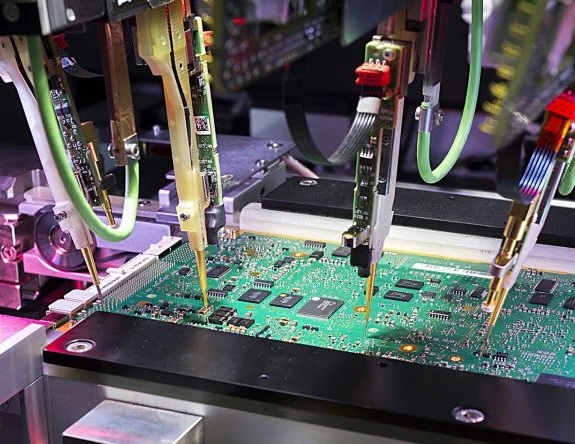
Hi guys welcome to the new post. In this post, we will learn What is a PCB Flying Probe Test. PCB boards are complex and structured and have high-density components and some testing processes of old types like manual testing and bed-of-nails testing are limited due to high cost, longer duration and testing process. This is where the PCB flying probe test comes to use, offering a flexible and effective solution for testing PCBs. So let’s get started Introduction to flying probe testing
What Is Flying Probe Testing?
Flying probe testing is a process where an in-circuit test method is used for testing PCB board assembly.
In this testing method, many probes are used to make electrical contact with the testing points of PCBA. The probes are flown on the board surface and make contact with testing points.
The test results are monitored to find that the board is fulfilling the required parameters. Flying probe test is a less expensive method to check board and is used in high-volume manufacturing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PCB Flying Probe Test
Advantages
- The main advantage of this test is the less costly process to test boards and circuits. Since probes can easily be free they reach points of the board without configuring them, It reduces time and labor costs for testing and makes low-cost tests.
- Flying probe tests provide accurate results. The probe has featues to measure the electrical parameters of the board with accurate values. It is important to make sure that the board fulfills certain design needs.
- This test is a high-speed test. The probe can move fast over the board, helping the test to finish in a short time. It is best when time is important like products have to deliver in a short time.
- It is a flexible test. probes can programmed to move in different configurations helps to test different boards. It makes to test differnt products with the same test.
- This test is safe to perform, and prevents from making contact with any other components. It reduces the chances of any damage that can result of faulty circuit boards.
Disadvantages
- The flying probe testing does not power up the circuit, SO not get the real strucrue that ICT provides.
- The flying probe does not have features to inspect the ball grid array. Since the probe needed access points for connection to components.
- It is a high-cost test, normally prices are not high but higher than other tests like AOI.
- This test needed the setup of a test probe and other instruments which can be time-consuming. It can be difficult when testing a larger number of boards in a short time.
- This test also has limited flexibility. This test needed special instruments and was not flexible like others. it can cause issues when testing boards with different designs and sizes as test probes can be needed to set with each other
Applications of PCB Flying Probe Test
This test has many applications due to its flexible nature and easy testing process. Some main applications are
- This test is normally used for testing PCB boards in the electronic industry. Their flexibility make them best to use for differnt PCB testing processes, like prototype development to small and medium production runs.
- The flying probe test system comes sith both in-circuit tests and functional tests (FCT) to make sure quality and accuracy of assembled boards.
In-Circuit Testing
In this test connection and functions of individual components of boards are checked like resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits. it helps to find manufacturing faults, like open circuits, short circuits, and component misalignments that affect board working.
Functional Testing
This test checks the overall operation of the assembled board by simulating working in real-world conditions. it an be testing power supply, quality of signal and communication interfaces, and checking accurate operations of embedded software.
The main benefit of the flying probe test system for board testing is the feature to handle different board designs and testing needs without needing the requried testing fixtures.
How Does Flying Probe Testing Work?
Some steps involved in flying probe tests are explained here
1. Load PCB
- In this first step board is configured on the testing platform with accuracy
2. Optically Align Board
For testing the board optical camera is aligned on the board
3. Import Test Program
Test data is imported for CAD
4. Probe Test Points
Probes touch on different options to find the testing nodes
5. Perform Electrical Tests
Tester started and measured on the base of programmed tests.
6. Move Probes
Change the position of probes to cover all nodes
7. Repeat Tests
Steps four to six are repeated to tell verification is completed.
8. Display Results
Now configure the results of this test about finding the faults
Flying Probe Testing vs. ICT Testing
- ICT testing uses certain test fixtures with many spring-loaded probes and flying probe testing uses movable robotic probes.
- ICT testing is best for board having easily accessible test points and flying probe testing can handle more designs with buried or hard-to-reach components.
- ICT has comprehensive coverage and finds different faults like signal quality issues, flying probe tests have high flexibility for PCB designs that have limitations for some test coverage areas.
- ICT testing is a high-speed operation as it does many tests with the use of many probes and flying probe tests are performed in sequence and slow process.
- ICT tests need development test fixtures that can be time and flying probe testing is fast since it is not based on dedicated fixtures.
- Flying probe tests can perform both electrical connectivity and functions featues of the board and ICT testing based on electrical integrity.
Process Flow for a Flying Probe Test
Test Program
The process started to make a flying probe testing program. This program provides direction for probes for assessing the board, defining the test type, the voltage measured, and the testing points’ position.
Set Probe
During the test program at position test probes are configured on point. These probes are configured with a platform that helps ot move over the x, y, and z axes to make sure the correct position over the required testing point on board
Program applications
Over getting accurate position test program is applied. Probe makes connection with board testing points and uses requried voltage levels. Programs measure important electrical features of test points like capacitance, current, resistance, and inductance.
Result
Now configure the result and check that it is according to requirements
Circuit Board Testers
Here commonly used circuit board testers, are listed
- In-Circuit Testers (ICT):
- Flying Probe Testers
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) System
- X-ray Inspection Systems
- Functional Testers
Read also:
- Types of PCB Board
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Materials
- Double Sided PCB Board, Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- Single Sided PCB Board, Construction, Working, Features & Applications
- How to Get High Quality and Low Cost PCB Board
- What is Polyimide PCB Board
FAQS
What is the difference between flying probes and ICT testing?
ICT testing provides detailed coverage and can find different types of faults like electrical integrity problems. FLying probe test is flexible for PCB designs that an have limitations for certain test coverage areas.
What is the FPT test in PCB?
The flying probe test (FPT) is an automated testing process. One or more automated probes are used over the cross-section of the board. These probes are inspected from pin to pin. The mounted component function is monitored in this test
What is GPT vs FPT?
GPT or (Giant Perpendicularity Test) and FPT (Flying Probe Test) are 2 completely different concepts. GPT is defined as a testing method employed to determine the perpendicularity or alignment of properties or structures, generally in mechanical or engineering contexts. While, FPT is a testing process specifically used for board, where robotic probes are employed to make electrical connections with test points on the board
What is MPT vs FPT?
| Feature | MPT | FPT |
|---|---|---|
| Testing method | Manual | Automated |
| Application | Surface hardness or resistance | Board testing |
| Technique | Penetrating with a specialized tool | Robotic probes making contact with test points |
| Parameters | Hardness, resistance | Electrical parameters |
Why is GPT used?
GPT, or Giant Perpendicularity Test, is employed to evaluate the perpendicularity or alignment of a feature or structure. It helps to ensure that components or structures are accurately aligned according to certain tolerances. GPT is used in mechanical and engineering industries to check the accuracy and quality of parts, assemblies, or structures.
What is FPT technology?
FPT is a technology used for testing printed circuit boards. It uses robotic probes that move across the board and make contact with certain testing points to find electrical features and defects.
What does FPT mean in mechanical?
Functional Performance Testing (FPT) puts the Direct Digital Control (DDC) system through manipulating each condition the HVAC controls and equipment faces
What is the meaning of FPT in PCB?
Flying probe tested is used at the last phase of the PCB manufacturing process for testing and validation of board functions. In bare board, it is used for finding defects like opens and shorts.
What size of PCB is optimal for flying probe testing?
Flying probe work well for small to medium size boards with dimensions of 18” x 24”. Larger boards are difficult to handle
Can flying probes accommodate thick or odd-shaped PCBs?
The larger thickness changes an restrict flying probe access. Some edge is clreance is best