 Hello, readers welcome to new post. Here we will discuss Difference Between Capacitor and Battery. A battery is a device that transforms chemical energy in electrical energy and provides static charges to deliver the power. The capacitor is an electronic component that is used for energy storage in form of an electrical field.
Hello, readers welcome to new post. Here we will discuss Difference Between Capacitor and Battery. A battery is a device that transforms chemical energy in electrical energy and provides static charges to deliver the power. The capacitor is an electronic component that is used for energy storage in form of an electrical field.
Both of these are used for energy storage and proving the energy but come with differences that we will discuss here. So let get started Difference Between Capacitor and Battery.
Difference Between Capacitor and Battery
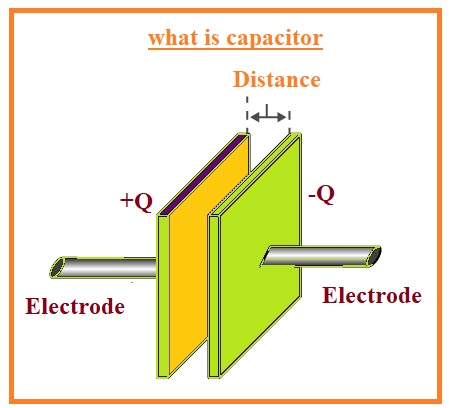
What is Capacitor
- The capacitor is a passive component that comes with two pins and stores energy in form of an electrical field.
- The capacitor effect is called capacitance. There is some value of capacitance that exists in the conductors in circuitry but the addition of capacitors enhances the capacitance.
- Capacitors are also called condensers and condensator.
- There are different types of capacitors on the basis of shapes and structures.
- Most capacitors consist of two pins that are metallic plates and have dielectric material for separation.
- The capacitor can be foil thin sheet and electrolyte. The use of nonconducting dielectric material work as to enhance the charging capacity of the capacitor.
- The material used for dielectrics is glass, ceramic paper, mica, and air.
- Capacitors are used in different devices as electrical circuits.
- If volts are given to the capacitor terminals through a battery electrical field is created about the dielectric that results in positive charges on one electrode and negative charges on the other electrode.
- There are no current flows in the dielectric material. But flow of charges through source circuit.
- The energy stored in the capacitor is 1/2 CV2.
- It is an insulator for dc current means dc can not pass through it
- Current leads volts by 90 degrees in case of ac circuits
- For dc circuits capacitor connects in series combination with resistance current at start large then goes to 0
- The unit of the capacitor is Farad
- Commonly used types of capacitors are Electrolyte, and ceramic.
- It works as short circuit fo ac circuits mean ac passes through it and block dc
- Capacitor gets energy from the circuitry store it and then release that energy.
- It is a passive element
- Its charging and discharging speed is larger than the battery normally one to ten seconds
- Its life cycle is 30000 hours
- volts can store is 2.3 to 2.75 V
- Expensive than the battery
- Operating life is ten to fifteen year
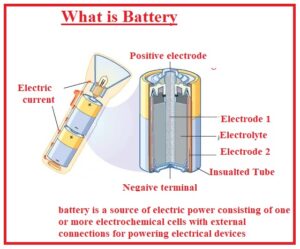
What is Battery
- A battery is the electric power source that comprises of one and more than one electrochemical cell having the external points for delivering the power.
- During delivery, the power positive terminal work as a cathode, and the negative terminal is the anode.
- The negative pins of battery electrons’ sources move through exterior circuitry to positive point.
- If the battery is attached to load reduction and oxidation reaction transforms the high energy reactants to less energy output.
- The primary type of battery-only used one time the alkaline battery is a primary battery.
- The secondary battery can be recharged again and again. Its examples are lead-acid batteries of automobiles and lithium-ion batteries.
- The battery used to give power to the circuit
- It is the active component
- It works as a dc device since provides the static charges
- During the discharging gives the constant value of volts
- Its charge and discharge time is high normally ten to sixty minutes
- Its specific power is 1000 to 3000
- It can work for five to ten years
- Its structure is smaller than the capacitors
That is all about the Difference Between Capacitor and Battery all paramerts has discuss that will guide you to get details. For further detail ask in the comments.






