 Hello, readers welcome to the new tutorial. Here we will discuss Difference Between Thermoplastics and Thermosetting Plastics. These two terms are basic types of plastic and polymer and are categorized on basis of heat. The basic difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting is that if heat is given to them thermoplastic become soft and changes to any other shape while thermosetting becomes hard on heating.
Hello, readers welcome to the new tutorial. Here we will discuss Difference Between Thermoplastics and Thermosetting Plastics. These two terms are basic types of plastic and polymer and are categorized on basis of heat. The basic difference between thermoplastic and thermosetting is that if heat is given to them thermoplastic become soft and changes to any other shape while thermosetting becomes hard on heating.
Here we will discuss their basic difference and some other paramerts. SO let get started
Difference Between Thermoplastics and Thermosetting Plastics
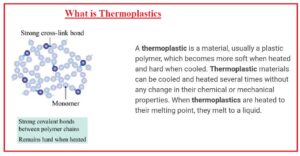
What is Thermoplastics
- Thermoplastic is a polymer substance that becomes moldable at a certain value of temperature when gets cold.
- Some thermoplastic has a high value of molecular weight. The polymer chains are related to intermolecular forces that become weak with the increment in temperature resulting in liquid material.
- In this condition thermoplastic can be converted into different shapes are mostly used to make parts through use of a different technologies such as compression molding, and injection molding.
- Thermoplastic has a difference from thermosetting polymers that make the chemical bonding.
- On heating not melted but decomposes.
- Numerous thermoplastic polymers get reinforced with fibers. This reinforcement enhances the physical features certainly heat deflection temperature
- For reinforcing glass fibers are used.

what is Thermosetting Plastics?
- The thermosetting polymer is known as thermoset obtain through the irreversible process through the process when soft liquid become hard.
- For this process heating of radiation is applied through high pressure or there is the mixing of catalyst.

- Heat is not given outer but through a combination of resin to the curing agent or catalyst.
- The initiating material for the creation of thermoset malleable is used.
- Thermosetting plastics normally have strong nature than thermoplastics since has 3D configuration of bonds.
- Their features are that become totally deform if high pressure is applied and shows high brittle nature than the thermoplastics
- COnvntiaonlly used thermoset plastic can not be melted and change shape when get cured.
- Thermosetting plastics has resistance to corrosion
- Their structure is stable
- They show less thermal conductivity
- It gives the high strength-to-weight ratio
- They show water-resistant nature
- They have a wider range of colors
That is all about the Difference Between Thermoplastics and Thermosetting Plastics all details have been explained. If you have any further query ask in the comments. Thanks for reading have a good day see you in next post.