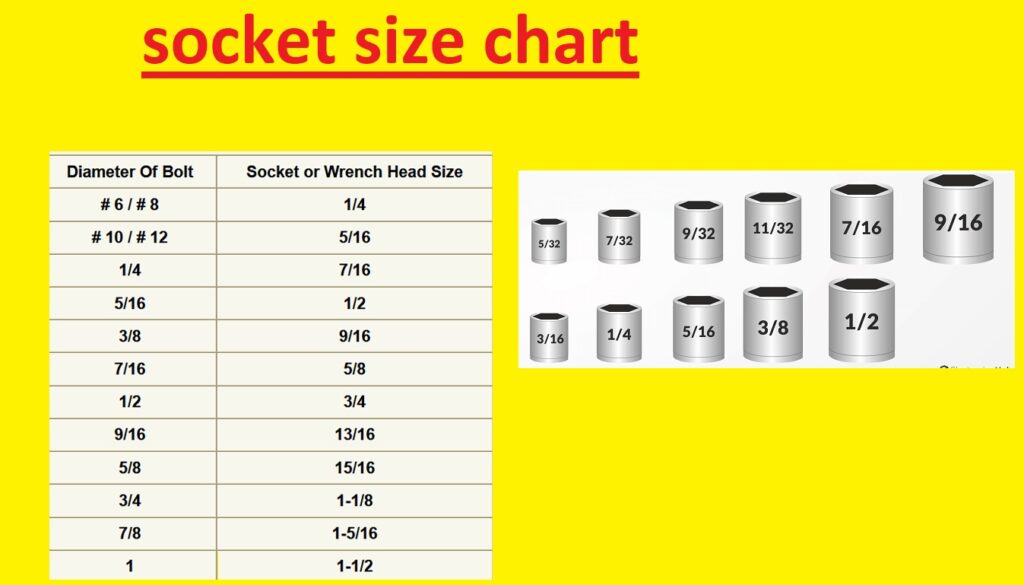
Hi friends welcome to the new post. Here we will learn Socket Size Chart – Socket Sizes in Order from Smallest to Largest. The socket is used on the base of the dia of opening in the Socket wrench that fixes the but or bolt. Socket size measuring unit is inches commonly used size for a socket is one inch or 1/4 inch/ The correct socket size is important to the accurate fit of snugness on the bolt or nut saving from slipping
Using a socket does not help the wrench grip the nut accurately with the use of a large socket. That does not provide the torque needed to lose or tighten the fastener. Standard sockets are metric socket sizes. The metric socket size measuring unit is millimeter the ais about six millimeters to 19mm
When you choose the socket size it is good to measure the bolt or nut to make sure that the selected socket is correct. There are charts used to find the correct sizes of bold or nut So let’s get started with the Socket Size Chart
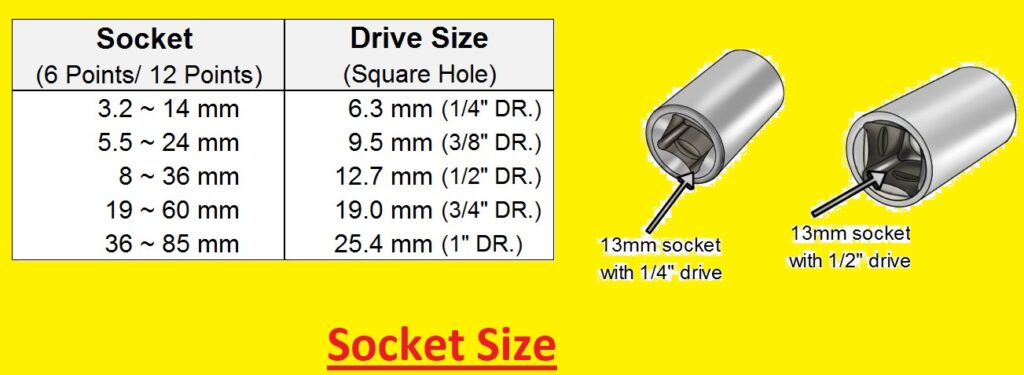
Different Drive Sizes
common drive sizes for socket wrenches are mentioned here
- 1/4 inch It is a small drive size and used for small-size modules and in handheld ratches
- 3/8 inch – It is a medium-sized drive size that is unique and used for different functions. it is best for automotive work.
- 1/2 inch – it has a larger size and is used for heavy during operation. best for working on large-size machines or vehicles
- 3/4 inch – It also has a large size and is not commonly used as previously mentioned. It is used for different operations such as larger engines or heavy machines.
- With these four drive sizes the are some others that are less used are 5/8 inch and 1 inch.
Types of Sockets
There are different types of sockets, but they can be defined in 2 types:
- Mechanical sockets used to grip and turn faster such as nuts and bolts. They come in different sizes and shapes according to fasteners.
- Network sockets are employed for communication between two computers having differnt networks. They have different types and each has its advantages and disadvantages.
Types of mechanical sockets
- Hex sockets are commonly used sockets. It comes with six points that can be fitted in the six points of nut or bolt.
- 12-point sockets have twelve points that fit in the 12 points on a bolt or nut. They are used in tight spaces where a hex socket will not fit.
- Torx sockets have a star-shaped pattern of points that fit into the star-shaped recess on a Torx bolt.
- Spline sockets come with a pattern of pints that fit into the splined recess on a splined bolt.
- Deep sockets are larger than standard sockets and are used for bolts or nuts that exist in deep holes.
Types of network sockets
- Stream sockets come with bidirectional connections between two computers. They are used for applications that require high data to send such as video streaming and heavy diles transfer
- Datagram sockets come with unreliable, many connections between 2 computers. they are used for chat and gaming.
- Raw sockets give direct access to the network layer. They are employed for network debugging and security applications.
Shallow vs. Deep Sockets
| Feature | Shallow Sockets | Deep Sockets |
|---|---|---|
| Length | Short | Long |
| Reach | Easy to reach in shallow spaces | it can easily reach in deep spaces |
| Versatility | it is versatile | it is best for deep spaces |
| Price | Less cost | High costly |
 Metric Socket Sizes Chart
Metric Socket Sizes Chart
| Drive Size | 1/4″ | 3/8″ | 1/2″ | 3/4″ | 1″ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4mm | 4mm | 4mm | 4mm | 4mm | 4mm |
| 5mm | 5.5mm | 5.5mm | 5.5mm | 5.5mm | 5.5mm |
| 6mm | 6mm | 6mm | 6mm | 6mm | 6mm |
| 7mm | 7mm | 7mm | 7mm | 7mm | 7mm |
| 8mm | 8mm | 8mm | 8mm | 8mm | 8mm |
| 9mm | 9mm | 9mm | 9mm | 9mm | 9mm |
| 10mm | 10mm | 10mm | 10mm | 10mm | 10mm |
| 11mm | 11mm | 11mm | 11mm | 11mm | 11mm |
| 12mm | 12mm | 12mm | 12mm | 12mm | 12mm |
| 13mm | 13mm | 13mm | 13mm | 13mm | 13mm |
| 14mm | 14mm | 14mm | 14mm | 14mm | 14mm |
| 15mm | 15mm | 15mm | 15mm | 15mm | 15mm |
| 16mm | 17mm | 17mm | 17mm | 17mm | 17mm |
| 17mm | 19mm | 19mm | 19mm | 19mm | 19mm |
| 18mm | 21mm | 21mm | 21mm | 21mm | 21mm |
| 19mm | 22mm | 22mm | 22mm | 22mm | 22mm |
| 20mm | 24mm | 24mm | 24mm | 24mm | 24mm |
| 21mm | 27mm | 27mm | 27mm | 27mm | 27mm |
| 22mm | 28mm | 28mm | 28mm | 28mm | 28mm |
| 23mm | 30mm | 30mm | 30mm | 30mm | 30mm |
| 24mm | 32mm | 32mm | 32mm | 32mm | 32mm |
SAE Vs Metric Wrenches
SAE wrenches have sizes in inches, and metric wrenches have sizes in millimeters. The main difference is there uses SAE wrenches used for SAE fasteners and metric wrenches are used for meter fasteners. If you use the incorrect type can casues damage to the fastener head or tool.
SAE Socket Sizes Chart
| Drive Size | 1/4 inches | 3/8 inches | 1/2 inches | 3/4 inches | 1 inch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5/32″ | 5/32″ | 5/32″ | 5/32″ | 5/32″ | 5/32″ |
| 3/16″ | 3/16″ | 3/16″ | 3/16″ | 3/16″ | 3/16″ |
| 7/32″ | 7/32″ | 7/32″ | 7/32″ | 7/32″ | 7/32″ |
| 1/4″ | 6.5mm | 6.5mm | 6.5mm | 6.5mm | 6.5mm |
| 9/32″ | 9/32″ | 9/32″ | 9/32″ | 9/32″ | 9/32″ |
| 5/16″ | 8mm | 8mm | 8mm | 8mm | 8mm |
| 11/32″ | 11/32″ | 11/32″ | 11/32″ | 11/32″ | 11/32″ |
| 3/8″ | 10mm | 10mm | 10mm | 10mm | 10mm |
| 13/32″ | 13/32″ | 13/32″ | 13/32″ | 13/32″ | 13/32″ |
| 7/16″ | 11mm | 11mm | 11mm | 11mm | 11mm |
| 15/32″ | 15/32″ | 15/32″ | 15/32″ | 15/32″ | 15/32″ |
| 1/2″ | 12.7mm | 12.7mm | 12.7mm | 12.7mm | 12.7mm |
| 9/16″ | 14mm | 14mm | 14mm | 14mm | 14mm |
| 5/8″ | 16mm | 16mm | 16mm | 16mm | 16mm |
| 11/16″ | 17mm | 17mm | 17mm | 17mm | 17mm |
| 3/4″ | 19mm | 19mm | 19mm | 19mm | 19mm |
| 1-1/16″ | 21mm | 21mm | 21mm | 21mm | 21mm |
| 1-1/8″ | 22mm | 22mm | 22mm | 22mm | 22mm |
| 1-3/16″ | 24mm | 24mm | 24mm | 24mm | 24mm |
| 1-1/4″ | 27mm | 27mm | 27mm | 27mm | 27mm |
SAE to Metric Conversion Chart
| SAE | Metric |
|---|---|
| 1/16″ | 1.6 millimeter |
| 5/32″ | 3.17millimter |
| 3/16″ | 4.76 millimeter |
| 7/32″ | 5.95 millimeter |
| 1/4″ | 6.35 millimeter |
| 9/32″ | 7.93 millimeter |
| 5/16″ | 8.99 millimeter |
| 11/32″ | 10.21 millimeter |
| 3/8″ | 10.95 millimeter |
| 13/32″ | 11.91 millimeter |
| 7/16″ | 11.11 millimeter |
| 15/32″ | 12.7 millimeter |
| 1/2″ | 12.7 millimter |
| 9/16″ | 14.3 millimeter |
| 5/8″ | 15.87 millimter |
| 11/16″ | 17.46 millimter |
| 3/4″ | 19.05 millimter |
| 1-1/16″ | 20.63millimeter |
| 1-1/8″ | 22.22 millimeter |
| 1-3/16″ | 24.13 millimeter |
| 1-1/4″ | 25.4 millimeter |
What are the 3 socket sizes?
Commonly used socket sizes in standard socket size are 1/4 inch, 3/8 inch, 1/2 inch, 3/4 inch
Standard socket sizes chart
| Drive Size | SAE | Metric |
|---|---|---|
| 1/4″ | 5/32″, 7/32″, 3/16″, 1/4″ | 4millimeter, 5millimeter, 6millimeter, 7millimeter |
| 3/8″ | 3/8″, 1/2″, 9/16″ 7/16″, | 6millimeter, 8millimeter, 10millimeter, 12millimeter |
| 1/2″ | 5/8″, 11/16″,1/2″, 9/16″, 1″, 1-3/8″ | 10millimeter, 12millimeter, 15millimeter, 17millimeter, 20millimeter, 22millimeter |
| 3/4″ | 5/8″, 3/4″, 7/8″ 11/16″, | 15millimeter, 17millimeter, 20millimeter, 22millimeter |
| 1″ | 3/4″, 7/8″, 1-3/4″, 2″ 1″, 1-1/2″, | 20millimeter, 22millimeter, 25millimeter, 30millimeter, 32millimeter, 38millimeter |
Why do sockets have 3 holes?
Sockets come with three holes as they are created to handle 3 pronged plugs. The three-prong plug provides the hot, neutral, and ground wires in electric circuitry. The hot wire handle carries current to different devices the neutral wires take current to the power supply and the ground wire offers a safe path for current to flow if there is a short circuit.
The three-hole socket is arranged in a certain order. The hot wire is directed to the upper hole neutral to the middle hole and ground to the lower hole. This layout ensures that current passes through devices that help users to protect from electrical shock.
Some of the socket has two holes. Due to devices plugged into the socket not having a ground wire. However, it is good to note that devices with two-pronged plugs must be connected to the sockets that have a structure for two-pronged. Plugging 2-pronged plug-in sockets that are made for 3-pronged can be dangerous since it causes shock hazards.
Shallow vs. Deep Sockets
The shallow socket is name of a normal socket. In some conditions, it may not touch the nut before the bolt hits end of the socket which makes working difficult. For these operations, deep sockets are used. Nroammly measurement of one inch for length we can use deep sockets for places that are not easy to access. it can done with a driver that has an extension.
What is the size of a socket?
The commonly used socket types are 8mm, 10mm and 14mm.
What are the 4 socket sizes?
4″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″ or 1″.
Why are sockets in mm and inches?
MM is used for metric fasteners like nuts and bolts and inches are used for imperial fasteners.
How many inches is a 17mm socket?
| SAE | Metric | Inch |
|---|---|---|
| 17mm | 0.669 | |
| 11/16″ | 0.688 | |
| 18mm | 0.709 | |
| 23/32″ | 0.719 |
What are the 2 systems for socket sizes?
Two different methods are used for hex-size measurement of sockets. SAE systems use inches and imperial or metric systems uses mm.
What is a 17mm socket in standard?
17mm = 0.67 inches
How many types of sockets are there?
There are four types of sockets exist. Comonly used are stream and datagrams and rare are raw and packet-sequenced sockets.
What is the best type of socket?
¼-inch drive sockets is the best and most compact for cramped spaces ⅜-inch drive sockets are most common, used for different uses.
Read Also:
- What Size Socket for Spark Plug Needed? 2023 Complete Guide
- How Many Receptacles on a 20 amp circuit
- 30 Amp Wire Size: What AWG Wire You Need?
- 125 Amp Wire Size and Breaker Guide
- What Size Wire for 200 AMP Service Underground
- What is 4/0 aluminum wire rated for?
Faqs
- What are the socket sizes in order?
Commonly used socket sizes in sequence are
- 1/4 inches
- 3/8 inches
- 1/2 inches
- 3/4 inches
- 1 inch
In Europe metric sizes used here are some given
-
4 millimeter
-
5.5 millimeter
-
8 millimeter
-
10 millimeter
-
13 millimeter
-
How do I know my socket size?
The size of the nut or bolt that has to be tightened or lost socket size is measured. The socket size mentioned on the bolt or must and the chart of socket size can also used
- What are the socket sizes in mm?
There is the same value of sizes in mm as in inches just convert the units. As a 1/4 inch socket is like a 6.35 mm socket, a 3/8 inch socket is like a 9.52 mm socket,
- What are the 5 common socket drive sizes?
1/4″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″ or 1″. are comonly used socket drive sizes.
- What is the average size of a socket?
The most commonly used types are 8 mm, 10 mm, and 14 mm sockets.
- What size is a 3 4 socket?
it is the fourth largest socket size in the imperial system. Larger-sized nuts and bolts use these sockets and are used in car wheels and engine mounts.
- What are the 3 types of sockets?
There are 3 main types of sockets:
-
Six-point sockets:
-
Eight-point sockets:
-
Twelve-point sockets:
What is socket size?
The diameter of the opening in the socket is called socket size. The size of the socket must fulfill the size of the bolt or nut
- What is the socket’s maximum size?
The socket type defines the size of the socket. 6 points sockets come about tone inches 8 point and 12 points soket has a size of about 3/4 inch.
- Which socket size is best?
A 3/8” drive socket is very commonly used that helps to handle 1/4″ and 1/2” sockets. As the 1/4″ sockets are slightly narrower, they come with a deep reach that others
- What is a 5 amp socket?
A 5 amp socket can handle a five-ampere current. It is used for small current users devices that are radios lamps, and fans.
- What size is a Type C socket?
A Type C socket is an electrical socket that changes the devices with the use of a USB-C connector. This socket is like the standard USB-A socket, but it comes in a different shape. Its main applications are high-speed charging and data transfer speeds.
- What are the socket sizes from smallest to biggest?
There are four common sizes 1/4″, 3/8″, 1/2″, and 3/4″.
- What is the order of socket sizes?
Socket sizes are defined in small size to larger like a 1/4″ socket set can have these sizes: 4mm, 5mm, 6mm, 7mm, 8mm, 9mm, 10mm, 11mm, 12mm, 13mm, 14mm, and 15mm.
- What is the largest socket drive size?
The largest socket drive size is one inch.
- What are the common metric socket sizes?
The most common metric socket sizes are 8 mm, 10 mm, and 14 mm sockets.
- What is the smallest ratchet size?
The smallest ratchet size is 1/4″.
- What are the three most common socket drive sizes?
The most common socket drive sizes are 1/4″, 3/8″, and 1/2″.
- What are the different types of sockets?
There are different types of sockets, such as
Standard sockets:
Deep sockets:
Impact sockets:
Spark plug sockets:
Oxygen sensor sockets:
- Which is bigger 7 8 or 22mm?
7/8″ and 22mm are the same size. 7/8″ is slightly larger than 22mm, but their difference is that it not be found through the naked eye.
- How do you arrange power tools?
There are different methods to arrange power tools. The first one is to make groups based on their types like a group of drills, a group of saws, and a group of sanders.
- What are the different types of socket organizers?
There are three main types of sockets tray, rail, and wall-mounted. All types help to organize the sockets, but each has its method.
- How do you organize tools and screws?
There are some methods to organize tools and screws. Use the tool cabinet. Tool chests and tool cabinets have drawers for many tools and screws. Another is to pegboard. Pegboards have holes that can be used to hang tools and screws on hooks or pegs.
- What’s smaller than a 13 16 socket?
1/2 inch is smaller than a 13/16 socket.