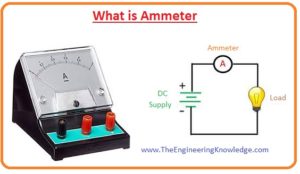
 Hello, friends, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we will explain what is ammeter. in 1820 Hans Christian oersted who belonged to Denmark discovered the relationship among current, magnetic field and physical forces (gravitation, electromagnetism, weak interaction, and strong interaction). He performed an experiment for this relationship he saw that the needle of compass moved towards north when current flows in nearing the wire. For current measurement, he used a tangent galvanometer.
Hello, friends, I hope all of you are having fun in your life. In today’s tutorial, we will explain what is ammeter. in 1820 Hans Christian oersted who belonged to Denmark discovered the relationship among current, magnetic field and physical forces (gravitation, electromagnetism, weak interaction, and strong interaction). He performed an experiment for this relationship he saw that the needle of compass moved towards north when current flows in nearing the wire. For current measurement, he used a tangent galvanometer.
In electrical and electronic engineering there is numerous meter are used like voltmeter for voltage measurement, ohmmeter for resistance measurement. In today’s post, we will have a look at ammeter its working, construction, applications and some other related parameter. So let’s get started with what is ammeter.
What is ammeter
- The ammeter is also known as ampere meter and used for measurement of electric current and the unit of the current measured by this meter is ampere so it also called ampere meter.
- the ampere meters used to find the small value of currents like mas, the ammeter used before the 19th century was only used in different laboratories since their working operation depends on the magnetic field of the earth.
- After the nineteenth century, some improvements were made in these meters and now they can be used at any location with higher accuracy.
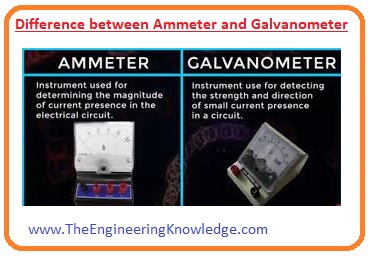
Difference between ammeter and galvanometer
- Now we compare ammeter and galvanometer and will observe what is the difference between these two meters.
- A galvanometer is used to find a very small amount of current passing through the circuit and an ammeter is used to find a larger ampere current.
- For the working of a galvanometer, there is a need of a magnetic field and in an ammeter there is no need of a magnetic field.
- The accuracy of the galvanometer is larger than the ammeter and the ammeter is less accurate.
- Due to larger accuracy, galvanometers can find a small amount of variation in current.
- A galvanometer can use only for direct current measurement while an ammeter can be used for both direct current and alternating current measurements.
- A galvanometer is used in bridge circuits for the measurement of current and an ammeter is used in electrical circuits.
- A galvanometer is a mechanical instrument while the ammeter is both electric and mechanical.
| Parameter | Ammeter | Galvanometer |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures current (amperes) | Detects and measures small currents or voltage differences |
| Sensitivity | Low to high (adjustable) | High |
| Scale | Linear | Non-linear |
| Deflection | Moderate to high (adjustable) | Low to moderate |
| Usage | Used in circuits with known resistance and current values | Used in sensitive experiments, testing, and calibration |
| Internal Resistance | Low | High |
| Shunt | May use a shunt resistor for high currents | Does not typically use a shunt resistor |
| Reading | Direct reading of current | Deflection indicates current/voltage |
| Conversion | Converts current to readable display | Converts current into the angular deflection |
| Calibration | Need calibration for accuracy | It needed calibration for accurate readings |
| Circuit Disruption | Low (minimal impact) | Higher (may affect circuit) |
| Examples | Used in household appliances, electronics | Used in scientific instruments, research |
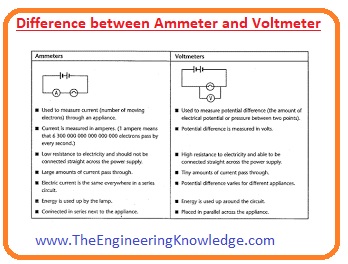
Difference between an ammeter and a voltmeter
Ammeter:
- It used for the measurement of current.
- Its resistance value is less as compare to the voltmeter.
- In-circuit it linked in series.
- This meter is more accurate than the voltmeter.
- Its range can not be varied.
Voltmeter:
- It used to find the value of voltmeter in any circuit.
- Its resistance value is high than the ammeter.
- It linked in parallel combination in the circuit for voltage measurement.
- Its accuracy is less than the ammeter.
- Its range can be varied.
| Feature | Ammeter | Voltmeter |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures current | Measures voltage |
| Symbol | ||
| Connection | Series | Parallel |
| Resistance | Low | High |
| Accuracy | High | Low |
| Range | Wide | Narrow |
| Applications | Measuring current in a circuit | Measuring the voltage across 2 points in a circuit |
Why is an ammeter connected in series and a voltmeter in parallel in a circuit?
- The ammeter is used to find the value of current in circuitry for accurate measurement of current it should pass through the ammeter.
- So it arranges in series in a circuit. If we place it in parallel and its resistance is also less so all current will flow through it and can damage this meter because we know that current always follows less resistance path.
- so it is always preferred to connect in series for current measurements.
- while the resistance of the voltmeter is high so if we place it in series then there will be less amount of current will flow through the circuit due to this it uses in parallel to measure the voltage across any element.
How to use Ammeter
- There are some steps you must follow to use an ammeter all these steps are mentioned here with detail.
- for the current measurement, we discuss it should be connected in series, first of all, you should create your circuit for which you have to use an ammeter.
- break the circuit where you want to measure current for this remove the wire at your desired location.
- than attached red lead of the ammeter to the positive terminal and black lead to the grounded terminal of the ammeter.
- after that place the ammeter in a circuit for which you are going to measure the current positive red lead of the meter should be attached to the positive terminal of a battery.
- and connect the black leads to the point that is close to the negative terminal of the battery. If these connections are not right then the meter can be damaged.
Types of ammeter
- now we discuss the types of ammeter that are listed here with the detail.
- moving coil ammeter
- digital ammeter
- electrodynamic ammeter
- hotwire ammeter
- integrating ammeter
- moving iron ammeter
- moving magnet ammeter
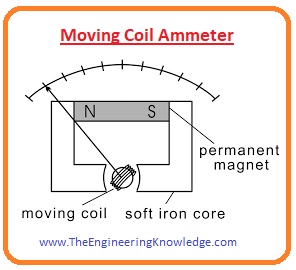
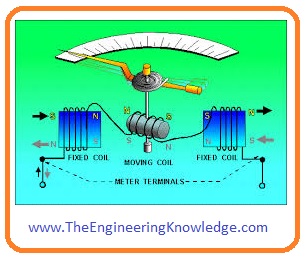
Moving coil ammeter
- this meter is also called d’arsonval galvanometer or we can say d’arsonval galvanometer is known as a moving coil ammeter.
- it measures the current through magnetic deflection this mete has coil when current passes through that coil it rotates in a magnetic field.
- the currently used ammeter is designed by Edward Weston and has 2 spiral springs for restoring force.
- the gap among the core of iron and permanent magnet poles allows the movement of a meter needle directly proportional to the current.
- the scale of this meter is linear. This meter has the ability to measure both direct and alternating current.
- the coil of this meter moves between the permanent magnet poles. When the current flows through the coil it moves in between poles of the magnet.
- the movement or deflection is directly proportional to the current flowing through the meter or coil.
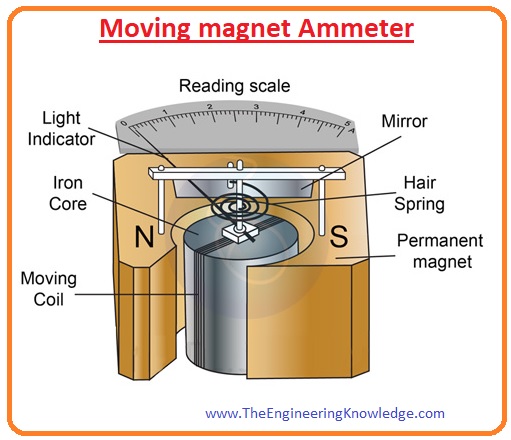
Moving magnet ammeter
- this is also used to measure the value of both dc and ac currents. This meter consists of a coil that is placed among the poles of a permanent magnet.
- after the movement of current through the coil, it shows some variation in its position the variation in coil position is directly proportional to the current flowing through the meter.
Electrodynamic ammeter
- it can also find the value of alternating and direct current passing through the circuit.
- its accuracy is larger than the moving coil meter and permanent magnet ammeter.
- its main feature is that there is no need of separate calibration for both ac and dc measurements.
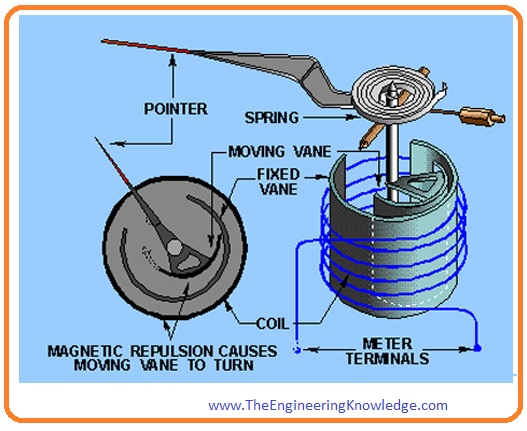
Moving iron ammeter
- this meter used an iron piece that shows some deflection when a force is exerted on this iron by the fix coil wire.
- this meter first was manufactured by Friedrich Drexler in 1884 who was an engineer of Austria.
- this meter has the ability to measure both direct and alternating current accurately. The iron piece of this meter comprises on the moving vane connected with the pointer and the second vane that is fixed and coil surrounds these vanes.
- when either direct current or alternating current flows through the coil it indued the field in both fields both fixed and moving vane the direction of the field is opposite to each other so these vanes repel one another.
- the moving vane moves opposite to the force applied by the helical spring and the deflection in the moving iron meter is directly proportional to the square of the current.
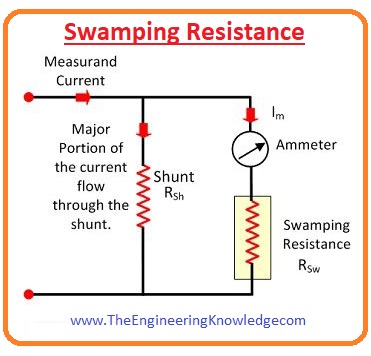
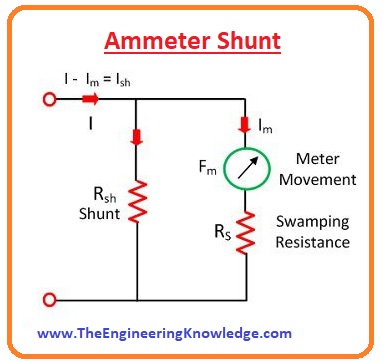
Ammeter shunt
- when the high value of current flows through the ammeter it can cause serious problems for a meter to avoid such problems a resistance is connected in parallel to the ammeter this resistance is known as ammeter shunt.
- if in any certain current flows through the circuit then most part of the current will flow through the shunt resistance and will not damage the meter.
Effect of Temperature on Ammeter
- the ammeter is a sensitive instrument that can get affected by the environmental temperature. The alteration in temperature value also varies the measured value of current or readings.
- the effect of temperature can be minimized by using the resistance called swamping resistance and have zero value of temperature coefficient.
- in-circuit it attached in series with the ammeter.
Faqs
What is an ammeter and what is it used for?
An ammeter is an electrical device that is used for the measurement of current passing through the circuit. It is attached in a series combination to measure the current
What is a voltmeter and what is an ammeter?
A voltmeter is an electrical instrument used to measure the voltage difference between 2 points in a circuit. It is configured in parallel with the circuit elements about which the voltage difference needed to be measured.
How does an ammeter affect current?
An ammeter comes with low resistance, so it does not affect the current in the circuit effectively. Though, if the ammeter has a high resistance, it can affect the current in the circuit and provdies inaccurate readings.
How is current measured in the ammeter?
The current is measured in an ammeter by passing the current in the coil of wire. The coil is attached with a pointer that moves along a scale. The amount of current passing through the coil is proportional to the deflection of the pointer.
What does a voltmeter measure?
A voltmeter measures the voltage difference between 2 points in a circuit. The voltage difference is calculated by passing the current through a resistor. The resistor is attached to a pair of probes that are configured at the 2 points in the circuit where the voltage difference is to be measured.
What happens if an ammeter is used as a voltmeter?
If an ammeter is used as a voltmeter, the high resistance of the ammeter will result in a large voltage loss across the ammeter. This will give an error reading of the voltage difference.
Does an ammeter measure voltage?
No, an ammeter does not measure voltage. It calculates current.
What happens if you put an ammeter in parallel?
If you put an ammeter in a parallel combination with a resistor, the ammeter gets damaged. it is due to the ammeter having a very low resistance and will draw a high current through it.
How do you use an ammeter in a circuit?
To use an ammeter in circuitry, we have to connect it in series with the circuit element through which the current needs to be calculated. The positive terminal of the ammeter must be connected to the positive side of the circuit and the negative terminal of the ammeter connected to the negative side of the circuit.
Does an ammeter increase current?
No, an ammeter does not increase current. It comes with very low resistance, so it does not affect the current in the circuit significantly.
How do you read an ammeter?
To reading an ammeter, we need to check the scale on the ammeter. The scale is divided into units of current, like amperes or milliamperes. The pointer on the ammeter will point to the current passing through the circuit.
Does an ammeter increase resistance?
No, an ammeter does not increase resistance. It has a very low resistance, so it does not affect the resistance of the circuit
How do you check an ammeter with a multimeter?
To measure an ammeter with a multimeter, set the multimeter to the current measurement range that is proper for the ammeter. Then, connect the positive probe of the multimeter to the positive terminal of the ammeter and the negative probe of the multimeter to the negative terminal of the ammeter. The reading on the multimeter must be the same as the reading on the ammeter.
What are two types of ammeters?
There are 2 types of ammeters: moving coil ammeters and digital ammeters. Moving coil ammeters uses a coil of wire that is configured with the pointer. The current passing through the coil deflects the pointer. Digital ammeters use circuitry that transforms the current into a digital signal. The digital signal is then displayed on a screen.
How do you check amps?
To check amperes, we can use an ammeter. Connect the ammeter in series combination with the circuit element through which the current needed to be measured. The positive terminal of the ammeter must be attached to the positive side of the circuit and the negative terminal of the ammeter must be connected to the negative side of the circuit. The reading on the ammeter will be the current passing through the circuit in amps.
What are the two important things to remember when using an ammeter?
The 2 important things to remember when using an ammeter are:
- The ammeter should connect in series with the circuit element through which the current needs to be measured. This is because the ammeter calculates the current passing through the circuit, and it can only do this if it is confirmed in series.
- The ammeter has low resistance. This is because the ammeter must not affect the current in the circuit significantly. If the ammeter comes with high resistance, it will draw a high current from the circuit, which can affect the ammeter or the circuit.
That is a complete post on ammeter I have mentioned each and everything related to ammeter if you have any questions about this post ask in the comments. Thanks for reading. See you in the next tutorial.









You made various fine points there. I did a search on the subject matter and found mainly persons will go along with with your blog.
Hi there very cool web site!! Man .. Excellent .. Superb ..
I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds additionally?
I’m satisfied to seek out a lot of useful info here in the post, we’d like develop extra strategies in this regard, thanks for sharing