 Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Charge & Current. The basic difference between charge and current is that charge is a physical feature of matter while current is the flow rate of charges. As the charge is a physical characteristic of matter so it bears a force when located in the electric field. There are 2 types of charges positive, negative neutral. Due movement of charges in a certain direction current is generated.
Hello, friends, I hope you all are doing great. In today’s tutorial, we will discuss the Difference Between Charge & Current. The basic difference between charge and current is that charge is a physical feature of matter while current is the flow rate of charges. As the charge is a physical characteristic of matter so it bears a force when located in the electric field. There are 2 types of charges positive, negative neutral. Due movement of charges in a certain direction current is generated.
In today’s post, we will have a detailed look at both charges and electric current with the details and compare them to find their differences. So let’s get started with Difference Between Charge & Current,
Difference Between Charge & Current
Charge
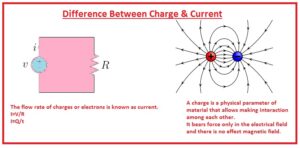
- A charge is a physical parameter of material that allows making interaction among each other.
- It bears force only in the electrical field and there is no effect magnetic field.
- Its measuring unit is the coulomb.
- The same type of charge has the force of repulsion and dislike has an attractive force.
- Material has no charge called neutral like neutron is neutral.
- The charge has a conserved feature that means if some amount of charge is subtracted from negative then the net charge remains the same.
- Charges exist in the particles of atoms like protons and electrons.
- The charge in the rest state has an electric field about it and in motion has a magnetic field.
- The combination of electrical and magnetic fields is called electromagnetic force.
- The coulomb is derived from the physicist Charles Augustin.
- Its other unit is ampere-hour.
Current
- The flow rate of charges or electrons is known as current.
- I=V/R
- I=Q/t
- At current due to both electric and magnetic field force exerted.
- It also called a combination of charges that are passing in the device.
- Chares in motion called charge carriers cause the current to flow.
- Normally charges are electrons that caused current.
- In the case of semiconductor material current flow due to holes and free electrons which means they have two charge carriers.
- In solution, current flows due to positive and negative ions.
- Ampere is flow charges in one second.
- Ammeter used to measure the current galvanometer also measures current
- Its measuring unit is Ampere.
- the electric field is produced by the current that controls the working of electrical devices like motors, and transformers.
- Current is denoted with I
- Ohm’s law explains the current that says voltage applied to the body has a proportional value of current about the body
- The device through which current passes is called the conductor and through which current does not flow is called the insulator
Charge vs Current
| Feature | Charge | Current |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | it is the quantity of electricity passing through a circuit | it is the rate at which charges flow through circuits |
| Unit | Coulomb (C) | Ampere (A) |
| Symbol | Q | I |
| Formula | Q = I x t | I = Q / t |
| Direction | It is positive or negative depending on the charge | It flows from high to low potential |
| Flow of energy | Potential difference explains the charges flow | the flow of current driven by the power sources |
| Flow of matter | Chares can pass through inductors and insulators | Current flows through conductors |
| Type of quantity | it is a Scalar quantity | it is a vector quantity |
| Resistance | Increasing the value of resistance decreases charge flow | The flow of current decreases with resistance increases |
| Ohm’s Law | Q = I x R | V = I x R |
| Measurement | It measured with an ammeter | it measured with an ammeter or a current meter |
| Effect on body | it can be generated through static shock or electrocution | it can generate shock or electrocution |
| Circuit elements | Charges stored in capacitors | Ressitaors cause resistance in the curent flow |
| Examples | lightning, Charging a battery, static electricity | Lighting a bulb, running a motor, charging a phone |
| Conservation law | A charge is a conserved quantity | Current is not a conserved quantity |
| Quantity | it can be transferred and accumulated | it not be accumulated only transmitted |
| Effect on voltage | Can change voltage | Can cause a voltage drop |
| Dependence | Its value depends on the current and time | it depends on voltage and resistance |
| Density | Charge density is calculated in Couloms per square meter | Amperes per square meter is the measuring unit of Current density |
FAQS
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the charge? | The amount of electricity passing through a circuit is known as a charge and is expressed in Coulombs (C). It is preserved (cannot be made or destroyed) and can be either positive or negative. |
| What is current? | The current, measuring unit is ampers, which is the rate at which electrical charge moves across a circuit. It is not created or destroyed and constantly flows from high potential to low potential. |
| Write main difference between charge and current. | A charge is the quantity of electricity, but the current is the pace at which that electricity flows and this is the major distinction between the two terms. While current is measured in Amperes, the charge is measured in Coulombs. |
| How are charge and current related? | The equation Q = I x t, where Q is the charge, I is current, and t is the time, relates charge and current. According to this equation, the charge is equal to the product of current and time, demonstrating their direct proportionality. |
| How charge and current affect circuit components differently? | Circuit components are affected differentially by charge and current. While current travels via resistors, charge can build up on capacitors. Additionally, a circuit’s resistance impacts the flow of current but not the flow of charge. As a result, various types of circuit components are affected differently by charge and current. |
That is a detailed post about the difference between charge and current. If you have any queries ask in the comments. Thanks for reading.