Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Single Phase & Three Phase. There are 2 classifications power systems first one is a single phase and the second one is 3 phase. The phase is used to drive such loads that needed less power and the three-phase is used in industries where high rating load is used.
Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Single Phase & Three Phase. There are 2 classifications power systems first one is a single phase and the second one is 3 phase. The phase is used to drive such loads that needed less power and the three-phase is used in industries where high rating load is used.
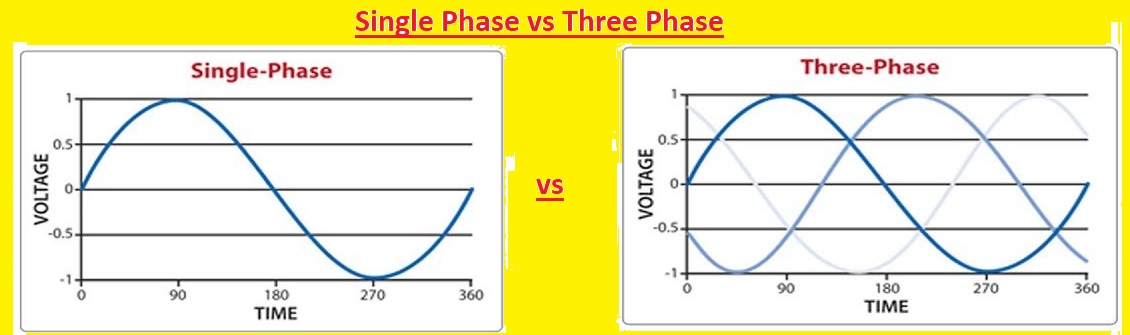
The basic difference between a single-phase and 3-phase system is that in a single-phase one conductor and one neutral wire is used while in 3 phase supply, 3 conductors and one neutral wire are used to make the circuitry. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at both single-phase and three-phase with a detailed compare them to find their differences. So let’s get started with the Difference Between the Single Phase & Three Phases.
Difference Between Single Phase & Three Phase
Single Phase
- In a single-phase, system power is delivered through a single conductor.
- it uses a neutral wire to operate as returning path for current.
- The transfer of power through the system is less than the 3-phase system.
- The system is less complicated than the 3-phase system.
- In this system, 2 wires are used for the completion of circuitry.
- The circuit creation for this system is very basic and less costly since uses fewer conductors.
- It can be used to operate the load value of twenty-five hundred watts
- With benefits if has some drawbacks that devices that are single phases not run directly they needed certain types of circuitry to run at single-phase
- 230 volts are transferred in this system.
- It is also called the Split phase.
- Its efficiency is less than the 3 phases.
- High loads can not operate on it
- In single-phase system failure of power exits.
- Power loss is larger in this system.
- It is less expensive than the 3-phase system.
- It used to run home appliances like ac fridge, motor
- The power for single phase load can get from a three-phase system making the connection between one phase and neutral
- the electric train run at single-phase power,
Three-phase
- In this system, power is delivered through 3 conductors.
- It used 4 wires for the completion of the circuit. and transmission of power one is the neutral wire and the other three are phase
- There is no failure of power that occurs in this system.
- Normally two main types of connection first one is Y which has four wires and the other is delta which has three wires
- different types of connection are done in this system like Y to Y, Delta Delta, Delta Y
- This power system is used at the industrial level where high loads like machines used
- In this system, 415 volts can be transferred.
- The three-phase motor can be easily run in this system and does not need a special circuit
- Due to the use of four-wire, this system is more expensive than a single phase
- High power transmitted through this system
- It has no other name as a single phase.
- The system used in the three-phase is more complicated than the single phase.
- Power losses are less than the single phase.
- Its efficiency is larger than the single phase.
- It is used in larger industries where the high load is operated.
Single Phase vs Three Phase
| Point | Single Phase Power | Three Phase Power |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Power is delivered through a single AC waveform | Power provides through three AC waveforms |
| Number of Conductors | Two (one hot wire and one neutral wire) | Four (three hot wires and one neutral wire) |
| Voltage | Lower voltage compared to three-phase power | Higher voltage compared to single-phase power |
| Current Waveform | Single sine wave | Three separate sine waves, evenly spaced and balanced |
| Power Delivery | Less consistent and efficient compared to three-phase power | More consistent and efficient |
| Power Output | Lower overall power output | Higher overall power output |
| Efficiency | Less efficient compared to three-phase power | High efficient |
| Common Applications | Residential, small commercial applications | Industrial, and commercial applications |
| Motor Compatibility | Good for small motors and household appliances | Suitable for large motors and industrial machinery |
| Transmission Cost | Lower cost compared to three-phase power | Higher costs due to larger conductors and infrastructure |
| Power Distribution | Used in residential areas and small commercial buildings | Used in larger commercial and industrial settings |
| Power Quality | Slightly less stable compared to three-phase power | stable and balanced |
| Electrical Safety | Requires less robust grounding systems | Requires more extensive grounding and protection systems |
| Equipment Size | Smaller equipment size due to lower power requirements | Larger instruments size due to higher power demands |
| Equipment Cost | Generally lower costs due to smaller size and power requirements | Generally higher cost due to larger size and power demands |
| Installation Complexity | Easier installation process | complex installation process |
| Harmonics | it is susceptible to harmonic distortion | Less susceptible to harmonic distortion |
| Load Balancing | challenging to balance loads | Easy to balance loads |
| Power Interruptions | prone to interruptions and voltage fluctuations | Less prone to interruptions and voltage fluctuations |
| Overall Power Demand | Best for lower power demands | Good for higher power demands |
Advantages of Three Phase Power
- Higher power output: Applications requiring more power can use it since the combination of three different waveforms increases the overall power output.
- Smoother power delivery: The three-phase configuration offers a constant power supply, that results in smoother operation and reduced electrical noise.
- Cost savings in transmission: Three-phase power transmission is more effective and needs smaller conductors compared to single-phase power, causes to cost savings in infrastructure and distribution systems
Advantages of Single Phase Power
- Simplicity in the installation: Single-phase power systems are simple and less costly for residential applications since they are simpler to connect and need fewer components.
- Suitable for residential applications: When compared to industrial or commercial applications, residential residences have relatively reduced power needs, making single-phase electricity an excellent option for powering them.
- Common household appliances: Different household appliances, like air conditioners, and refrigerators, , and TVs, operate on single-phase power. It is the standard power supply used in most homes.
Common Applications
Single phase power applications are explained here
- Lighting fixtures
- Computers and electronics
- Residential air conditioning units
- Small appliances
Three phase power used in this operations
- Industrial machinery
- Manufacturing equipment
- Motors and pumps
- Large commercial buildings
So friends that is a detailed post about the difference between single-phase and three-phase if you have any queries ask in the comments. Thanks for reading. Have a good day.