in which SMT components are connected on board. It is measured through dividing number of components connected by tie take to connect them