 Hello fellows, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at MOSFET Analog Switching. The MOSFET stands for metal oxides field effecct transistor also called MOS transistor. It is type of insulated gate field effect transistor which constructed with the controlled oxidation of semiconductor material. Like BJT this type of transistor has three terminals called gate, drain and source.
Hello fellows, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at MOSFET Analog Switching. The MOSFET stands for metal oxides field effecct transistor also called MOS transistor. It is type of insulated gate field effect transistor which constructed with the controlled oxidation of semiconductor material. Like BJT this type of transistor has three terminals called gate, drain and source.
It used in different switching and amplifications applications. In today’s post we will have detailed look at its use as analog switching. So lets get started with MOSFET Analog Switching.
MOSFET Switching Operation
- E-MOSFET or enhancement MOSFET is used for switching applications due to their threshold characteristic VGS(th).
- If the gate to source voltage is less than threshold value, there is off state of MOSFET.
- When the value of source to gate is larger than the threshold value, there is on state of MOSFET.
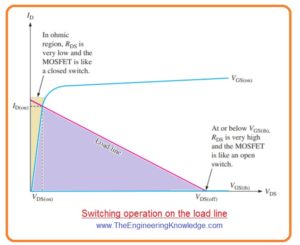
- If the value of VGS is changing among VGS(th) and VGS(on), the MOSFET is operating as switch it explained in below figure.
- In off condition for VGS<VGS(th) the transistor is functioning at the lower part of load line and behaves like an open switch or large RDS.
- If VGS is very large than the VGS(th), the component is operating at upper portion of load line in the ohmic region and behaves like a closed switch or very less value of RDS.
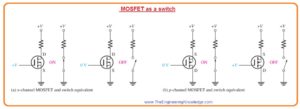
What is Ideal Switch
- In figure denoted as ‘a’ when the gate of n channel MOSFET is +V the gate is at more positive level than the source by quantity larger than the VGS(th).
- The MOSFET is on state and look as close switch among the drain and source.
- If the value of gate voltage is 0 there will be zero volts for gate to source.
- The MOSFET is in off state and looks like an open switch among the drain and source.
- In figure denoted as ‘b’ when the gate voltage of p-channel MOSFET is zero volt the gate has less positive value then the source by quantity larger than VGS(th).
- The MOSFET is in on state and look like closed switch among the drain and source.
- When the gate is +V the gate to source voltage is zero. The MOSFET is in off state and look as an open switch among the drain and source.
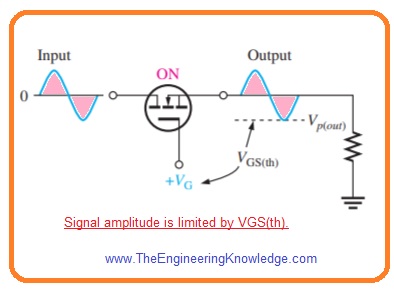
MOSFET Analog Switch
- The MOSFET is usually used for switching of analog signals. Generally a signal given to the drain can be switch through the source with the voltage on the gate.
- The main limitation is that signal level at source should not cause the gate to source voltage to be less than VGS(th).
- In below figure N channel MOSFET analog switch is shown.
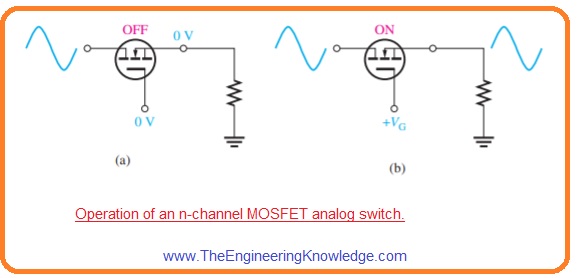
- The signal at the drain is attached to the source when the MOSFET is on through positive VGS and dettached when VGS is zero.
- If the analog switch is on as shown in below figure.
- The minimum gate to source voltage exits at negative peak of signal.
- The difference among VG and -Vp(out) is gate to source voltage at time of negative extreme and should be equal to or larger than the VGS(th) to retain the MOSFET in conduction.
VGS = VG – Vp(out) ≥ VGS(th)
MOSFET Analog Switch Applications
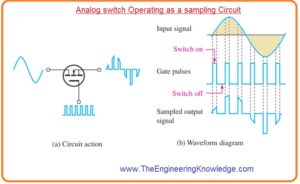
Sampling Circuit
- One application of analog switch is ADC transformation.
- The analog switch is used in sample and hold circuit to sample the input voltage at specific ratio.
- Every sampled signal values is momentarily stored in a capacitor till it can be transformed into a digital value through ADC.
- To make this MOSFET is on for small-time interval for one cycle of input signal through pulses given to the gate.
- In below figure some samples for clarity is shown.
- The least rate at which a signal can be sampled and rearranged from the samples should be larger than 2 time the maximum frequency comprises in the signal.
- The leas sampling frequency is named as Nyquist frequency.
fsample (min)>2fsignal (max)
- When the gate pulse has large level the switch is on and less part of the input wave existing during that pulse displays at the output.
- When the pulse wave has zero level the switch is off and output is zero volt.
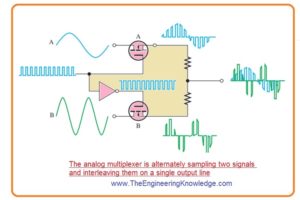
Analog Multiplexer
- For such applications where 2 signal are to be transmitted at single point analog multiplexers are used.
- In below figure a 2 channel analog sampling multiplexer is shown.
- The MOSFET is on and off in alternative fashion so ist signal sample is attached with the output and than another.
- The pulses are given to the gate of switch denoted as ‘A’ and inverted pulses are given to the gate of switch denoted as B.
- The digital circuitry named as inverter is used for that purpose.
- For high pulses switch A is on and switch B is in off state.
- When pulses are less or low switch B is on and switch A is in off state.
- It known as time division multiplexing since signal A displays on the output for time interval when pulse is high and signal B displays for time interval when pulse is low.
- That is, they are inserted on a time interval basis to broadcast on a single line.
Switched-Capacitor Circuit
- The other applications of MOSFET in switched capacitor circuits usually used in ICs programmable analog devices which called analog signal processors.
- As capacitors can be very easily connected in integrated circuits very easily as compare to resistances.
- Capacitors also occupy less place than the IC resistances and also loss less power or no power.
- Numerous types of analog circuitry uses resistances to find voltage gain and other features with the use of switching capacitor to emulate resistances dynamic programming of analog circuitry can be got.
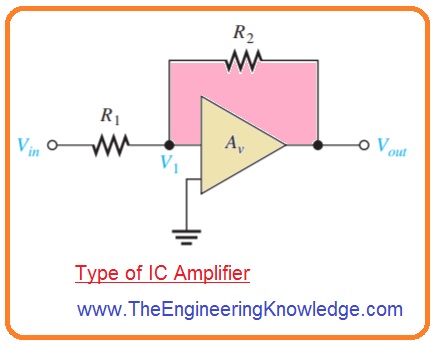
- For instance in specific catagory of integrated circuits amplifiers 2 exterior resistance are needed as shown in below figure.
- The values of these resistances make the voltage gain of amplifier as Av=R2/R1.
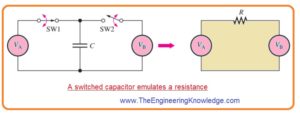
- The switched capacitor can be used to emulate resistance as shown in below figure with the use of mechanical switch technique.
- The switch one and switch two on and off after specific frequency for charging and discharging of C, according to values of voltage source.
- For IC amplifier for resistance R1 Vin and V1 are denoted as VA and VB correspondingly.
- For resistance R2, V1 and Vout are denoted as VA and VB, respectively.
That is detailed post about MOSFET Analog Switching if you have any question ask in comments. Stay tuned for next tutorial.