Hello dear readers I hope you all are having fun in your life. In today’s post, we will discuss What is Microcontroller. The creation of a microcontroller was done with the production of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors. or MOSFET. The first time in 1959 it was created by the Mohamed M.Atalla and Barwon when they were working at bell labs and ist time it was commonly explained in 1960. In this year Atalla also gave the instruction of MOS ICs that is IC chip created with the metal oxides field-effect transistors.
Hello dear readers I hope you all are having fun in your life. In today’s post, we will discuss What is Microcontroller. The creation of a microcontroller was done with the production of metal oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors. or MOSFET. The first time in 1959 it was created by the Mohamed M.Atalla and Barwon when they were working at bell labs and ist time it was commonly explained in 1960. In this year Atalla also gave the instruction of MOS ICs that is IC chip created with the metal oxides field-effect transistors.
With the passage of time in 1964 metal oxides, chips started usage of large numbers of transistors and manufacturing cost also decreases than the bipolar boards. The chips used in the 1960s become more advanced and used hundreds of transistors and leads to LSI which was according to Moore’s law. The usage of LSI chips in computing industries was the foundation of microprocessors since engineers started created a complete processor of a computer with the MOS large scale integration chip. By using the MOS large scale integration the ist multi-chip microprocessor 4 phase system ALq created in 1969 and Garrett Airesearch MP944 created in 1970. In 1971 ist single CIO microprocessor was Intel 404 created. It was manufactured by the Federico Faggin with the use of the silicon gate MOS technique. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at microcontroller working, application, types, pinout, and some related parameters. So let’s get started with What is Microcontroller.
What is Microcontroller
- The microcontroller or MCU is a small-sized computer assembled on the one MOS IC chip. In other words, it is like the Soc or system on chip which consists of a microcontroller as its one element.
- In a microcontroller, there is one or more than one central processing unit having memory and input outputs devises that can easily be programmed.
- The memory used in the microcontroller is of ferroelectric RAM, NOR flash OTP(One Time Programmable) Rom, and also random access memory.
- It is usually used in embedded applications, in personal computers, and some other general-purpose applications.
- The devices which are controlled automatically used microcontroller example of these devices are automobile engine control system, remote control instruments, toys, electronic devices, etc.
- By decreasing the physical size and price of such a device that used separate memory input-output devices and microprocessors than microcontroller is less expensive and control device and process digitally.
- For controlling of non-digital electronic system mixed-signal microcontrollers are used.
- Some types of microcontrollers operate on 4-bit words and use less value of frequency close to four kilohertz for less power usage applications.
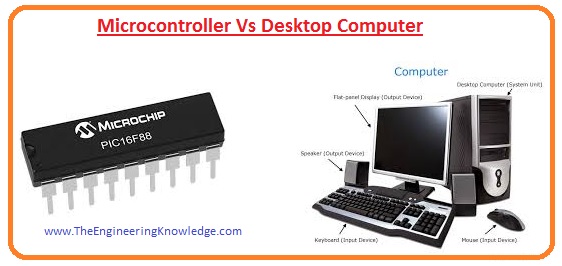
Microcontroller Vs Desktop Computer
- If we compare microcontrollers with the desktop computer that we come to know that the size of a desktop computer is larger than the microcontroller.
- The operation speed of the microcontroller is less than the normal PC.
- Wit some difference there is some similarities between these two microcontrollers have CPU like the normal computer.
- The Central processing unit of microcontroller has different word length ranging from four-bit to sixty-four bit.
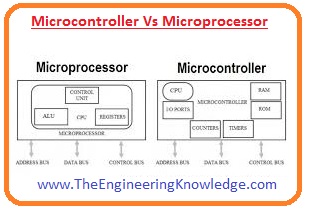
Microcontroller Vs Microprocessor
- It is considered that both microprocessors and microcontrollers are the same devices but it is not true both are different devices.
- The basic difference between them is that in microprocessors different external devices are used for communications but in the microcontroller, there is no exterior device is used but all components are inbuilt in the structure of the microcontroller. Due to this size and cost of a microcontroller is less.
- The microprocessor is mostly used in laptops’ personal computers and notepads while the microcontroller is only used in an embedded system.
- The clock given to the microprocessor has a large speed than the clock of the microprocessor and performs more operation. Microprocessors can operate on the frequency of one gigahertz.
Features of Microcontroller
- The generally used microcontroller are exits in complicated structure and has the ability to operate on word length of sixty four-bit.
- The already built element of the microcontroller are EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory), EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory), RAM (Random Access Memory), ROM, different timer input and output devices ports and reset buttons.
- The usage of RAm is to store data and ROM store different programs and some other parameters.
- For macro instructions, MC are created with the use of CISC architecture.
- For replacement of small instruction macro types instruction is used in the microcontroller.
- The currently used MCU uses less power than the older MCUs which operate on large power.
- The voltage operating range of MCU is 1.8 volts to 5.5 volts.
- The modern microcontroller provides features like EPROM and EEPROM which wich was missed in older versions.
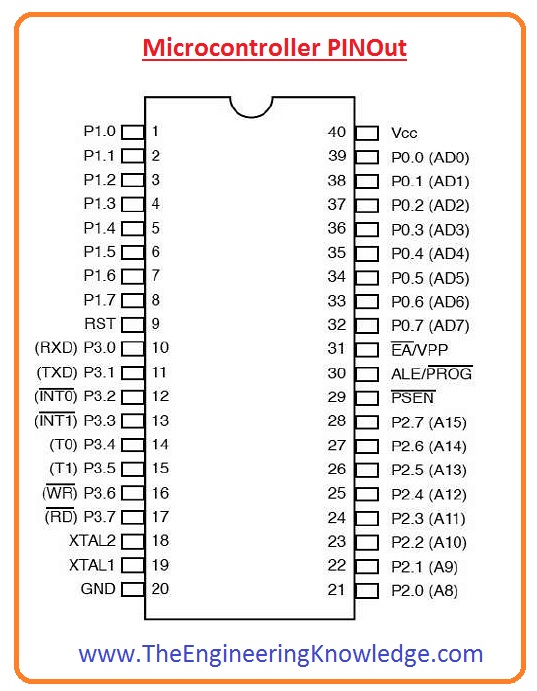
Microcontroller PIN Out
- There are forty common pinouts of the microcontroller which are described here.
Pinout 1 to 8
- These pinouts do not perform any function.
Pinout 40
- Vcc: It is input, where the power supply of the microcontroller is given usually plus five volts, are applied.
Pinout 20
- Vss: This pinout is ground terminals.
Pinout 32 to 39
- These pinouts are called port zero and operate as an input-output port. Lower order data is multiplexed is through this pinout.
Pinout 31
- It is ALE or address latch enable pinout which is used to demultiplex the address-data signal of port zero.
Pinout 30
- It is EA or external access input pinout that used to enable or disable the exterior memory interfacing. If external memory is not connected it remains high.
Pinout 29
- It is a PSEn pinout that used for reading of data from exterior program memory.
Pinout 21 to 28
- these pinout called port two. This port operates as an input/ output port. Large order address bus signal multiplexed through this port.
Pinout 18 and 19
- Exterior crystal is linked with the use of these pinouts and provides a clock to system.
Pinout 10 to 17
- These pinouts make port three. This port does some functions like interrupts, timer input control signal, etc.
Pinout 9
- This reset pinout.
That is a detailed post about the microcontroller if you have any further queries ask in the comments. Thanks for reading.