 Hello friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at Introduction to IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar transistor). The IGBT stands for an insulated gate bipolar transistor is three-terminal semiconductor components that operate as a switch. It provides both high efficiency and high-speed switching. In this module, there are 4 layers PNPN which is regulated through the metal oxide semiconductor gate structure with the absence of the regenerative process. IGBT is a new invented power electronic component before the creation of this module MOSFET and power bipolar junction transistor were commonly used.
Hello friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will have a look at Introduction to IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar transistor). The IGBT stands for an insulated gate bipolar transistor is three-terminal semiconductor components that operate as a switch. It provides both high efficiency and high-speed switching. In this module, there are 4 layers PNPN which is regulated through the metal oxide semiconductor gate structure with the absence of the regenerative process. IGBT is a new invented power electronic component before the creation of this module MOSFET and power bipolar junction transistor were commonly used.
The features provided by the IGBT is a combination of MOSFET and BJT. MOSFET provides high-speed switching with high impedance and BJT has a large value of gain and less saturation. These combine features of MOSFET and BJT are exits in the IGBT. The symbol of IGBT is a combination of symbolic representation of MOSFET and BJT. In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at its working, structure, symbolic representation and some related parameters. So let’s get started with Introduction to IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar transistor).
Introduction to IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar transistor)
- The IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar transistor) which provides conduction characteristics like bipolar junction transistor and voltage control like the MOSFET.
- It used in high voltage switching speed applications. There are three main terminals of IGBT gate, collector and emitter.
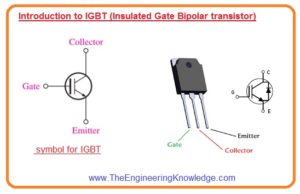
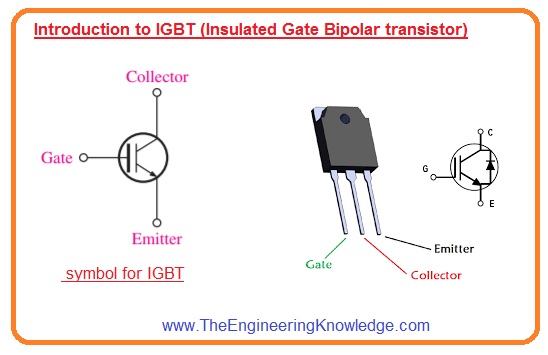
- In the below figure symbolic representation of IGBT is shown.
- You can see that it is like the BJT symbol with an extra bar that denoted the gate structure of MOSFET than base as above we discussed it a combination of MOSFET and BJT.
- The input characteristics of IGBT are like MOSFET and output like BJT. Bipolar junction transistor are able to conduct large current than field-effect transistor but there is no gate current for MOSFET due to insulated gate.
- The saturation voltage of MOSFET are less than the IGBT and similar to the bipolar junction transistor.
- The insulated gate bipolar transistor has some advantage over the MOSFET that it can bear large collector to emitter voltage larger than two hundred volts and has less saturation voltage when are in on condition.
- Similarly, IGBT has some advantages over BJT that its high switching speed.
- If we compare regards switching speed then switching speed of highest is MOSFET, second IGBT and at third place BJT.
Working of IGBT
- Similar to MOSFET the IGBT is also controlled with the voltage of gate.
- IGBT can be called as voltage controlled BJT with the less switching speed.
- Since it is regulated by voltage at insulated gate, the insulated gate bipolar transistor does not have input current and not load the driving source.
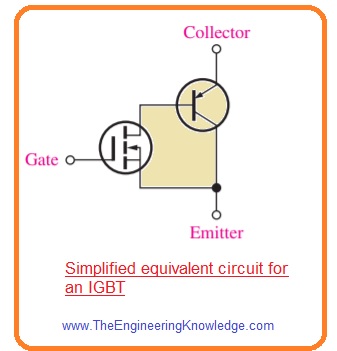
- In below figure the equivalent circuit of IGBT is shown.
- In this configuration input MOSFET and output is BJT.
- If the voltage at the gate is less than threshold voltage (Vthresh) with respect to emitter then it turn off.
- It turns on when by increasing voltage at gate than the threshold voltage.
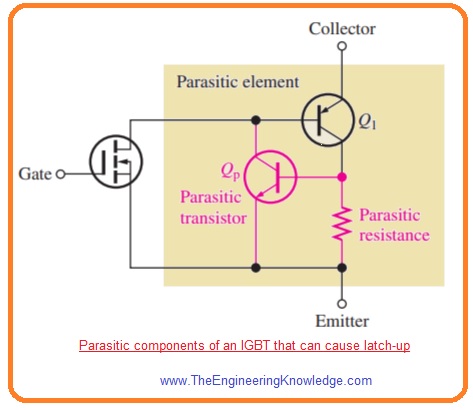
- The npnp configuration of the IGBT (insulated gate bipolar transistor) makes a parasitic transistor and an intrinsic parasitic resistance inside the IGBT it is shown in below figure.
- For normal operation there is no effect of these parasitic components.
- If Qp turns on, it efficiently combines with Q1 to make a parasitic element, it is shown in above figure where latchup state is exist.
- In latch up state IGBT remains on and can not be regulated with the voltage of gate.
- Latch up condition can be reduces by operating device in the certain limited conditions.
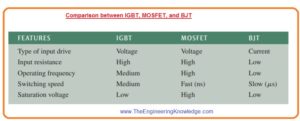
Comparison between IGBT, MOSFET, and BJT
Difference between IGBT and BJT
- IGBT is operated through gate voltage while BJT through current .
- There are three terminals of IGBT emitter, collector and base, terminals of BJT are emitter, base and collector.
- The power handling capability of IGBT is larger than BJT.
- IGBT is combination of BJT and FET.
- The internal structure of IGBT is more complicated than the BJT.
- IGBT is newly created device while BJT is older.
- Both components need has less value of voltage loss at on condition.
- Delay time of IGBT is less than the BJT.
- Forward and reverse blocking capabilities of IGBT is good then the BJT.
- In large voltage and current applications IGBT can be easily regulated.
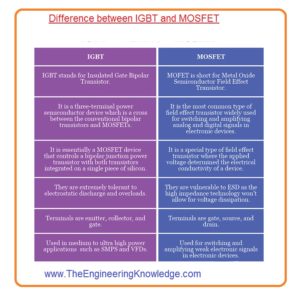
Difference between IGBT and MOSFET
- These are some differences between IGBT and MOSFET.
IGBT
- IGBT stands for an insulated gated bipolar transistor.
- It has three terminals emitter gate and collector.
- It is combination of BJT and FET.
- It used in medium to ultra-large power-consuming applications like VFD.
MOSFET
- MOSFET stands for metal oxide field-effect transistor.
- It is a type of field effect transistor and mostly used in digital and analog applications.
- It is three terminals modules which are drain gain and source.
- It used in switching and amplifier circuits.
IGBT Advantages
- These are some advantages of IGBT.
- It simple circuit is simple.
- It provides less on resistance.
- It has large voltage capability.
- It switching speed is fast.
- It is easy to handle.
- It has less on power dissipation.
- Its input impedance is high.
- It is regulate voltage.
- It can be easily on and off.
IGBT Disadvantage
- These are some disadvantages of IGBT.
- It has to latch up problems.
- It does not resist high reverse voltage.
- It has large turn off time.
- Its price is large.
So friends that is detailed post about IGBT if you have any query ask in comments. Thanks for reading. Have a good day.


Like!! Thank you for publishing this awesome article.