Hi, friends welcome to the new post. In this article, we will discuss the What is Hot Wire Anemometer? It is mostly used to calculate the velocity of fluids and is also used in industries. In this post, we will discuss its different factors such as construction, applications,, limitations, and working. So, let’s get started Introduction to Hot Wire Anemometer
What is Hot Wire Anemometer?
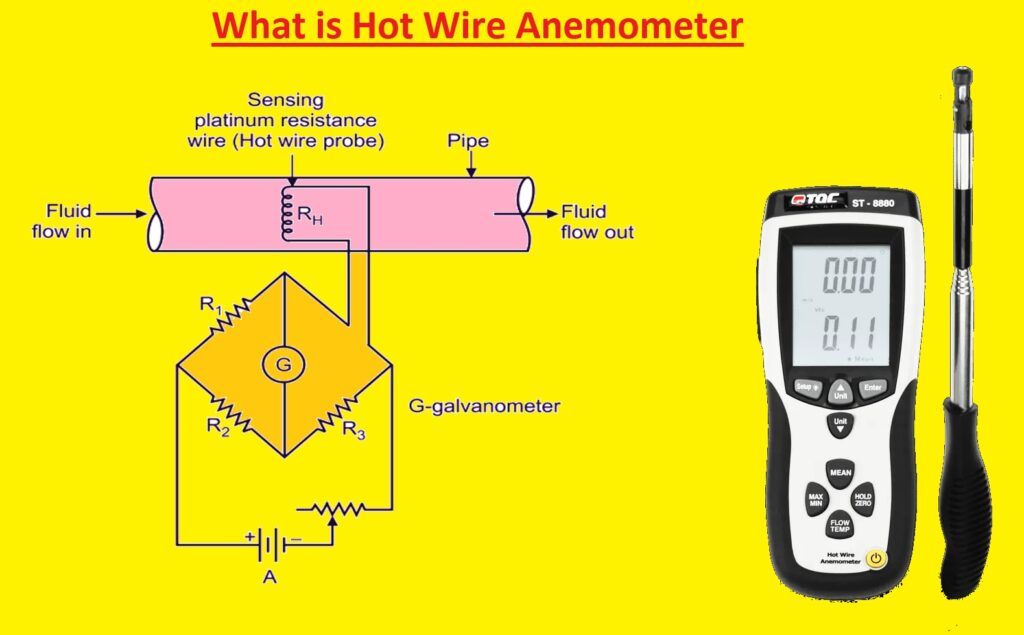
- A hot wire anemometer (HWA) instrument that used to measure the velocity and direction of fluid flow such as liquid or gases. It works by heating small, sensitive to electrical signal wire calculates changes in its resistance, and becomes low temperature when any liquid moves over it. If its wire is high temperature that means it has high resistance
- For measuring the direction and velocity of fluid heat loss of wire used that is positioned in fluid flow. The wire is heated with an electric current. Hot wire is placed in fluid flow heat is shifted from wire to fluid and temperature is reduced. Resistance of wire helps to measure fluid rate flow.
- How to wire anemometer used as a research device for fluid mechanics. it works on the heat transfer rule for high-to-low temperatures
Definition of Hot Wire Anemometer?
A hot wire anemometer is an accurate instrument that is used for the calculation of the velocity of fluids. It works based on heat transfer from high-temperature wire to fluid close to it. With measuring cooling parameters causing fluid flow, this device measures the correct value of velocity
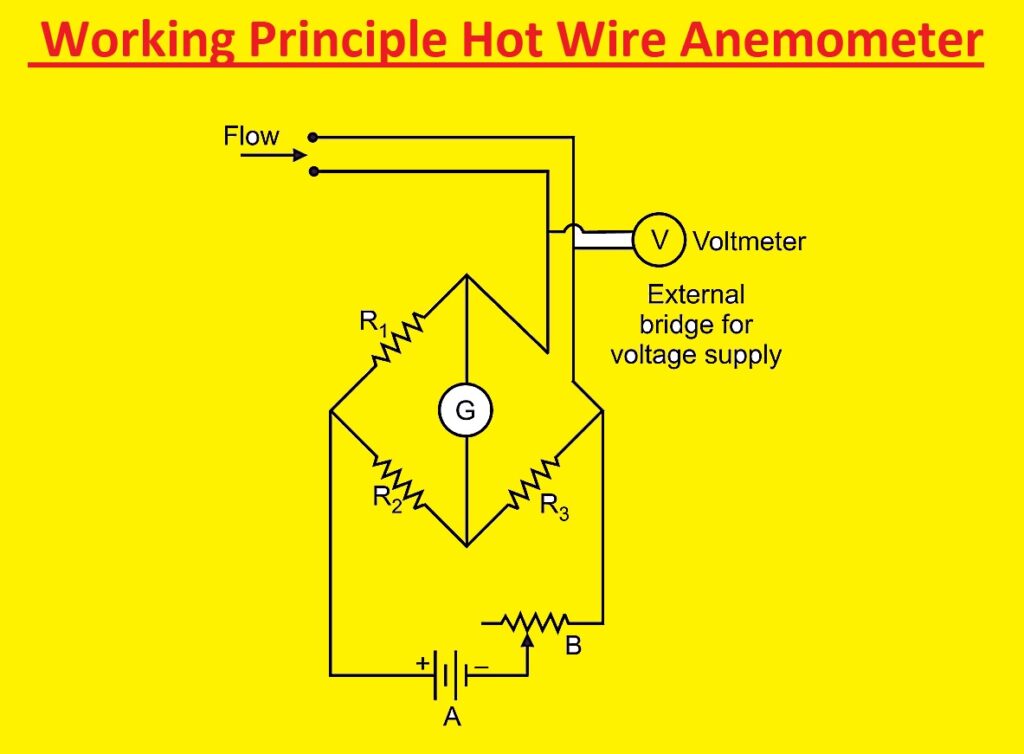
Working Principle Hot Wire Anemometer?
There are many designs of hot wire anemometer but some come with two probes having tungsten, platinum, or platinum-iridium wire stretched for constant temperature circuit types of anemometer, glass-coated thermistor bead connected. it works by sending current through the wire. That curent causes the wire to heat. If gas or fluid flows over the device, it cools the wire.
The cooling process shows the existence of motion energy and the amount of time takes the wire to cool, making it possible to find the velocity of fluid when moving over the wire.
Construction
There are two main parts of hot wire anemometer
- Conducting wire
- Wheat stone bridge.
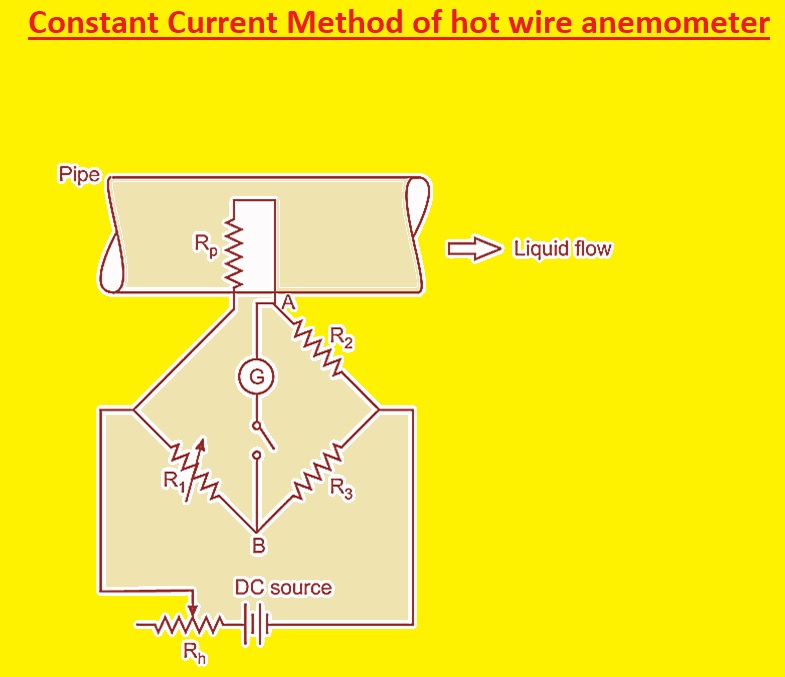
Constant Current Method of hot wire anemometer
In this configuration, an anemometer is connected in the flow of fluid for which the rate has to be measured. The current of constant value is flow through wire. The Wheatstone bridge is at a constant voltage.
If the wire is positioned in the stream of liquid heat is shifted from wire to fluid. The heat is directly proportional to the resistance of a wire. If heat decreases that means the resistance of the wire also decreases. The Wheatstone bridge measures change in resistance that is the flow rate of liquid.
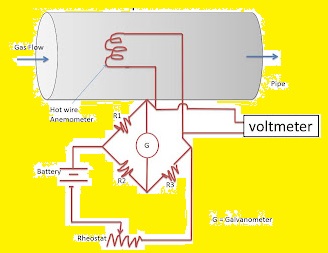
Constant Temperature anemometer
In this design, the wire is heated with current. The hot wire when connected to the stream of fluid, heat transfers from wire to fluid. So temperate of the wire varies and also varies resistance. It operated on the rule that the temperature of the wire is constant. The total current needed to get the wire in the starting condition is equal to the gas flow rate.
How to Measure the rate of a fluid with Hot Wire anemometer
- hot wire anemometer. Make ready. Here meter is connected to a power source, calibrated, and set meter in a fluid stream
- Heat the hot wire. Current flows in the wire. Current values varied to a value that would heat the wire to the required temperature.
- Hot wire temperature variation measured. It attaches hot wire with a bridge circuit. Resistance changes explained fluid velocity
- Calculate the velocity of the fluid. The velocity of the fluid measured with these equations
velocity = K x (Rhot – Rambient)^(1/n)
Applications of a hot wire anemometer
The common use of a hot wire anemometer is finding the relation between temperature and velocity of turbulent flow. It can used as a research tool for fluid mechanism and used for conventional turbulent analysis and laminar boundary fluid flows
How to use a hot wire anemometer
its use is simple. Just hold the probe free in fluid or air flow that is tested, while the anemometer is on the state. The outcome will be in numbers on screen or it can shifted to an external screen if there is proper software. The result normally gets easily in very little time
What is Hot Wire Anemometry
The hotwire anemometry (HWA) technique is used for calculating velocity and fluid direction with small-level heating, sensitivity of wire, and changes in resistance when it cools with fluid flow. High-temperature wires have high resistance. When fluid moves on the wire it reduces heat in the wire. resistance reduces the amount of heat loss and is directly proportional to the velocity of the fluid
What is Hotwire flow meter?
A hot wire flow meter device operates on the principle of heat transfer to measure fluid velocity. It has a thin wire current based on heated configured on fluid. When fluids move on wire decreased heat from wire resistance increases in results.
Limitations
- This wire is delicate and breaks if not accurately used
- Different environmental conditions like temperature, humidity, and pressure affect it
- it does not measure the velocity of corrosive or chemically reactive fluids.
- it is high cost
Industry Use
Hotwire anemometers industrial used explained here
- Environmental monitoring
- HVAC and building automation
- Aerospace and automotive
- Research and development
- Manufacturing and process control
Advantages of a hot wire anemometer
- its size is very small which reduces the disturbance of airflow that is needed to measure.
- The wire is also a small time constant which means hot wire anemometers are sensitive to fast variations in velocity.
- Its use is also easy
- It has good frequency response featues and high spatial resolution.
Disadvantages of hot wire anemometer
- It has thin wire there is a chance of the wire’s physical strength.
- It can be affected by the value of atmospheric temperature so it is used for the resulting calculation.
What is a hot wire anemometer used for measuring of gases?
What is a hot wire anemometer and LDA?
What are the two types of hot wire anemometer?
What is the difference between an anemometer and a hot wire anemometer?
Is a hot wire anemometer a common instrument?
What are examples of anemometer?
FAQs
What is the working principle of a hot wire?
Hotwire device operation is based on the thermal effect the length of the wire increases since the heating effect due to current passing caused this. As current passes in the platinum-iridium wire gets heated and expands
What is the work of a hot wire anemometer?
A Hot Wire Anemometer is used to measure velocity and fluid direction by calculating the heat loss of wire heated by the current configured on the fluid stream. In a fluid stream, heat is moved to the wire and its temperature decreases
How is a hot wire anemometer based on the principle of heat transfer?
Hotwire anemometer uses the operation that heat removed from a high-temperature sensor with the movement of fluid is equal to the velocity of the fluid
What is the material of construction for a hot wire anemometer?
It consists of two probes with sire stretched. The wire is made of platinum, tungsten, or platinum-iridium. A small, glass-coated thermistor bead used a constant-temperature circuit
What is the construction of a hot wire anemometer?
The hot wire anemometer comes with a thin bout five-micrometer dia, heated by current, placed in the flow of fluids. The liquids affect teh wire and decrease the resistance
Which metal is used in an anemometer?
tungsten is mostly used in anemometer
What are the applications of an anemometer?
Anemometers have different applications, which are
- The anemometer measured the rotation that is used for calculating the speed of wind. Anemometer measures wind speed and pressure, It is also used in practicals of physics that need air flows
What is the common name for an anemometer?
It is also called a wind indicator, weather vane
What is the range of a hot wire anemometer?
Its range is between 0.3 … 30.0 m/s / 0.98 … 98.4 ft/s.
What is a constant temperature anemometer?
A Constant Temperature Anemometer (CTA), called a hot wire anemometer uses the cooling fact of convective heat flow to measure fluid velocity. The high-speed fluid will quickly get cool