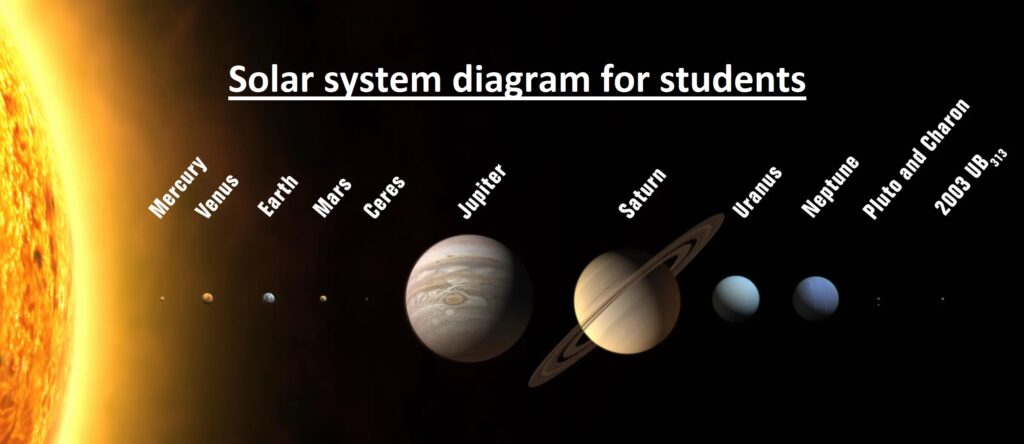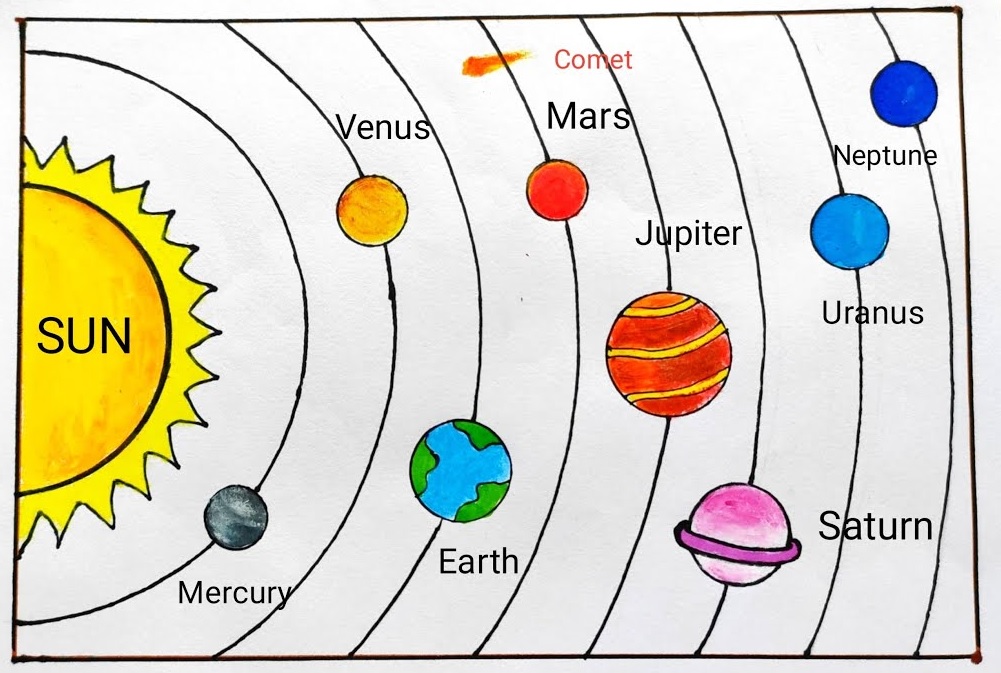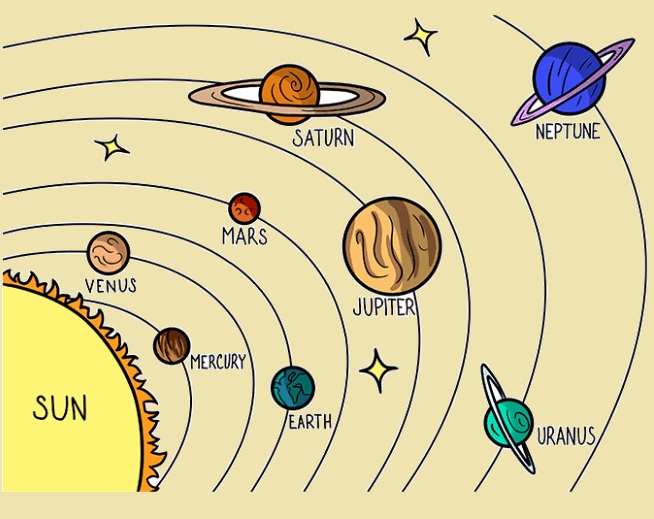
Hi, friends welcome to the new post. In this post, we will have a look at the Solar System Diagram. Scientists and other students of science want to know the solder system details and about the celestial objects. We will cover the details of simpler system complications here and define elements of the system diagram and their importance. We will cover the all details of the solder system with a diagram. So let’s get started Solar System Diagram.
Introduction to Solar System Diagram
The Sun, comets planets moons, asteroids, and other celestial bodies are part of the solar system. The gravitational force of the sun has affected these elements which connect and each component effectively considers the balance in the universe. Comsomislical studies is defined as getting the details of the solar system that also provides planet study, space travel, and other parameters.
Sun:
- The Sun is known to start existing at the midpoint of the solar system The Sun is later in size hot plasma created with hydrogen and helium. All planets, moons, and other large bodies are moving around the sun through the gravitational force of the sun.
- The dynamics of this configuration are controlled by the sun which also offers heat and light needed for continued life on Earth.
- The photosphere, that is sun’s surface is a sphere that releases heat and light. The chromosphere and the corona, are neighboring layers that can be seen during solar eclipses or with the use of certain tools. The sun also faces differnt processes such as solar flares, sunspots, and solar configuration, which add to its attraction
Planets: Cosmic Neighbors
- A total of 8 planets exist in the solar system that come with their features. These planes are The planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Saturn, Uranus, Mars, Jupiter, and Neptune are listed in order of proximity to the Sun. There are different features sizes, and compositions for these planets. Mercury is a small-sized planet and it is close to the sun. The thick atmosphere of Venus is called the “sister planet of Earth,” the hottest planet in the solar system.
- Eart is a colored planet that is considered a diversified planet and comes with life. The biggest volcano and deepest canyon in the solar system can exist on Mars known as Red plant
- The high volume of gases exists in the front of Mars. The larger plenty is Jupiter comes with a strong magnetic field and different clouds.
- Satruan is famous due to its good ring system which has a ring structure with ice particles. The ice particles Uranus and Neptune are differentiae don the base of their blue color and skewed axes.
Moons:
- Moons or some other types of natural satellites cover the different planets existing in the solar system. This moon that are natural satellite that comes in different sizes and cultures. The moon which is called Luna is the only natural satellite in on universe and is still under study.
- The moon of Santa Titan is the only moon in the system that has a thick atmosphere. The Moon of Jupiter is also known due to its volcanic activity. Io, Ganymede, Europa, and Callisto, the Galilean moons of Jupiter, are some important moon
Asteroids and Comets
- The older solar system comes with comets and asteroids that affect the solar system used now. Rock-like asteroids that mostly exist between Jupiter and Mars in the asteroid belt are about the sun in a circle-like configuration. Small-size pebbles to small planer cases are in their sizes.
- Comets are icy bodies tha originate from the edge of the solar system. The ice that exists on the comet vaporizes at it goes towards the sun, making a bright coma, and mostly lies away from the sun. Astronomer always know about the comets and their discussion provides the details of solar system structure and production
Read our latest post: What is Charging by Conduction?
How to draw the diagram of the solar system?
draw and label the solar system is shown here
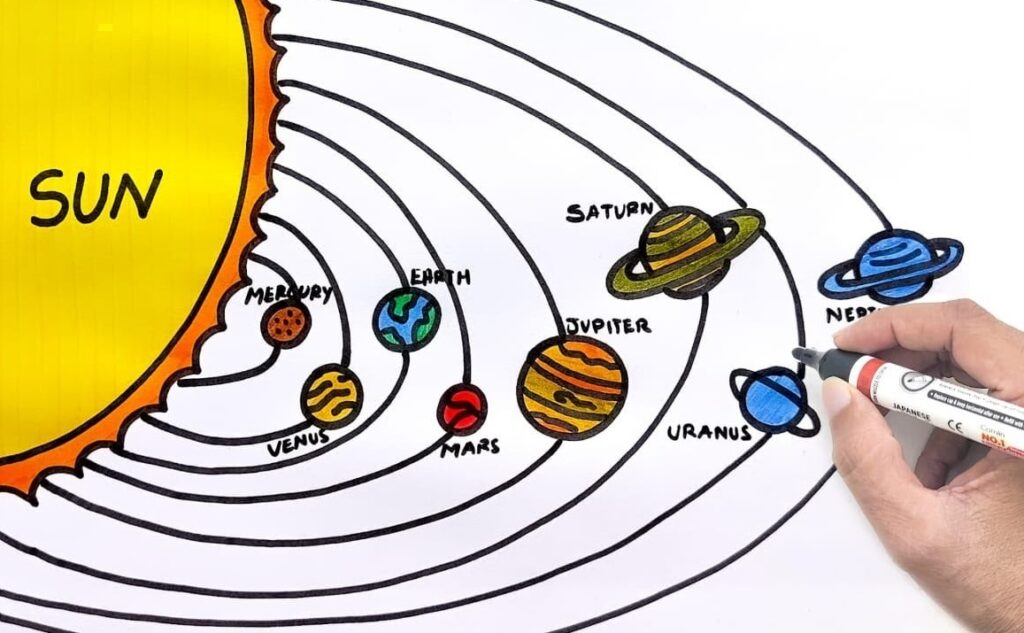
- Gather materials: There is a need of large size paper sheets or poster board, some colored pencil markers and a ruler must be needed
- Plan layout: Decide the location of each plane in the graph. We can draw a horizontal line to show the ecliptic, which is about a flat plane where different planets orbit the sun
- Draw the Sun: To show the sun start making a drawing circle in measurement form at the midpoint of the paper. To show its different parameters use yellow or orange color in the circle
- Add the planets: Now draw different circles to show each plane at the same distance from the sun with the use of a ruler to make accurate distance. On the base of the proper sizes of planets, the sizes of circles can be different. To make accurate sizes we can use scale or reference guidelines
- planet labeling: Now write the name planet close to the circle of each planet. To make a proper difference in planes use different close combinations
- Ad other celestial bodies: If there is a need to add some more details in the diagram add asteroids, moons, and comets. To draw these bodies make small sizes circles or different shapes close to the planets
- Provide more information: If there is a need to add more details related to planets and other celestial bodies, we can add some labels and captions on diagrams. We can define the size of planets, their structure, and different features on the diagram.
- colors used for details: There can be differnt color combination cabinets used on diagrams with pencils or markers. Bleu color can be used for Earth denoting, red for Mars, and other types of color combinations used for giants Jupiter and Saturn. We can add more runs for Saturn or different colors on Jupiter to define the planet’s well-known storms.
- Consider a background: In the solder system diagram on paper we can add a background color that has more details. To make proper details and an attractive solar system diagram we added stars, galaxies, or even the Milky Way.
- Review and finalize: After completion of the diagram, we can check the diagram and do a proper inspection of the photo. If there is improvement needed in the diagram we can make
Solar Panel System Diagram
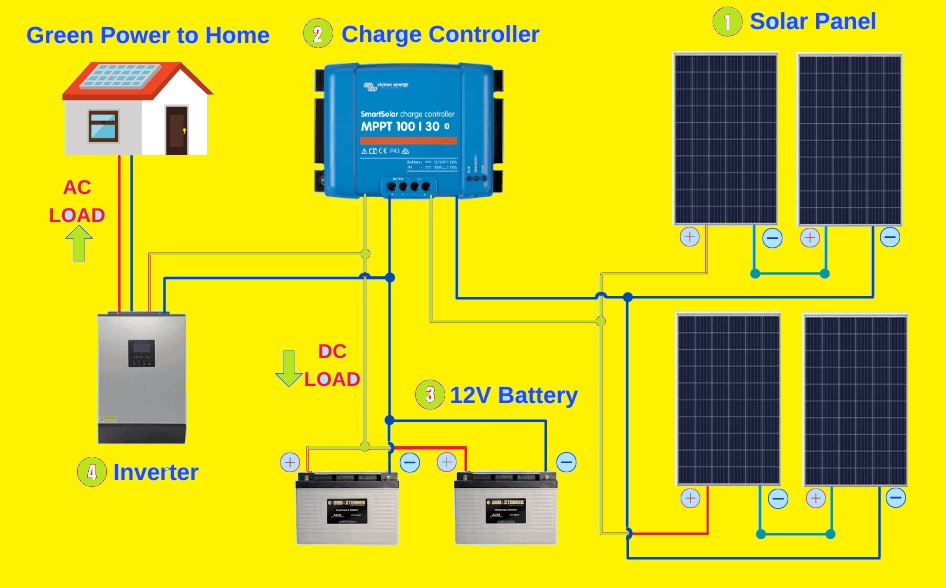
The parts and energy flow in a solar power system are shown in a solar panel system diagram. The main parts of solar panel systems are explained here
- Solar Panels: Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic are a source of energy. These panels are created with the use of solar cells that work the photovoltaic effect to transform sunlight into direct current
- Mounting Structure: To source and put solar panes where they can get high light sun They are connected to the building such as roof or ground-based racks
- Inverter: An inverter gets the DC electricity generated by the solar panels. The inverter converts the direct current power into AC current which is the electricity used in our homes and offices
- Electrical Panel: The electrical panel, breaker box, or distribution board, gets the AC energy from the inverter. Electricity is provided by the building through an electrical panel, that runs the different devices connected and lights
- Utility Meter: A utility meter connected to grid-connected solar panel installations to measure the power made by the solar panels. This meter recoded the power used and generated provided data for net metering or feed-in tariffs.
- Grid Connection: These connections are used for grid-connected solar panel connections. When solar panels provdies large power requirements they can be sent to the grid and mostly get credits or payment. With that power is taken from the grid when solar energy production inadequate
- Monitoring System: The operation and energy output of the solar panels can be noted in real-time through homeowners or system operators in differnt solar panel connections.
- Battery Storage: To use after that like during times of poor solar generation or power off. different solar panel systems with battery storage can store more current produced by all day. Battery storage devices can increase the self-consumption of solar energy and provide backup power.
Explore Our Coins Articles:
- How Many Nickels in 2 Dollars?
- How Much Does a Roll of Pennies Weigh
- How Much Does a Quarter Weigh in Grams
- How Much Does a Dime Weigh?
- How Much Does A Nickel Weigh?
Composition of the Solar System
There are different celestial body lines in the solar system, and they move about the sun Let’s discuss them
- Sun: In the middle of the solar system there is the sun which has about 74 percent hydrogen and helium to make a large part of the sun’s mass. In the middle of the sun, three is nuclear fusion reaction is done by these gases and releases light and heat
- Planets: The planes that exist in the solar system come with different compositions. The stone-like elements silicates and metals make different types of terrestrial planets Venus, Earth, Mercury, and Mars. These rocky bodies come with a flat structure and air tha is not thick
Jupiter and Saturn are gas giants that also have hydrogen and helium similar to the sun. But there is atmospheres also added small quanity of other substances like water, ammonia, and methane.
With the hydrogen and helium, Uranus and Neptune which are icy planes also come with larger quanity of ice and water, ammonia, and methane.
- Moons: The moon is a Natural satellite, tha comes with different components based on its creation and and how they exist. Some moons such as the moon of eat are created with rock and metals. Other planet moons are ice and deep seas, for example, Jupiter’s Europa and Saturn’s Enceladus.
- Asteroids: Rock-like asteroids, that mostly come in the asteroid belt among Mars and Jupiter, around the Sun-like circle. Some are made with silicate rock, and with a combination of iron and nickel. So their size and structural layout is like a sphere and defined as a dwarf planet.
- Comets: Ice-covered bodies known as comets lie in the outer region of the solar system. They are made of water ice dust, rocks, and frozen gases. Comet releases bright coma and come with a tail that is directed away from the sun as they get close to the sun., where het resulted the ice becoming vapor
- Dwarf Planets: As they are like planes dwarf planets such as Pluto and Eris come with junk in their orbits. They are created with different materials such as ice, rock, and organic substances.
Inner Solar System
- Venus, Mercury Earth, and Mars are the 4 terrestrial planets that exist in the inner solar system. These types of planets are small in size and created with the use of metal and rock. Then the external planets, are closer to the Sun and have smaller orbital periods.
- As mercury is close to the sun it faces eh high temperature. Venus is the hottest planet due to its greenhouse effect that is caused by a thick atmosphere. Earth, The 3rd planet, is defined due to its large quality of water ecosystems, and life. Earth has lived and after that Mars also have
Outer Solar System
- The gas giants, that have Saturn, Uranus, Jupiter, and Neptune, are part of the outer solar system. These planets are made of hydrogen and helium and are larger than their terrestrial equivalents.
- The Great Red Spot is a storm that has raged for many years on Jupiter,tha is the largest planet in the system/ The Galilean moons, which are the biggest in the solar system,
- Saturn is magnificent and comes with rings and when seeing from orbit these rings are created with frozen particles, offering a good look.
- The Neptune and Uranus axis of rotation are called the ice giants and are defined at sharp angles. Due to the differnt seasons and proper atmospheric occurrences that follow, these are topics of search
Dwarf Planets:
The solar system comes with different types of dwarf planets with a combination of eight planets. Despite being small planes certain celestial bodies, like Pluto and Eris, comes with some coon features. Astronomers’ discussion and disagreements about Pluto’s consideration as a dwarf planet helped them detail the complexity of celestial bodies
Kuiper Belt: Icy Objects Place
The Kuiper Belt is a larger size area that comes with frozen objects and exists beyond Neptune’s orbit. Differnt comets and other small things, as dwarf planets such as Pluto, exist in that particular location.. It can be defined to get the understanding of solar systems created and made.
Diagram of the solar system
diagram of a solar system is seen here
How do you draw a solar system diagram?
For drawing the solar system diagram started withdrawing the larger size circle to the left side of the page for the sun. After that eight circles on the right side of the sun that used as planets of the solar system. Now give names to these 8 circale as Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Solar system diagram for students
The solar system comes with SUN and other planets around the sun. The things around the sun are 8 planets and their moon, dwarf planets, and countless asteroids, comets, and small, icy objects. However, with that most of the solar system is space.
Drawing of the solar system
drawing of the solar system is made here by a student
Conclusion: diagram of a solar system
The knowledge of solar system diagrams comes with different types o information and knowledge to study the journey of detailed space. Scientists are still trying to find the secrets and other parts of the celestial bodies like the sun burning to cold areas of Kuiper Belt. Enhancing knowledge about the asteroids planetary science, comets,ce, asteroids, and exoplanets does three main things: it develops technology and motivates us to continue getting advances
FAqs
- How do you understand the solar system?
The solar system is complicated and is a very vast field so there is a need for deep understanding to discuss all features. But the are some factors tha help to get some details of this system.
First, it is good to know that the solar system is based on gravity. it is the gravity of the sun that maintains plants in orbit it and the gravity of plants maintains monn to move around them
Different types of compone make solar systems. The sun is the moon and some comets, asteroids, and meteoroids in the solar system
At last, there is a need to get an idea of the different forces tha make the solar system. The sun’s heat and light cause the solar wind tha be a stream of charged particles. The solar wind make attraction with the magnetic fields of planets making auroras
- How do you explain the solar system to a child?
- First of all, we will define the basics of the solar system tha are the sun planets and gravity.
- Three can be basic language and discussion can be used for child knowledge
- Visual photos or charts can used solar system to practically define the system
- Use stories, games, and other activities to engage children.
- What is a solar system for Basic 6?:
- The Sun is known as a star and lies at the midpoint of the solar system
- All panes are moving around the sun in the form of elliptical orbits.
- The is different sizes and compositions of all planets.
- Planes come with the moon with different features and parameters
- Some of the bodies of the solar system are asteroids, comets, and meteoroids.
- What is solar system’s best answer?
Here is answers
- The Solar System is the gravitationally connected system of the Sun and the objects moving about the sun
What are 5 basic solar systems?
- Single-star solar systems: They come with a single star and a very common type of solar system in the Milky Way galaxy.
- Binary star solar systems: it has two stars that orbit each other.
- Triple star solar systems: it has three stars that orbit each other.
- Planetary nebulae: These solar systems are the remains of stars that not exist
- Brown dwarfs: They are not stars but are more massive than planets.
Explore Our Latest Articles:
- What are the 8 planets of the solar system?
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
- What are the 5 parts of the solar system?
Sun, the planets, the moons, the asteroids, and the comets are five parts of solar system
- How many planets are there?
There are 8 planets in the solar system.
- Who named the planets?
Ancient Greeks and Romans given the planets names
- Which is the hottest planet?
Venus is hottest planet
- What is called solar system?
helio system is other name of solar system
- Which is the coldest planet?
Neptune. is The coldest planet
- What is my planet called?
Earth.
- How big is the solar system?
it is about 100 billion kilometers across.
- What is the size of the Sun?
1.4 million kilometers is dia of sun
- How old is the solar system?
4.5 billion years old.
- What color is Jupiter?
reddish-brown is color of hupiter
- What color is Saturn?
yellow-brown color.
- Why is Earth called the Blue Planet?
Earth is Blue planet due to its blue oceans.
- Where are stars created?
Stars made in nebulae, that is gas and dust.
- Which is the smallest in the solar system?
Mercury is smallest planet
- Why Pluto is not a planet?
Since it not fuflfil the citerain fo palnet. The planet must be exis in orbit around sun and also have some mass to clerts orbit their bodies and can move,But pluto not fullfil third paramtes so it not be planet
- What Colour is Mercury?
Mercury is a grayish-brown color.
- What is in a universe?
The universe is everything that exists, all space and all of time.
- Which planet is green?
No plant is green colored
- Is Jupiter hot or cold?
Jupiter is ahot planet. here is 15 million degrees Celsius at its core
- What colour is Earth?
blue and green is color of earth
- Which planet is called black planet?
Mercury. is called black planet
- What planet is pink?
Not planet has pin color
- Which planet is yellow?
Saturn is yellow
- Does it rain on Jupiter?
Yes, on jupiter there is rain of ammonia and methane.
- How hot is Earth?
15 degrees Celsius is average temperature on Earth
- Can humans go to Venus?
Yes, humans can go to Venus. but difficut processs
- What colour is water?
There is not color of water
- How old is the earth?
4.5 billion years old.
- What color is air?
There is not color for air