 Hello friends, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we are gonna have a look at What is motor and its practical implementation in industries. In 1740 an inventor of Scotland Andrew Gordon and American scientist Benjamin Franklin invented the first electric motor that was electrostatic. The working principle of these motor was depending on Coulomb’s law. There are numerous types of motor nowadays have been invented. There are 2 main types of the motor first one is DC motors and the second one is AC motors.
Hello friends, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we are gonna have a look at What is motor and its practical implementation in industries. In 1740 an inventor of Scotland Andrew Gordon and American scientist Benjamin Franklin invented the first electric motor that was electrostatic. The working principle of these motor was depending on Coulomb’s law. There are numerous types of motor nowadays have been invented. There are 2 main types of the motor first one is DC motors and the second one is AC motors.
These motors are further divided into subtypes like in AC motors subtypes are single-phase induction motor, three-phase induction motor, and synchronous motor. Similarly in dc motors, there are further subtypes like dc series motor, dc wound motor, shunt motor, compound motor. In the coming tutorial, we will discuss all these motors with the detail. In today’s post, we will detail at the electrical motor, its applications, working, advantage, and practical implementation in our daily life. So let’s get started with what is Motor.
What is Motor
- The motor is such an electric device that transforms electric power into mechanical power.
- The working of these motors depends on the interaction of the field at the stator with the flux generated by the current armature windings at the rotor.
- The input to the motor can be provided according to their types if they are dc motor then input will be provided with the battery, rectifiers and if the motor is ac then its input will come from the ac power source, inverter, and ac generator induction generator or synchronous generator.
- Classifications of motors can according to input supply like AC or DC source, with that it can be classified with their internal structure, practical implementations, etc.
- With AC or DC motors, there are other types of electrical motors like brush motor, brushless motor, single-phase motor, 2 phase motor, 3 phase motor, etc.
- Less rating motors used in industries or in our homes for converting mechanical power into electrical power.
- While high rating motors almost hundred MW used in shipping propulsion, and in pump storage applications.
- Some motors are installed in different fans, pumping devices, drill machines, or some other devices like electric watches.
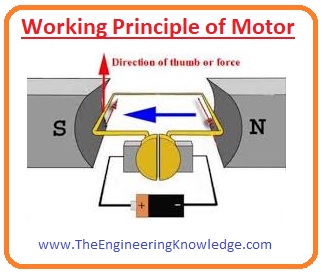
Working Principle of Motor
- As we discussed above motor is an electric device that transforms mechanical power into electrical power.
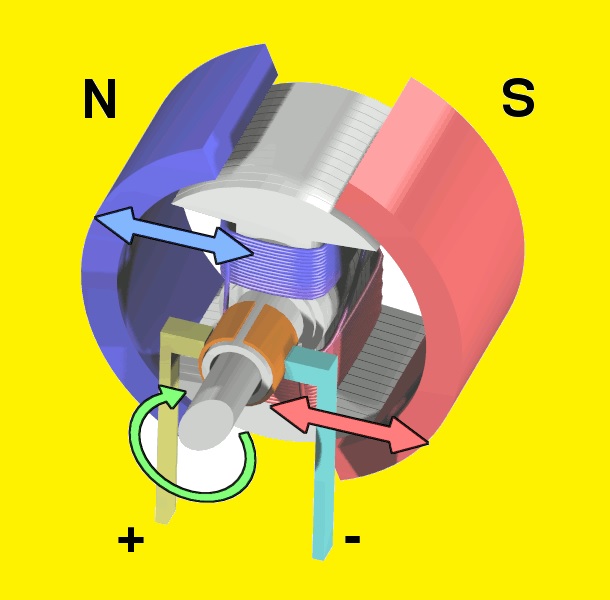
- Its working depends on the rule if a current-carrying conductor is put into the field and force is applied on that conductor and force direction can be found by applying the left-hand rule of Fleming.
- In the case of a motor current-carrying conductor will be a rotor of the motor and field is the poles magnetic field that is mounted on the stator of the motor.
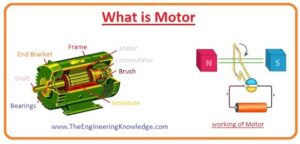
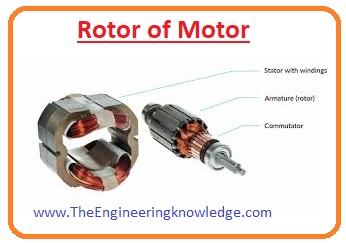
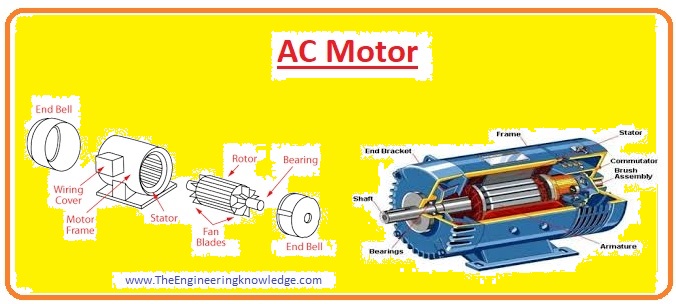
Construction of Motor
- There are two main parts of the motor first is rotor and the second is stator and some are sub parts that are described with the detailed.
Rotor
- The rotatory part of motor is rotor over which armature windings are wound and shaft of motor is connected.
- Some rotor has windings interact with the field of the stator and induced voltage through them and current and flux generated.
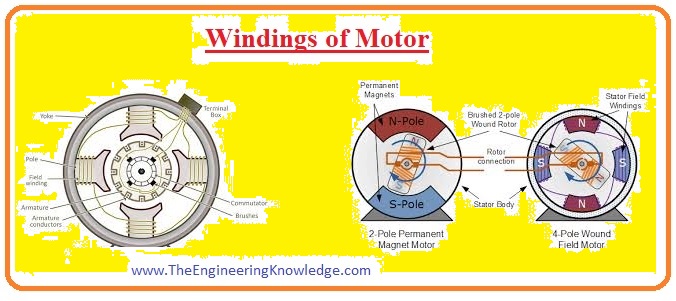
- While in some rotors instead permanent magnet is used that has its own field that interacts with the stator.
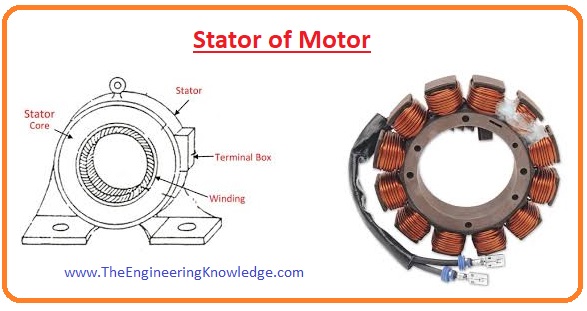
Stator
- The stator is a static part of the motor it provides protection to the internal structure of the motor from outer environment conditions and field windings are wound on the stator.
- Instead of field windings in some motor permanent magnets are used for field production.
- The stator is constructed with steel and laminations with some insulating materials are provided to reduce losses at the core of the stator.
Windings
- There are two main types of windings that are wound in any motor first is armature windings and the second is field windings.
- Armature windings are wound at the rotor of motor and field winding is wound at stator of the motor. In some motor instead of a field winding permanent magnetic is also used for the flux generation.
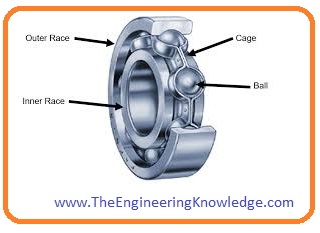
Bearings of Motor
- The rotor is sustained by bearings that permit the rotor to move on its axis.
- The bearings are mounted on the shaft of a motor to provide less friction during its rotation.
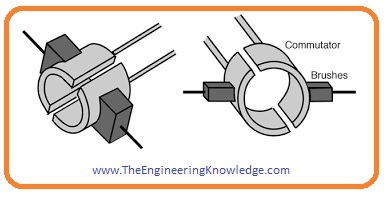
Commutators
- Commutators are the most important part of dc motor that used to transform ac into dc.
- Basically in dc motor ac voltage are produced that are converted into the dc voltage by using commutators, this process is known as
- Commutators are two parts of the ring that are attached at the shaft of motor and carbon brushes have connected these commutators through them output is taken out.
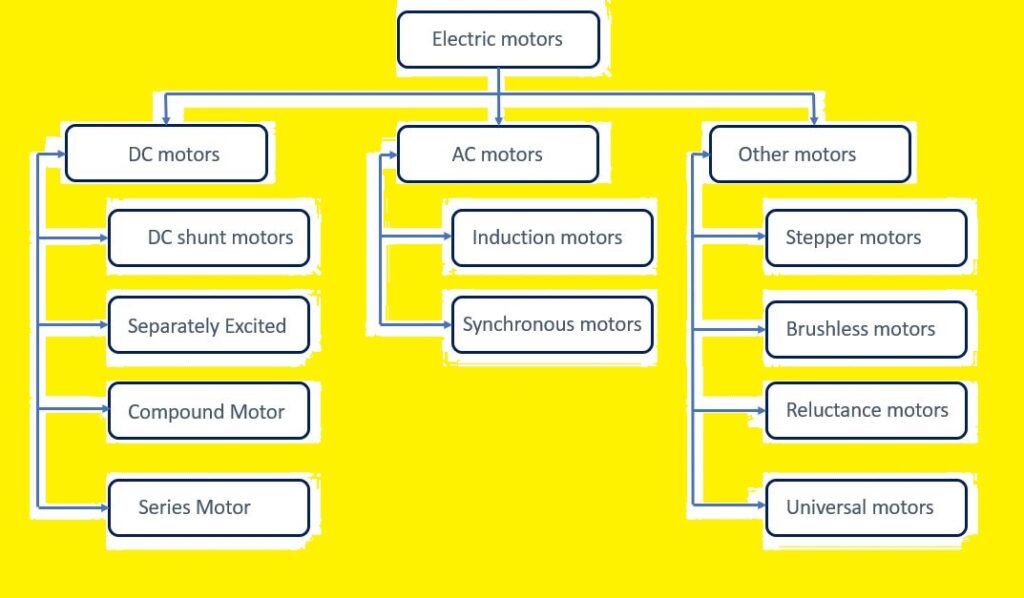
Types of Motor
- There are basic 2 types of the motor first one is dc motors and the second one is ac motor and some other of motors are listed here.
- DC motor
- AC Motor
- Special Motor
- Synchronous motor
- Induction motor
- Series motor
- Shunt motor
- Single Phase motor
- Three-phase Motor
- Now discuss these types with the detailed.
DC Motor
- DC motors are such electrical machines that transform dc electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- This motor is mostly used in robots, drill machines, and industrial tools. There are many sub types of dc motor like shunt dc motor, wound dc motor, shunt dc motor, series dc motor, etc.
AC Motor
- This type of motor converts alternating current input into the mechanical power as output.
- AC motor is mostly used in our industries, houses, and buildings.
- There are 2 main parts of this motor first one is the stator that has stator windings that are connected with the input supply and the rotating magnetic field is produced at that part.
- The second part of this motor is rotor where also magnetic field is produced at rotor permanent magnet is used for field production or AC or Dc windings are also used.
- There are different parts of this motor like an induction motor, synchronous motor, single-phase motor, three-phase motors.
- In our industries and homes, most used motors are induction motor either single-phase or three-phase.
Types of Motor According to Commutation
| Self-Commutated Motors | External Commutated Motors | |||
| Mechanical Commuted Motors | Electronic Commuted Motors | Asynchronous Motors | Synchronous Motors | |
| AC | DC | AC | AC | |
| Universal Motor | Separately Excited DC Motor
Series DC Motor Shunt Motor Compound Motor Permanent Magnet Motor |
Permanent Magnet Motor
Ferromagnetic Motor |
3 Phase Motors (SCIM WRIM)
Capacitor motor Resistance motor Split motor Shaded Pole Motor |
Permanent Split capacitor motor
Hysteresis motor Stepper Motor SYRM |
| DC Chopper | ||||
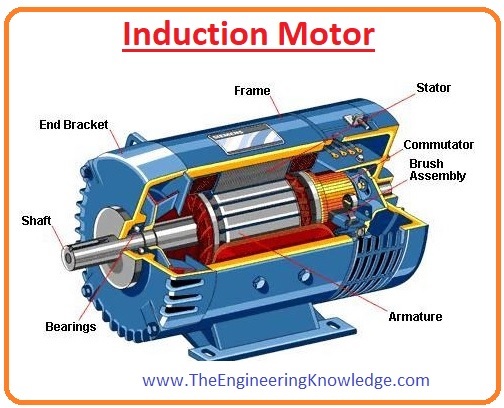
Induction Motors
- Induction motor is also known as asynchronous motor, the working principle of this motor depends on the faraday law of electromagnetic induction.
- Faraday law states that flux variation in any conductive device voltage induces in that device.
- The operation of an induction motor is also similar to the transformer that works on mutual induction.
- In the transformer core is static while in motor one part is static and other is rotating that called rotor, rotating field at the stator induced voltage in the rotor of the motor.
- There are many types of induction motor like the single-phase, three-phase, wound rotor motor, and squirrel cage rotor motor.
- In industries there,3 phase induction motor is mostly used.
Torque Motor
- A torque motor is a particular type of motor which can work indefinitely while stalled (stall is the slowing or stopping process) with the rotor locked from rotating, without suffering destruction.
- In this working operation, the motor will provide a steady torque to the connected load.
Synchronous Motor
- The synchronous motor is a type of motor that rotates at the synchronous speed.
- Synchronous speed is the rotation speed of the magnetic field at the stator.
- In this motor, the value of slip is zero slip is the difference among the speed of rotor rotation and field at the stator.
- This motor is used in such applications where constant speed is required.
Comparison of Motor Types
| Motor Type | Advantages | Disadvantage | Applications | Load connected |
|
Self-Commuted Motor |
||||
| Brush DC motor | It used for speed control.
Its price is less. |
Its repair cost is high. Its brushes damage that increases its maintenance cost. | It used in paper creating machines, treadmills, steel mills. | Its load mostly is rectifications circuits, transistors, direct current chopper regulator. |
| Brushless DC Motor | Its efficiency is higher, operating life is long, less expenses on maintenance. | It is expensive, it needs an electronic controller. | It used in radio-controlled cars, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. | It drives synchronous motor either single or three-phase. |
| Switch Reluctance motor | its efficiency is also high, less cost, operating life is also longer, and no need of permanent magnet in this motor. | Its iron losses are very higher and need a special electronic controller. | It used in aircraft, textiles machines, and electric cars. | It drives PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) |
| Universal Motor | This motor provides higher starting torque | Its repairing cost is high, operating life is less, create noise, only provides good efficiency at less ratings. | It used in vacuum cleaners, blowers. | It drives half and full-wave rectifiers circuits. |
| Asynchronous Motors | ||||
| Squirrel cage induction motor
Or wound motor |
It is a self-starting motor, less price, and ratings are one megawatt or more. | It needs a large starting current that decreases its efficiency. | It used in such applications where constant speed is need. | It used to drive single-phase induction motors. |
| Split phase capacitor start | It needs large power and starting torque. | Its speed is less than the synchronous speed. | It used in static power instruments. |
All these motors used to drive triac circuits |
| Split phase capacitor run | It provides high starting torque, there is no need of spate switch and its operating life is longer. | Its operating speed is less than the synchronous speed and its price is also high. | It used in blowers | |
| Split phase auxiliary starting winding motor | Its starting torque is less | Its speed is also less than the synchronous speed and needs a special starting circuit. | It used in static power instruments. | |
| Shaded pole motor | Its price is also less and operating life is longer. | Its speed is less than the synchronous speed, less initial torque, less efficiency, | It used in fans and record players. | |
| Synchronous Motors | ||||
| Wound rotor Synchronous motor | It operates at the synchronous speed, high efficiency, less P.F | Its price is high. | It mostly used in industries. | It used to drive PWM |
| Hysteresis motor | Its starting torque is high, less noise, less vibrating motor. | Less efficiency | It used in tape recorders, clock, timers. | It runs 2 phase capacitor start the motor, single-phase motor. |
| Synchronous reluctance motor | This motor provides less demagnetizations problems | It needs special controllers, not mostly used, and it is expensive. | It used in aircraft, textiles machines | It runs PWM inverters. |
So, friends, this is the complete post on the motor I have mentioned each and everything related to a motor in this tutorial. If you have any queries about this electrical devices ask in comments. Thanks for reading. See you in the next tutorial.








I like it when folks come together and share thoughts. Great website, stick with it!
This is really appreciated that you have presented this data over here, I love all the information shared. It will be very helpful to understand about what is motor. Great post to share, thanks for publishing this here!!
wonderful publish, very informative. I’m wondering why the opposite experts
of this sector don’t understand this. You must
continue your writing. I’m sure, you have a great readers’ base
already!